Search results for: 'signaling pathways metabolism'
-
 L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research. -
 L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch. -
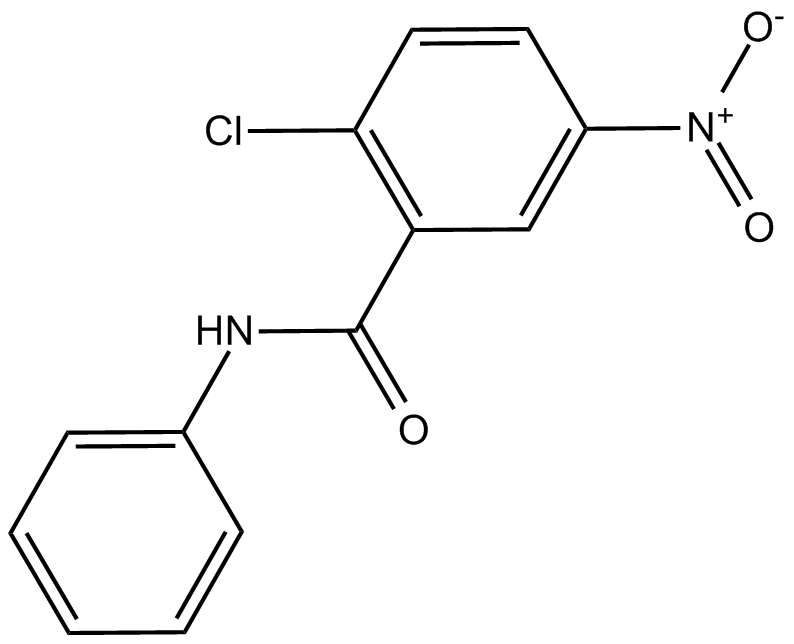 A4300 GW96621 CitationSummary: PPARγ antagonist
A4300 GW96621 CitationSummary: PPARγ antagonist -
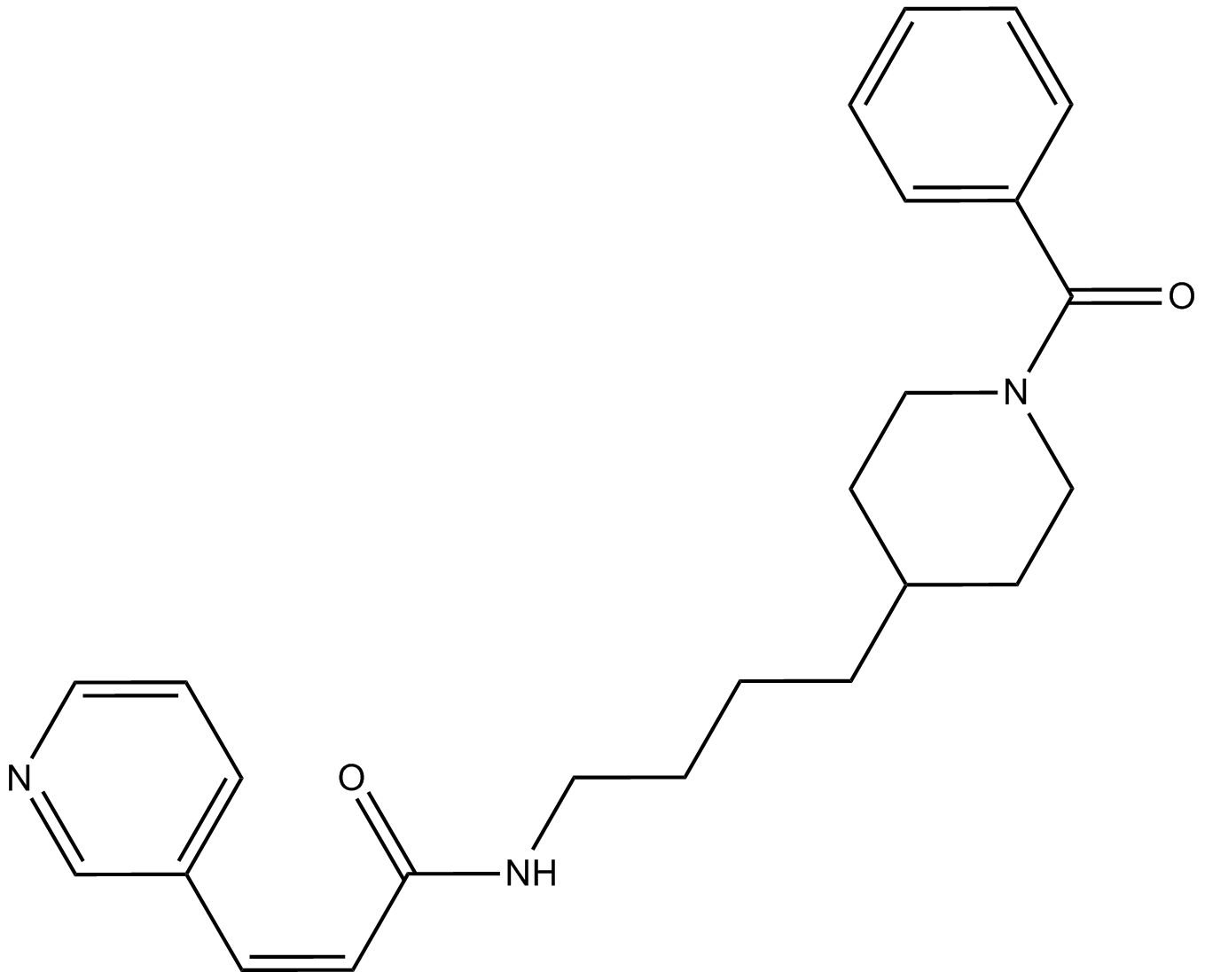 A4381 FK866 (APO866)9 CitationTarget: NamptSummary: NAMPT inhibitor, non-competitive, highly specific
A4381 FK866 (APO866)9 CitationTarget: NamptSummary: NAMPT inhibitor, non-competitive, highly specific -
 L1044P DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 178 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044P DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 178 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research. -
 L1026P DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 948 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026P DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 948 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch. -
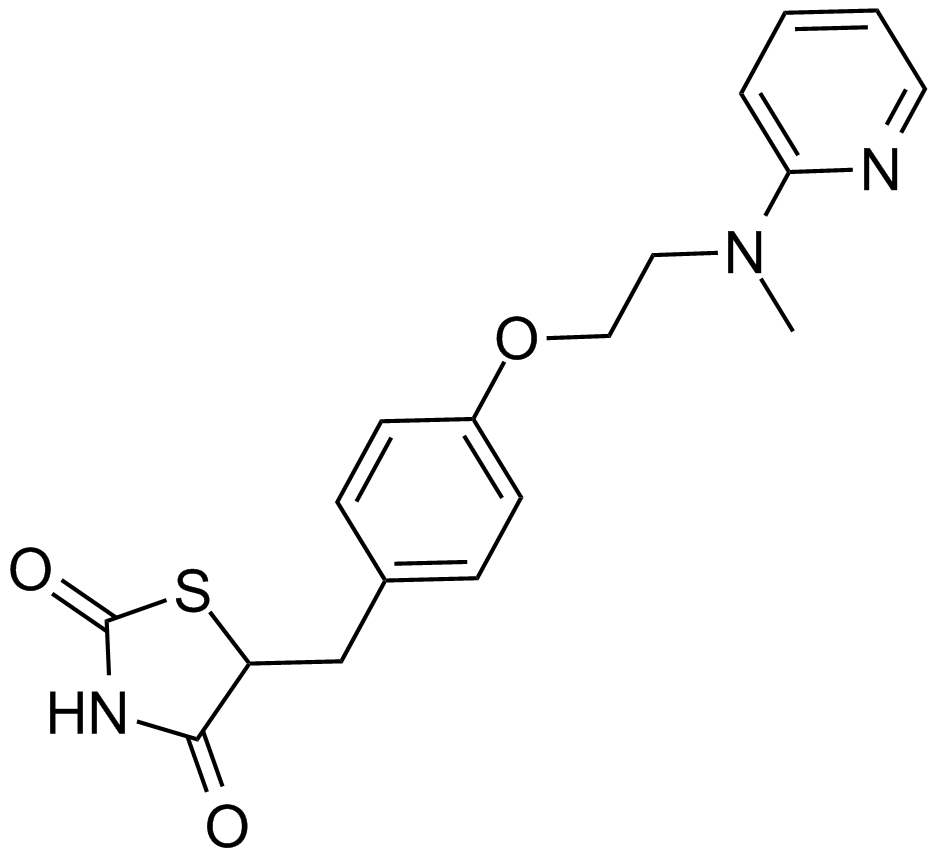 A4304 Rosiglitazone4 CitationSummary: Potent PPARγ agonist
A4304 Rosiglitazone4 CitationSummary: Potent PPARγ agonist -
 A5112 XL147Target: PI3KSummary: PI3K inhibitor,selective and reversible
A5112 XL147Target: PI3KSummary: PI3K inhibitor,selective and reversible -
 A2681 TGX-221Target: PI3KSummary: PI3Kβ inhibitor,potent,selective and ATP competitive
A2681 TGX-221Target: PI3KSummary: PI3Kβ inhibitor,potent,selective and ATP competitive -
 A5078 KU-0063794Target: mTORSummary: MTORC1 and mTORC2 inhibitor
A5078 KU-0063794Target: mTORSummary: MTORC1 and mTORC2 inhibitor


