Metabolism
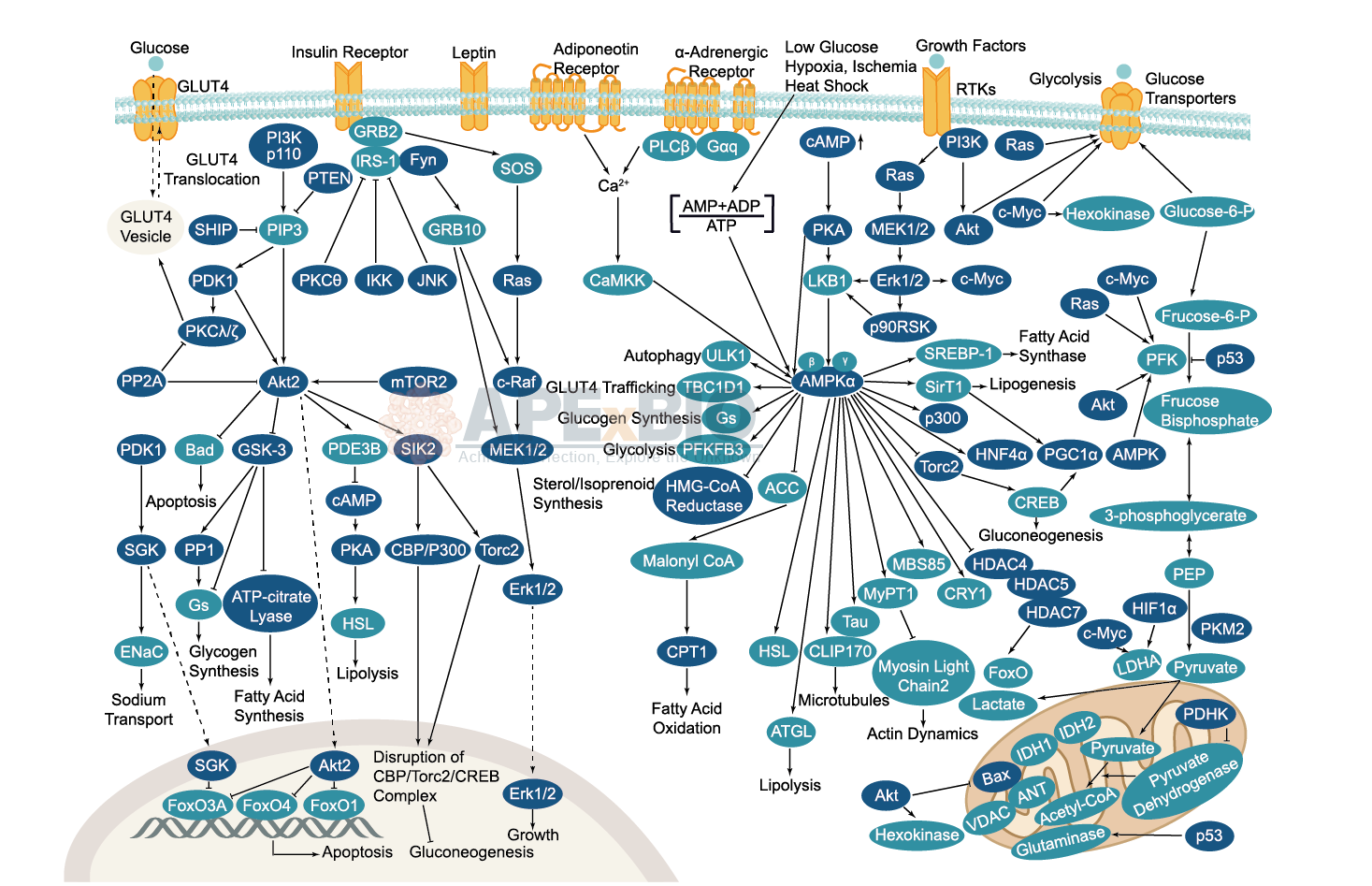
Serine/threonine kinase AMPK upregulates glucose uptake by promoting the expression and function of glucose transporters. AMPK is activated by increased AMP/ATP ratio, resulting from cellular and environmental stress, e.g. low glucose, heat shock, hypoxia and ischemia. AMPK activation positively modulates signaling transductions that refill ATP levels. Moreover, it also stimulates catabolic processes such as fatty acid oxidation and glycolysis through inhibition of ACC and activation of PFK2. AMPK negatively regulates various proteins which are important to ATP-consuming mechanisms, e.g. mTORC2, glycogen synthase, SREBP-1, and TSC2, causing the downregulation/inhibition of gluconeogenesis and glycogen, lipid and protein synthesis.
