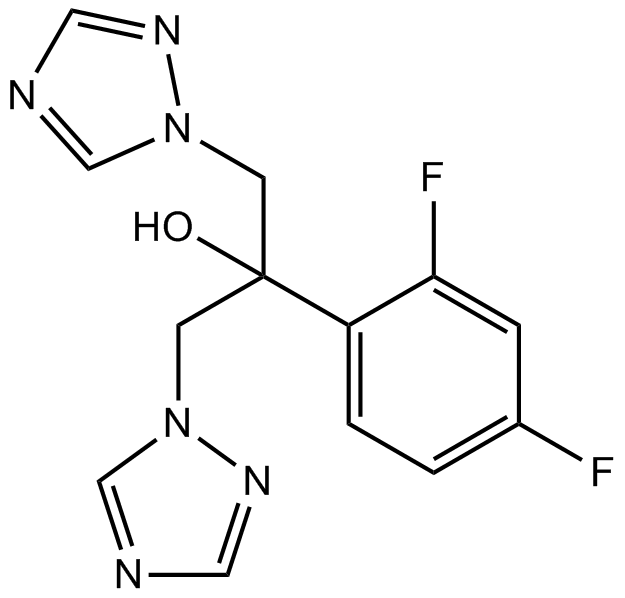
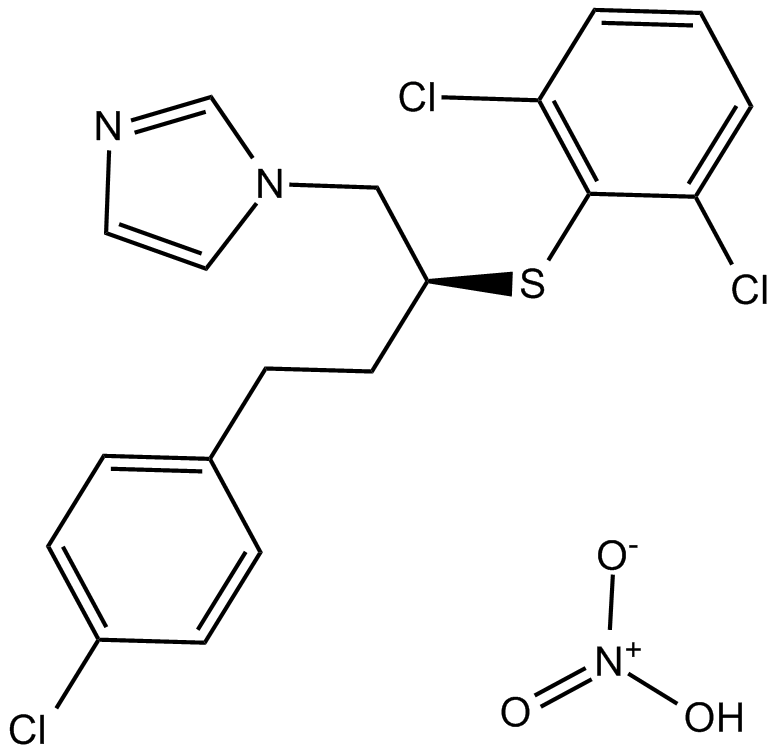
Fluconazole
Fluconazole (CAS 86386-73-4) is a triazole-based antifungal compound widely employed in biomedical research to investigate fungal pathogenesis and antifungal drug resistance mechanisms. It functions by inhibiting fungal cytochrome P450 enzyme 14α-demethylase, disrupting ergosterol biosynthesis and interfering with fungal cell membrane integrity. Fluconazole demonstrates inhibitory activity in vitro against various pathogenic fungi, with reported IC50 values ranging approximately from 0.5 μg/mL to 10 μg/mL, dependent on fungal strain and culture conditions. Researchers commonly utilize fluconazole to explore antifungal susceptibility profiles, quantify drug-target interactions, and model fungal infections in vitro and in vivo.
- 1. Jiadi Shen, Chenyu Weng, et al. "Protein Phosphatases 2A Affects Drug Resistance of Candida albicans Biofilm Via ATG Protein Phosphorylation Induction." International Dental Journal Volume 75, Issue 6, December 2025, 103873
- 2. Binyou Liao, Chuanli Zhang, et al. "Aloin remodels the cell wall of Candida albicans to reduce its hyphal virulence against oral candidiasis." Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Jan 24;109(1):21 PMID: 39853490
- 3. Xiuyi Liang, Agata J Pacuła-Miszewska, et al. "N-3-Methylbutyl-benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-one Exerts Antifungal Activity In Vitro and in a Mouse Model of Vulvovaginal Candidiasis." Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Mar 14;46(3):2480-2496. PMID: 38534773
- 4. Naemah Alkhars, Anthony Gaca, et al. "Antifungal Susceptibility of OralCandidaIsolates from Mother-Infant Dyads to Nystatin, Fluconazole, and Caspofungin." J Fungi (Basel). 2023 May 17;9(5):580. PMID: 37233291
- 5. Suvidha Menon, Xiuyi Liang, et al. "Antifungal Activity of Novel Formulations Based on Terpenoid Prodrugs against C. albicans in a Mouse Model." Pharmaceutics. 2021 Apr 29;13(5):633. PMID: 33946740
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 306.27 |
| Cas No. | 86386-73-4 |
| Formula | C13H12F2N6O |
| Solubility | insoluble in H2O; ≥10.9 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥60.9 mg/mL in EtOH |
| Chemical Name | 2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-1,3-bis(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propan-2-ol |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | OC(C[n]1ncnc1)(C[n]1ncnc1)c(ccc(F)c1)c1F |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
|
Cell lines |
The Candida albicans reference strain SC5314 |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >10.9mg/mL. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
|
Reacting condition |
10 μg/ml; dissolved in Milli-Q water |
|
Applications |
In wild-type Candida albicans SC5314 cells, fluconazole (10 μg/ml) and doxycycline (50 μg/ml) inhibited cell growth in a dose dependent way. |
| Animal experiment [2]: | |
|
Animal models |
C. albicans-infected p47phox-/- knockout mice |
|
Dosage form |
80 mg/kg/day for 13 days; diluted in saline; intraperitoneal injection |
|
Application |
In C. albicans-infected p47phox-/- knockout mice, fluconazole significantly reduced splenic counts of C. albicans (P =0.008). |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1]. Alessandro Fiori and Patrick Van Dijck. Potent Synergistic Effect of Doxycycline with Fluconazole against Candida albicans Is Mediated by Interference with Iron Homeostasis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Jul; 56(7): 3785–3796. [2]. Justina Y. Ju, Cynthia Polhamus, Kieren A. Marr, et al. Efficacies of Fluconazole, Caspofungin, and Amphotericin B in Candida glabrata-Infected p47phox-/- Knockout Mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002 May; 46(5): 1240–1245. | |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure