Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel

Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins which allow the flow of ions across the membrane. The ion channels can be broadly grouped into six families including calcium channels, chloride channels, potassium channels, sodium channels, gap junction proteins and porins. Not all ion channels are gated, such as certain type of K+ and Cl– channels, transient receptor potential superfamily of cation channels, the ryanodine receptors and the IP3 receptors, but most Na+, K+, Ca2+ and some Cl– channels are all gated by voltage. Ligand-gated channels are regulated in response to ligand binding (e.g. neurotransmitters signaling). These ligand-gated neurotransmitter receptors are known as ionotropic receptors. Various neurotransmitters couple to ionotropic receptors such as glutamate, acetylcholine, glycine, GABA, and serotonin.
-
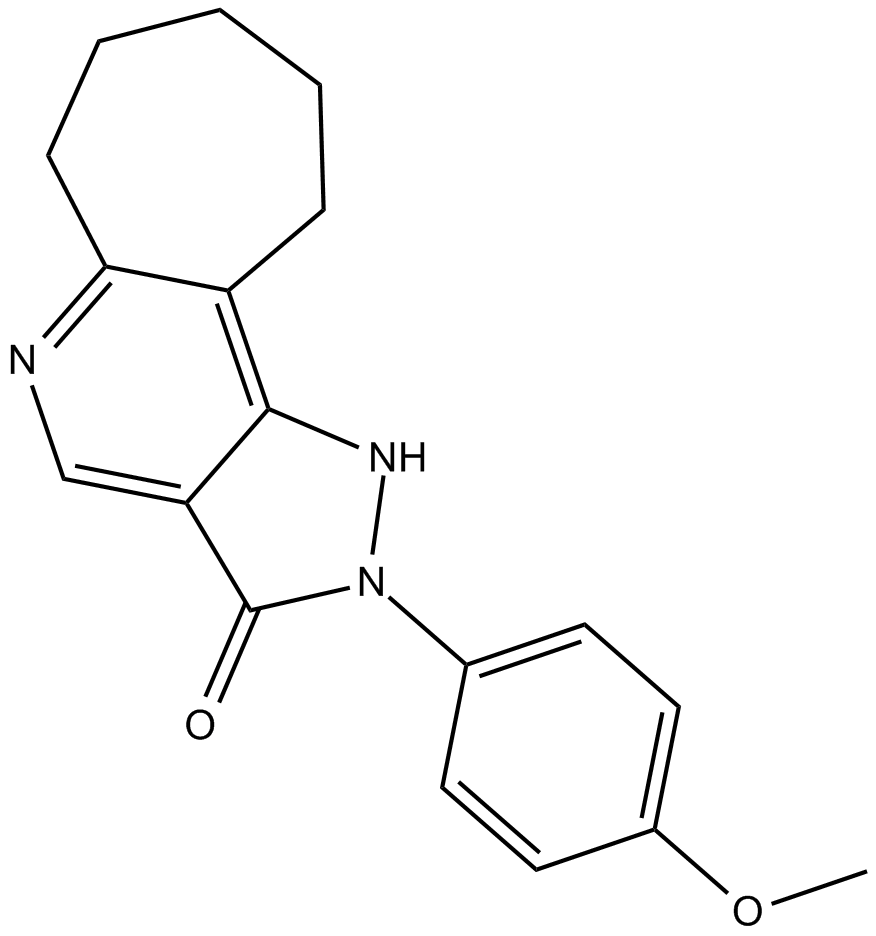 B7068 CGS 20625Summary: partial agonist for the benzodiazepine binding site of the GABAA receptor
B7068 CGS 20625Summary: partial agonist for the benzodiazepine binding site of the GABAA receptor -
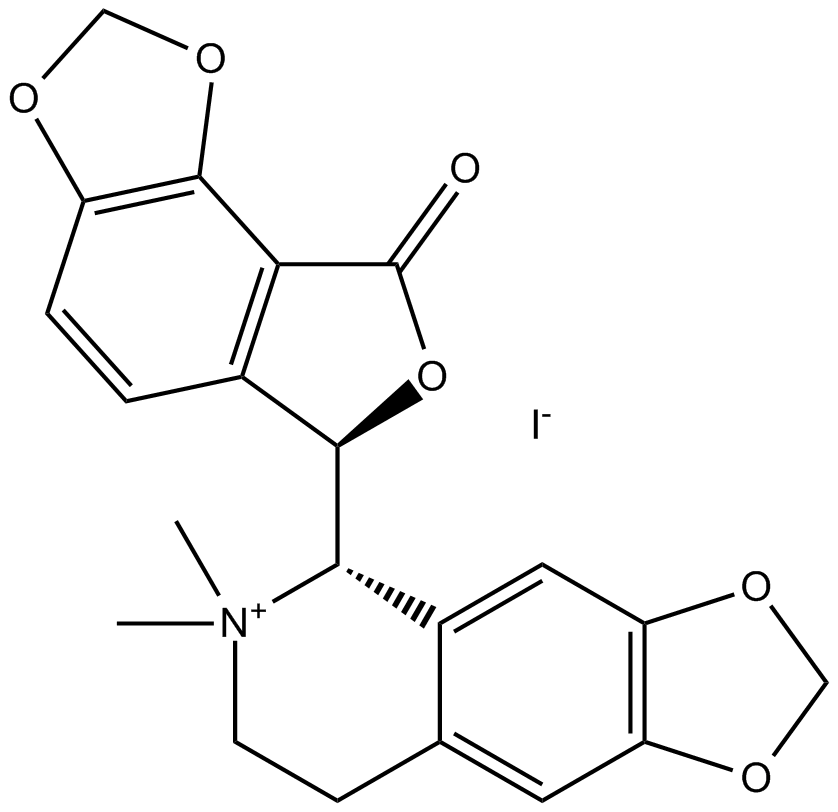 B7081 (-)-Bicuculline methiodideSummary: GABAA receptor antagonist
B7081 (-)-Bicuculline methiodideSummary: GABAA receptor antagonist -
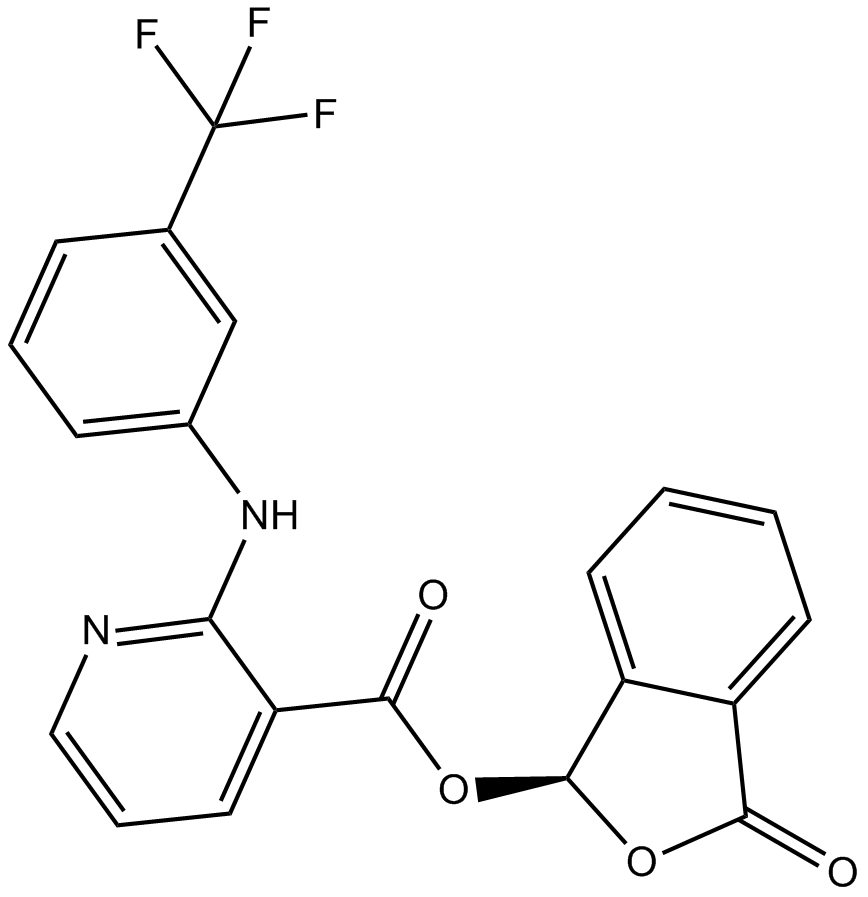 B7086 TalniflumateSummary: Calcium-activated chloride channel (CaCC) (hCLCA1/mCLCA3) blocker
B7086 TalniflumateSummary: Calcium-activated chloride channel (CaCC) (hCLCA1/mCLCA3) blocker -
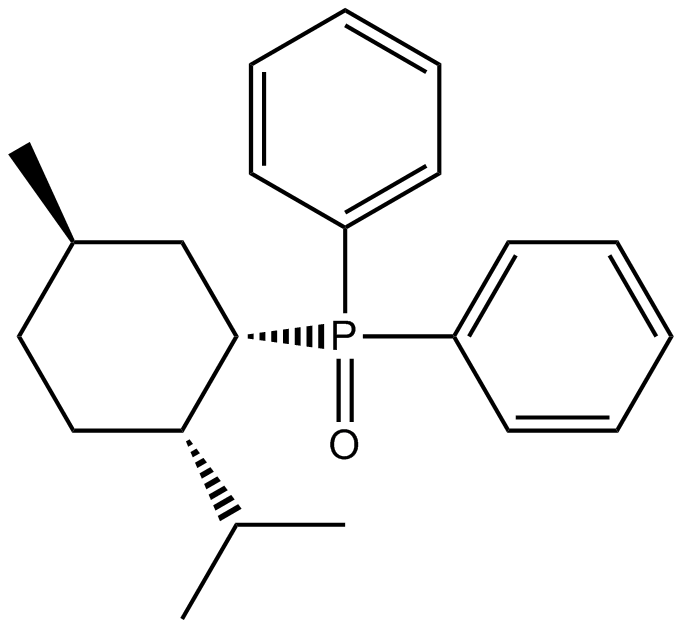 B7093 DPO-1Summary: Blocker of IKur ultrarapid delayed rectifier potassium current and KV1.5 channels
B7093 DPO-1Summary: Blocker of IKur ultrarapid delayed rectifier potassium current and KV1.5 channels -
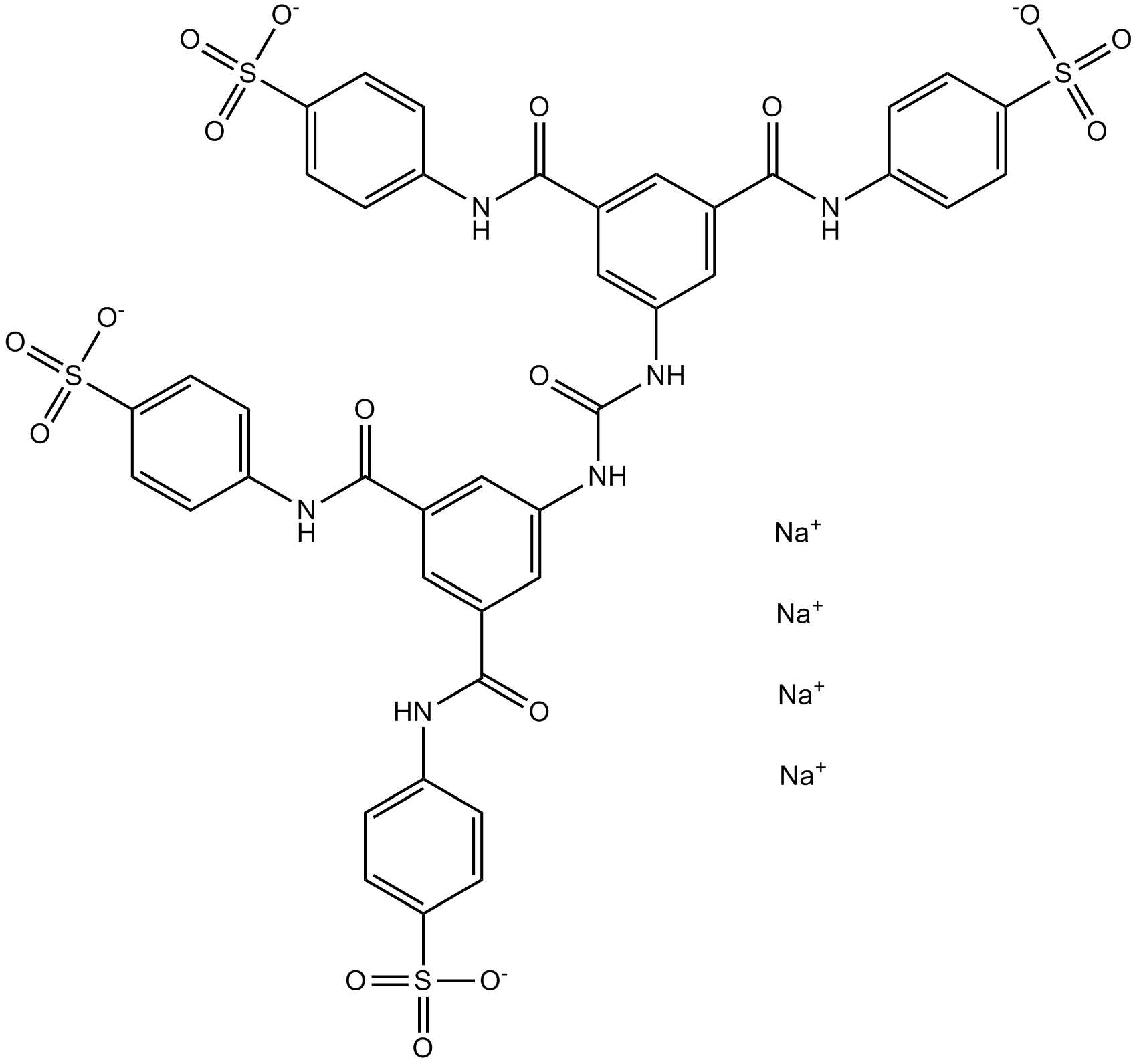 B7100 NF 110Summary: P2X3 antagonist
B7100 NF 110Summary: P2X3 antagonist -
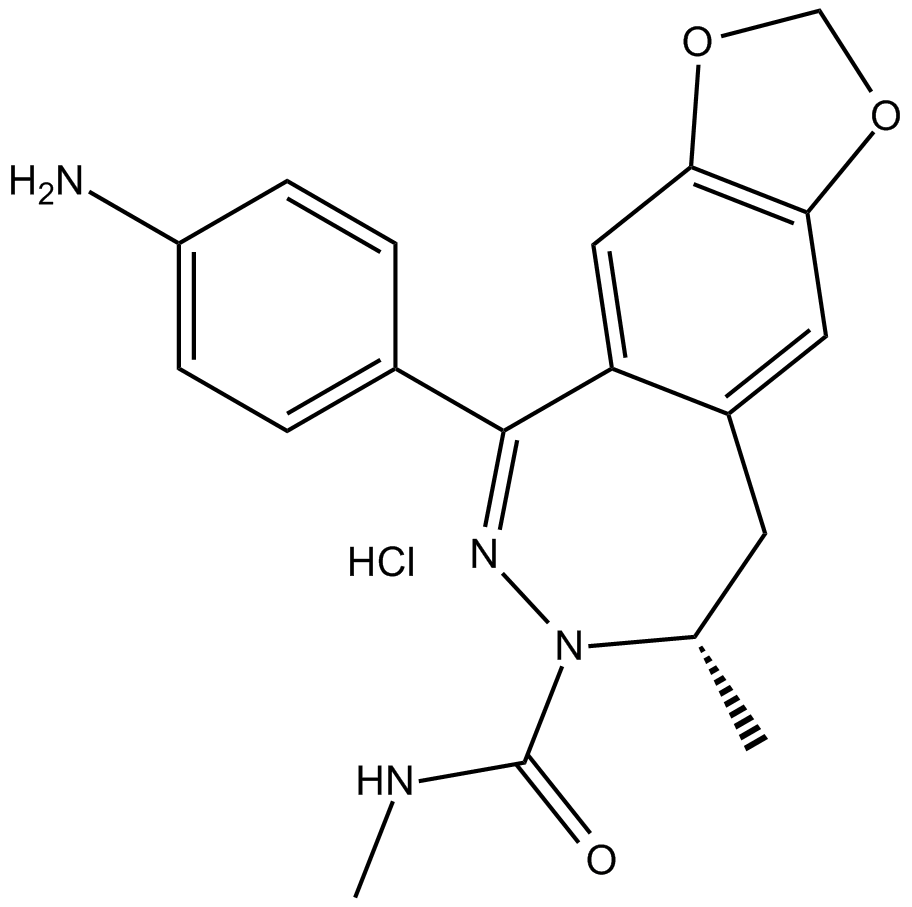 B7103 GYKI 53655 hydrochlorideSummary: AMPA and kainate receptor antagonist
B7103 GYKI 53655 hydrochlorideSummary: AMPA and kainate receptor antagonist -
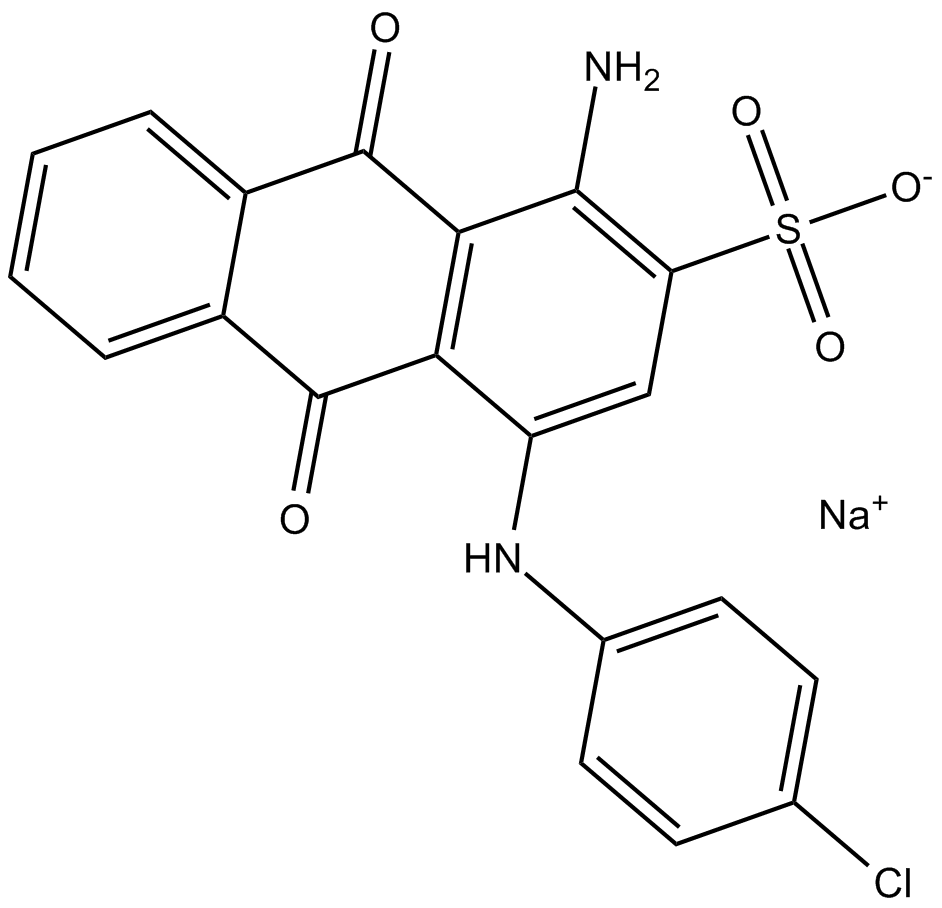 B7112 PSB 069Summary: NTPDase inhibitor
B7112 PSB 069Summary: NTPDase inhibitor -
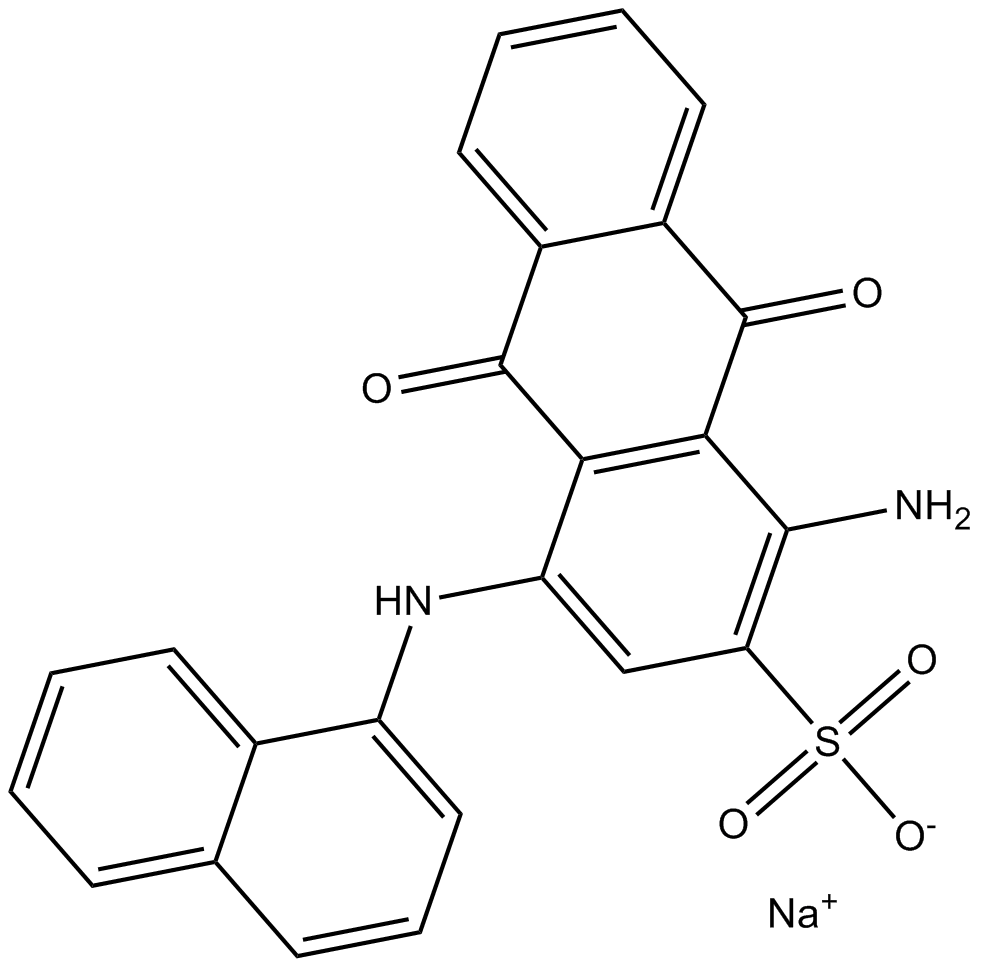 B7113 PSB 06126Target: NTPDasesSummary: NTPDase 3 inhibitor
B7113 PSB 06126Target: NTPDasesSummary: NTPDase 3 inhibitor -
 B7135 Co 102862Summary: voltage-gated sodium channel blocker
B7135 Co 102862Summary: voltage-gated sodium channel blocker -
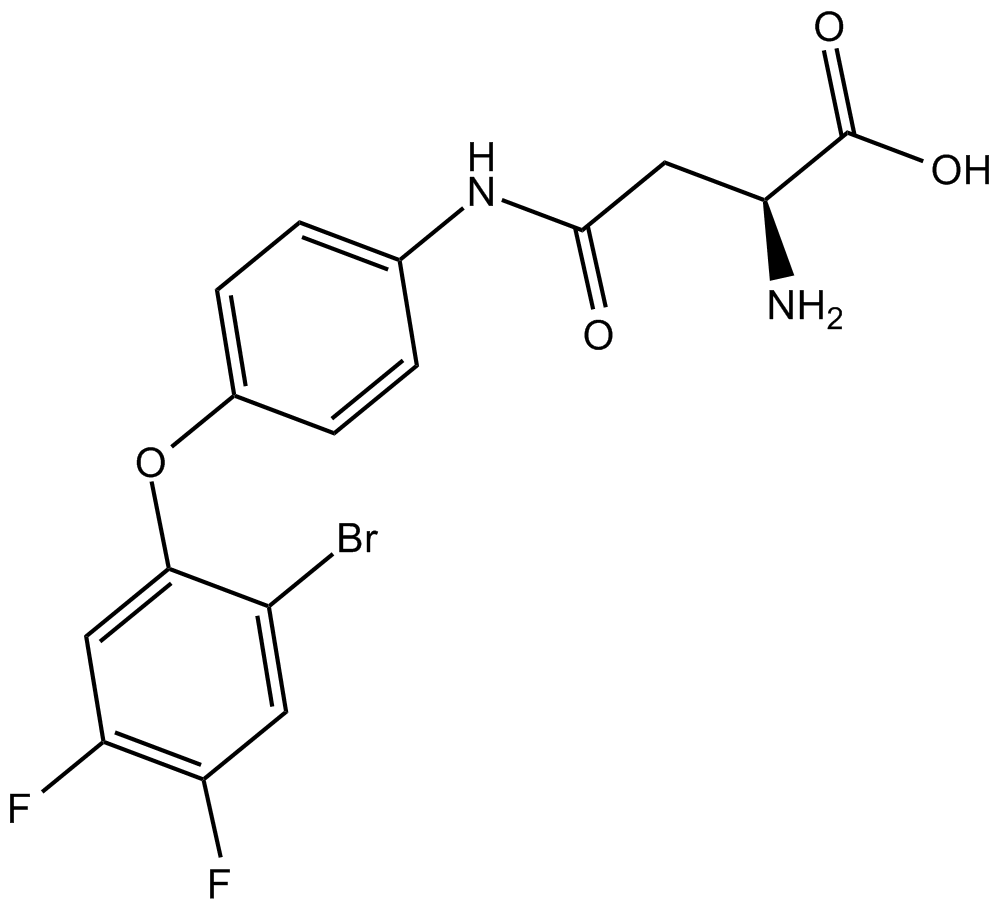 B7139 WAY 213613Summary: EAAT2 (GLT-1) inhibitor
B7139 WAY 213613Summary: EAAT2 (GLT-1) inhibitor