-
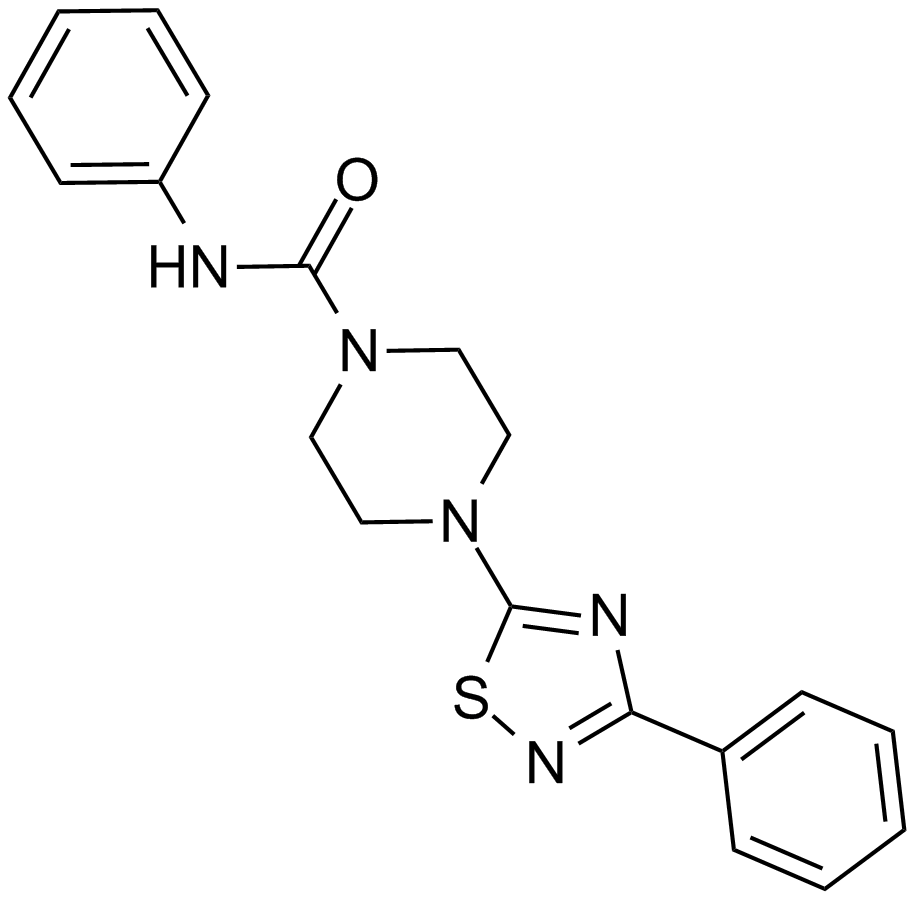 A4361 JNJ-1661010Summary: FAAH inhibitor,potent and selective
A4361 JNJ-1661010Summary: FAAH inhibitor,potent and selective -
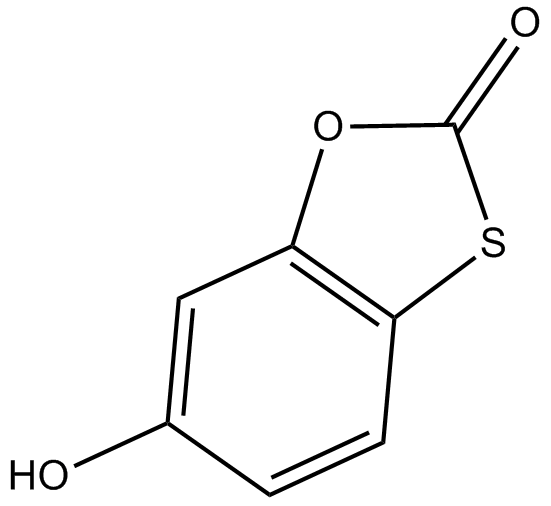 A4362 TioxoloneTarget: Carbonic AnhydrasesSummary: CAI inhibitor
A4362 TioxoloneTarget: Carbonic AnhydrasesSummary: CAI inhibitor -
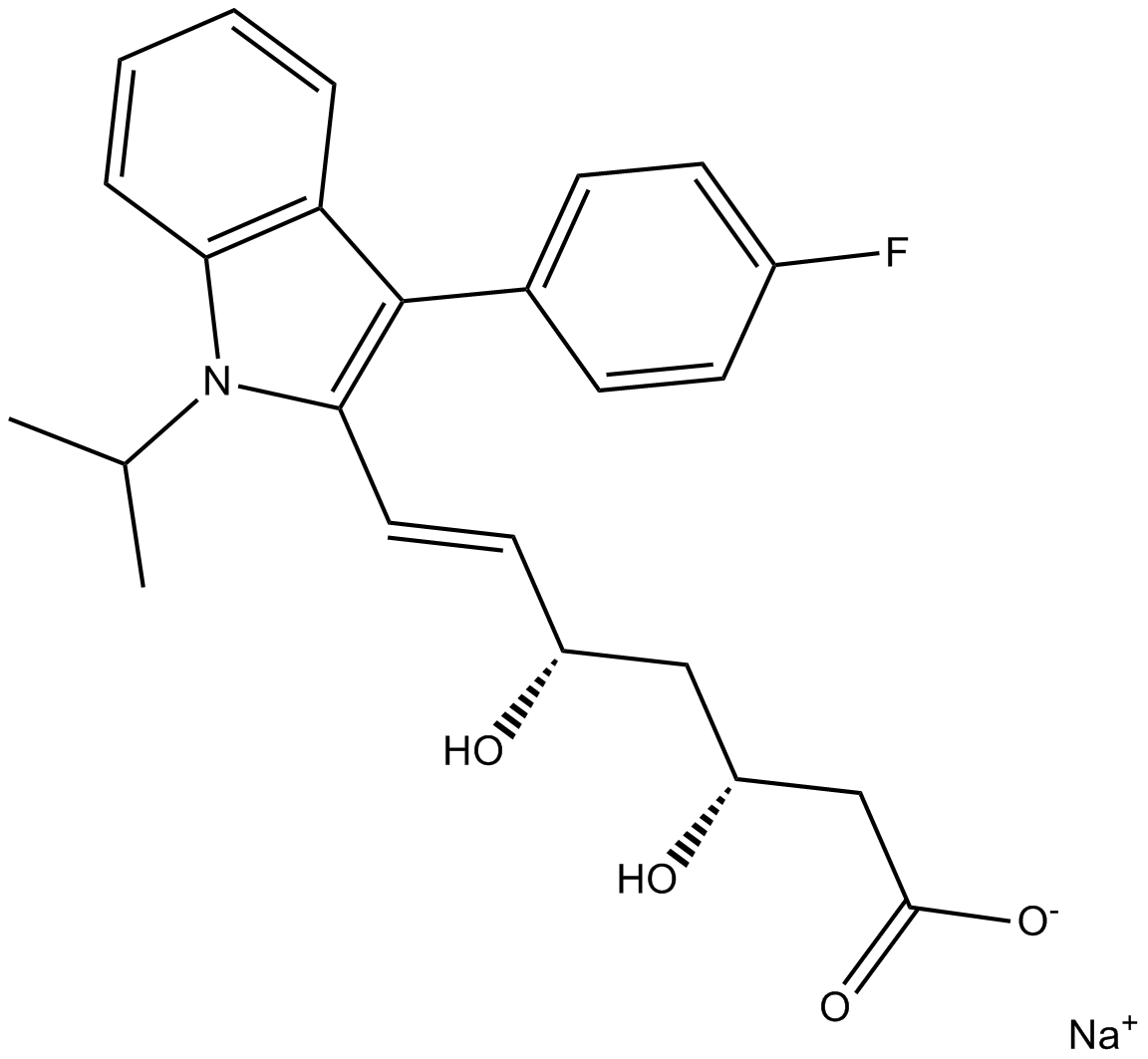 A4363 Fluvastatin SodiumSummary: HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor
A4363 Fluvastatin SodiumSummary: HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor -
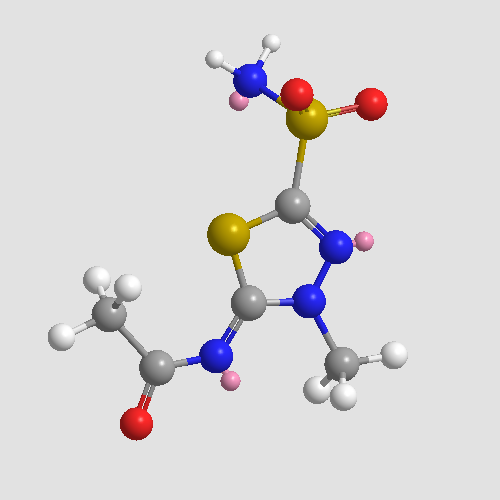 A4364 MethazolamideTarget: Carbonic AnhydrasesSummary: Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor
A4364 MethazolamideTarget: Carbonic AnhydrasesSummary: Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor -
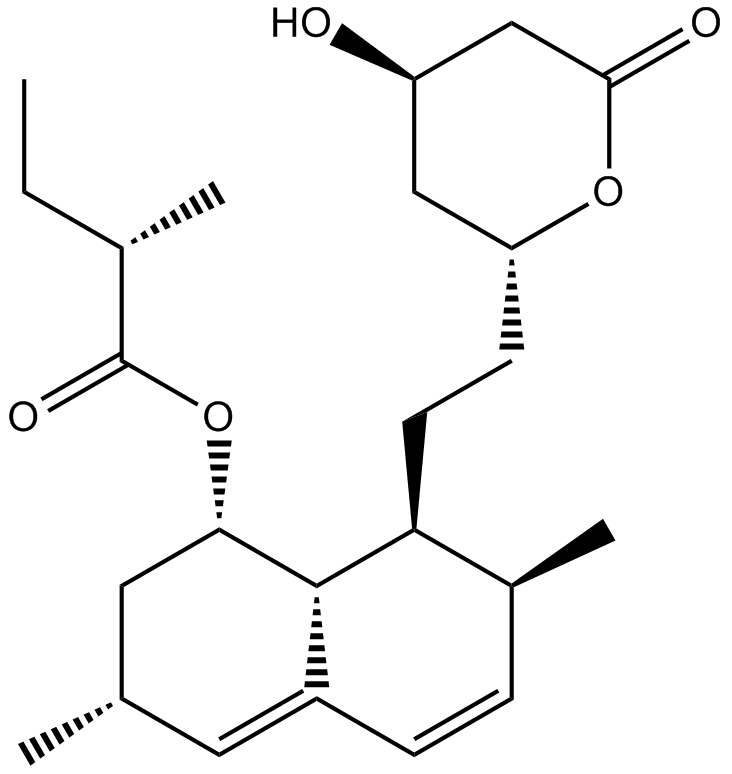 A4365 LovastatinTarget: HMG-CoA ReductasesSummary: HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor
A4365 LovastatinTarget: HMG-CoA ReductasesSummary: HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor -
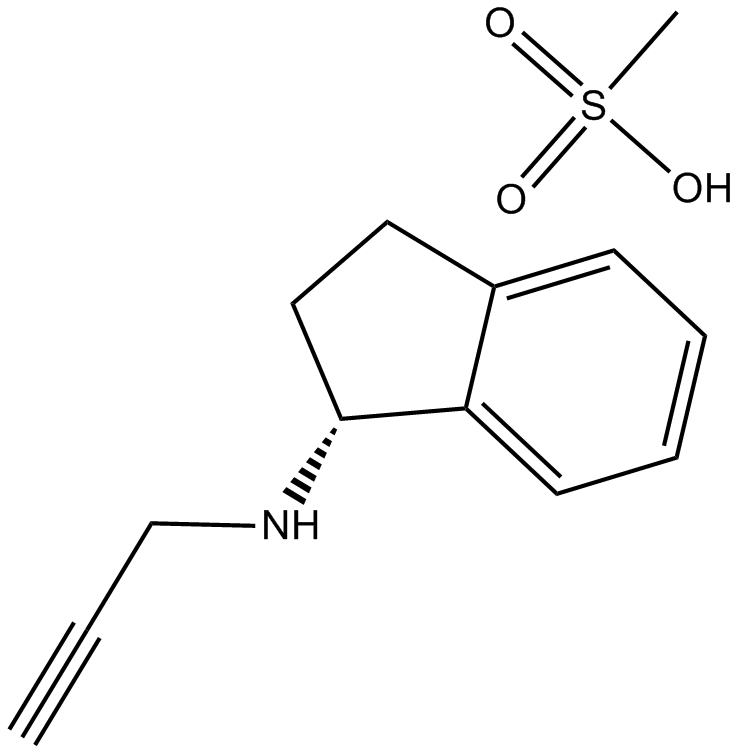 A4366 Rasagiline MesylateSummary: Irreversible MAO-B inhibitor
A4366 Rasagiline MesylateSummary: Irreversible MAO-B inhibitor -
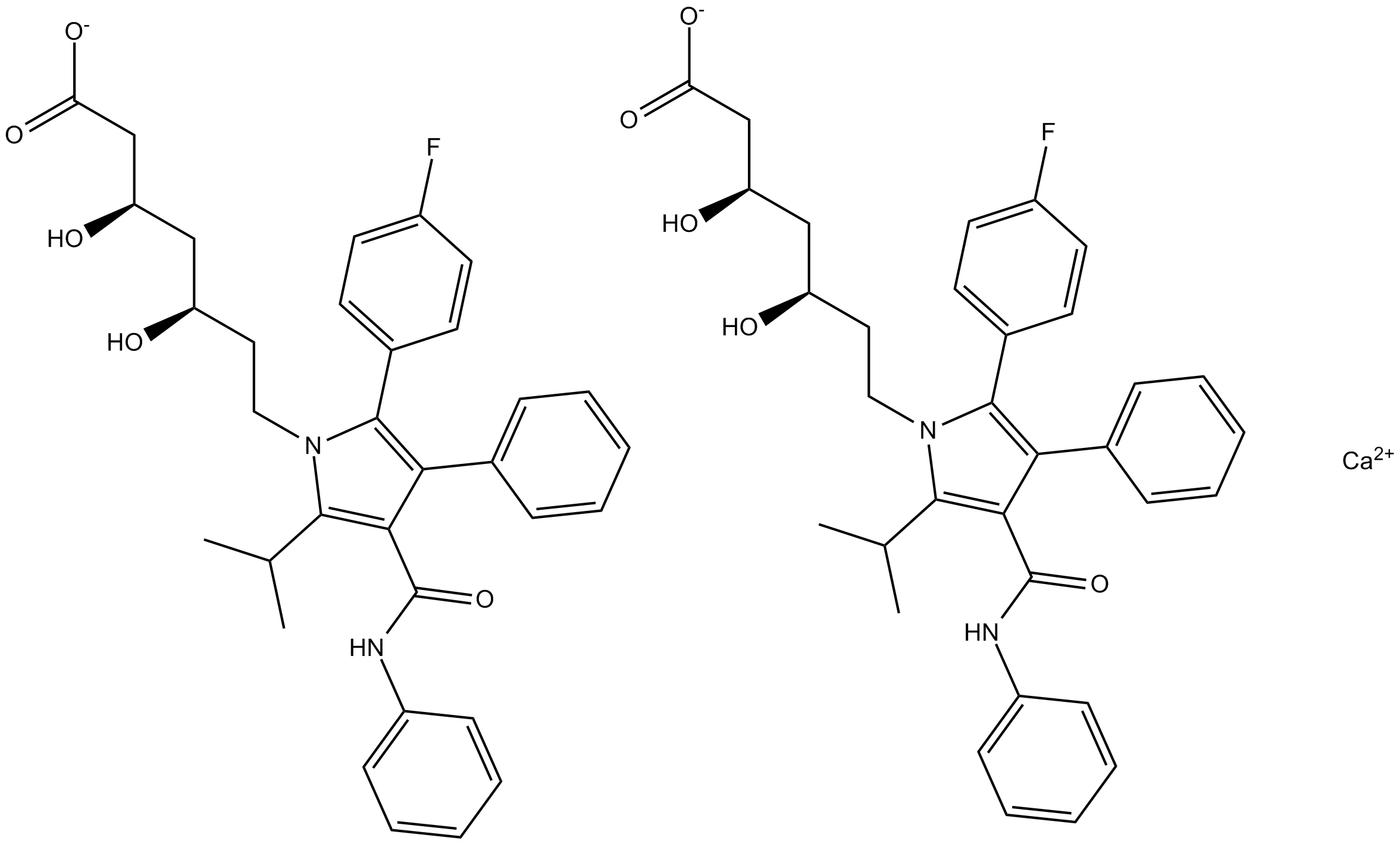 A4367 Atorvastatin CalciumTarget: HMG-CoA ReductasesSummary: HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor
A4367 Atorvastatin CalciumTarget: HMG-CoA ReductasesSummary: HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor -
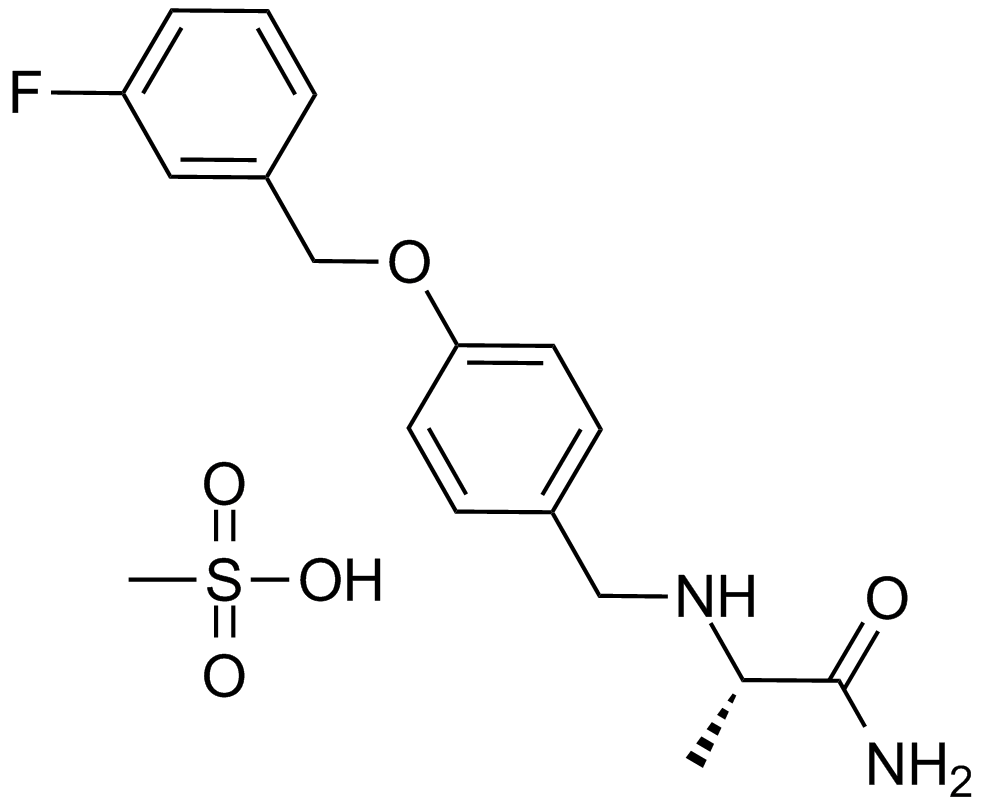 A4368 Safinamide MesylateSummary: MAO-B inhibitor,potent,selective and reversible
A4368 Safinamide MesylateSummary: MAO-B inhibitor,potent,selective and reversible -
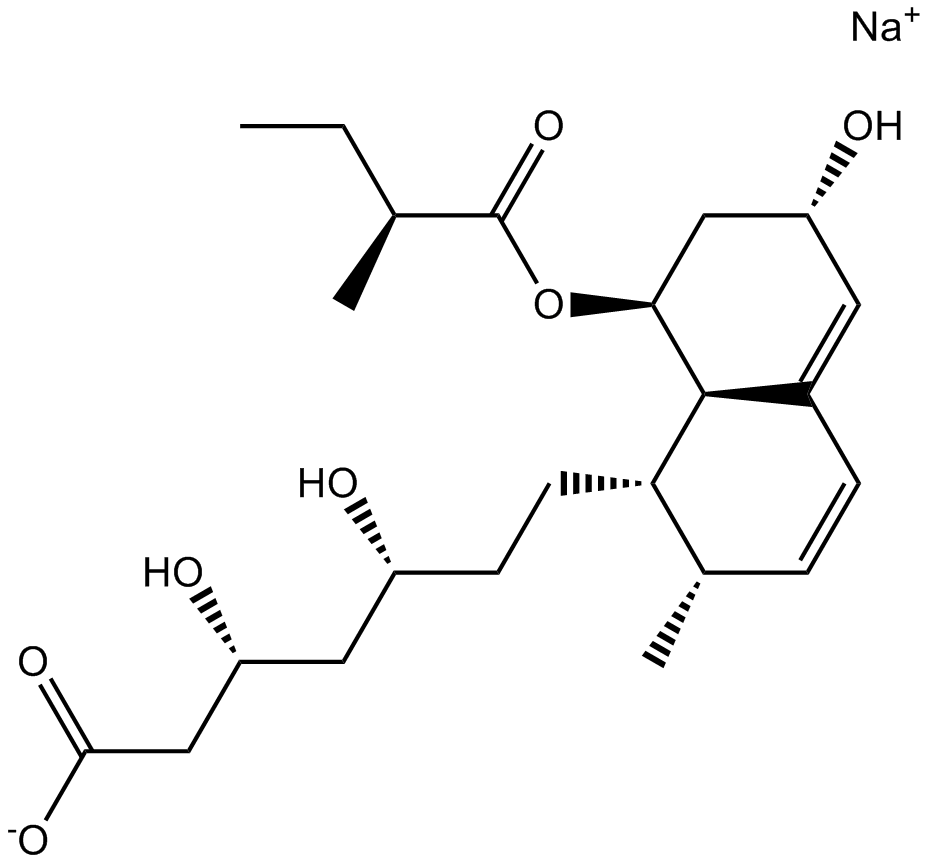 A4369 Pravastatin sodiumTarget: HMG-CoA ReductasesSummary: HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor,highly selective and competitive
A4369 Pravastatin sodiumTarget: HMG-CoA ReductasesSummary: HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor,highly selective and competitive -
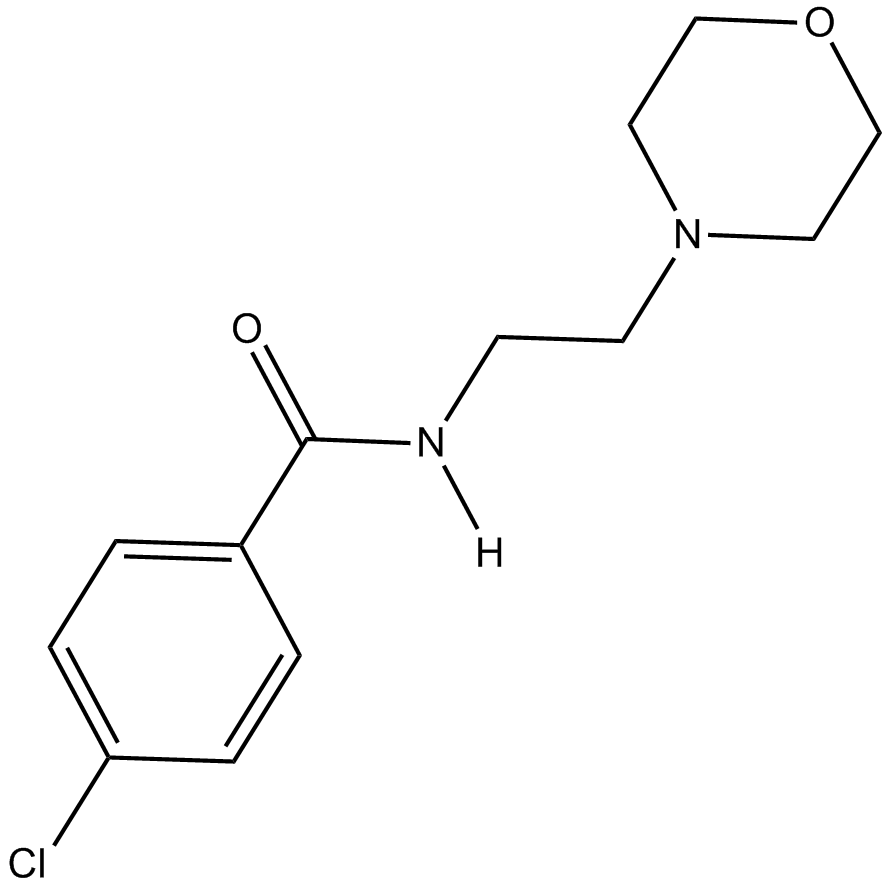 A4370 Moclobemide (Ro 111163)Summary: Reversible inhibitor of MAO-A
A4370 Moclobemide (Ro 111163)Summary: Reversible inhibitor of MAO-A

