Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel

Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins which allow the flow of ions across the membrane. The ion channels can be broadly grouped into six families including calcium channels, chloride channels, potassium channels, sodium channels, gap junction proteins and porins. Not all ion channels are gated, such as certain type of K+ and Cl– channels, transient receptor potential superfamily of cation channels, the ryanodine receptors and the IP3 receptors, but most Na+, K+, Ca2+ and some Cl– channels are all gated by voltage. Ligand-gated channels are regulated in response to ligand binding (e.g. neurotransmitters signaling). These ligand-gated neurotransmitter receptors are known as ionotropic receptors. Various neurotransmitters couple to ionotropic receptors such as glutamate, acetylcholine, glycine, GABA, and serotonin.
-
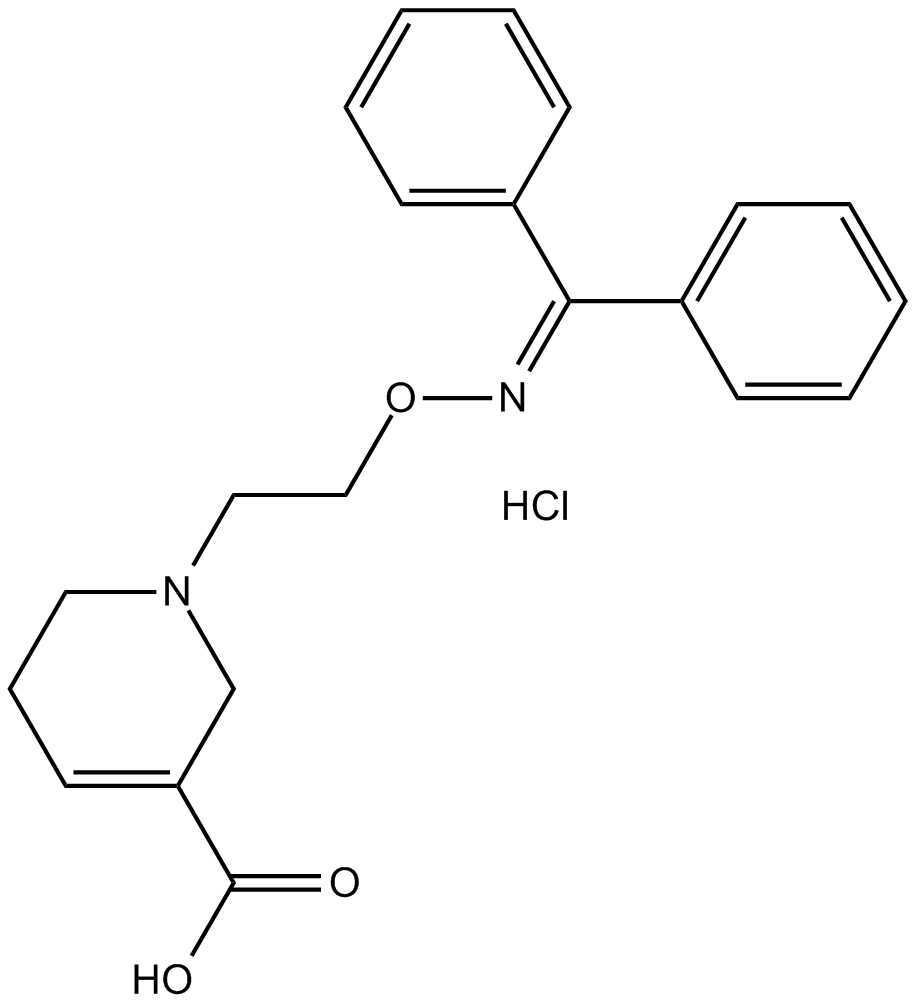 B6854 NNC 711Summary: GABA uptake inhibitor
B6854 NNC 711Summary: GABA uptake inhibitor -
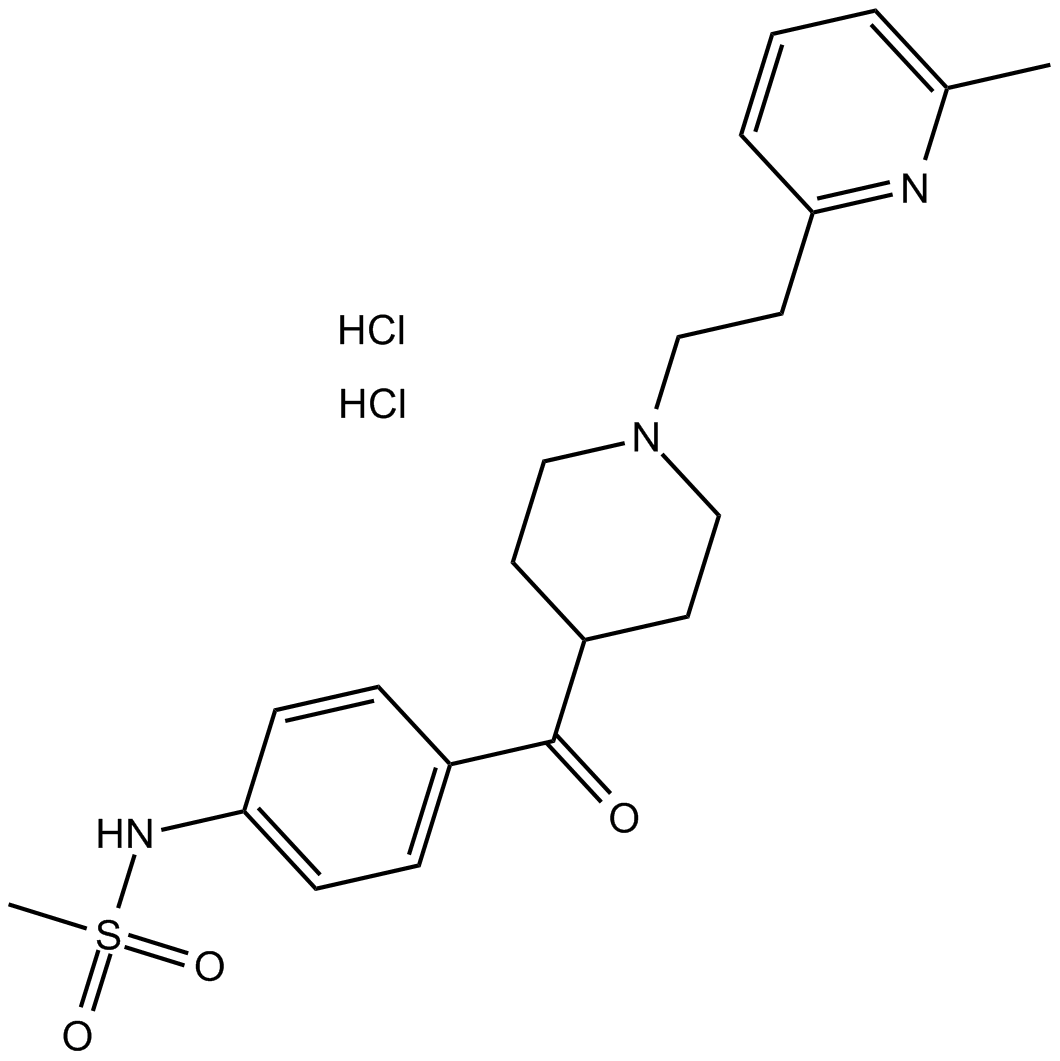 B6862 E-4031 dihydrochlorideSummary: A Kv11.1 (hERG) K+ channel blocker
B6862 E-4031 dihydrochlorideSummary: A Kv11.1 (hERG) K+ channel blocker -
 B6866 N-ArachidonylGABASummary: arachidonyl amino acid
B6866 N-ArachidonylGABASummary: arachidonyl amino acid -
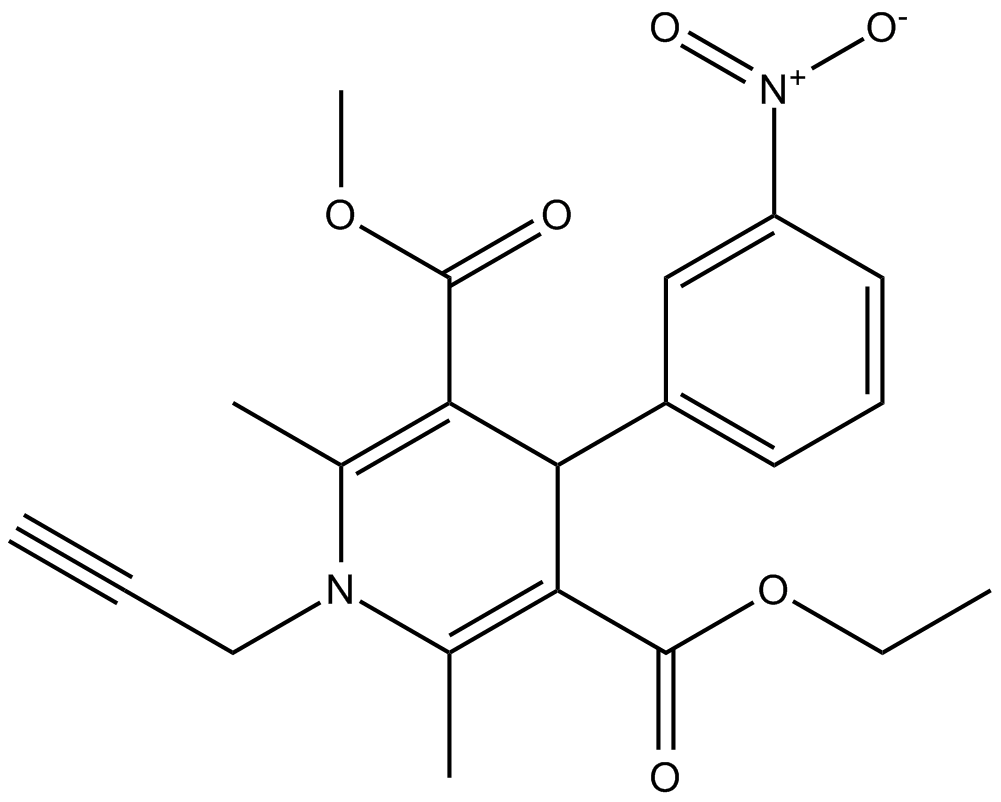 B6880 MRS 1845Summary: store-operated Ca2+ channels blocker
B6880 MRS 1845Summary: store-operated Ca2+ channels blocker -
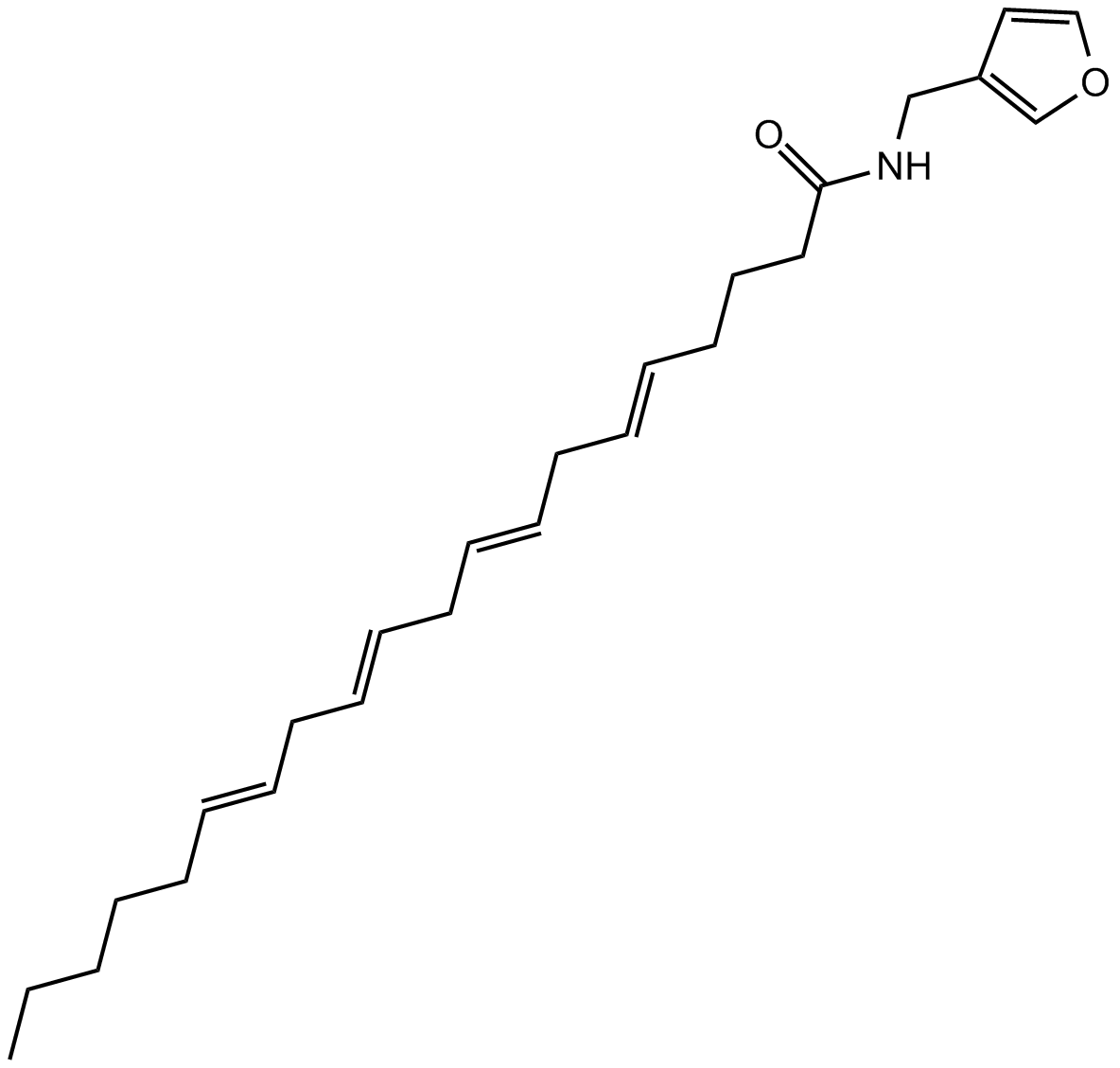 B6901 UCM 707Summary: endocannabinoid transport inhibitor
B6901 UCM 707Summary: endocannabinoid transport inhibitor -
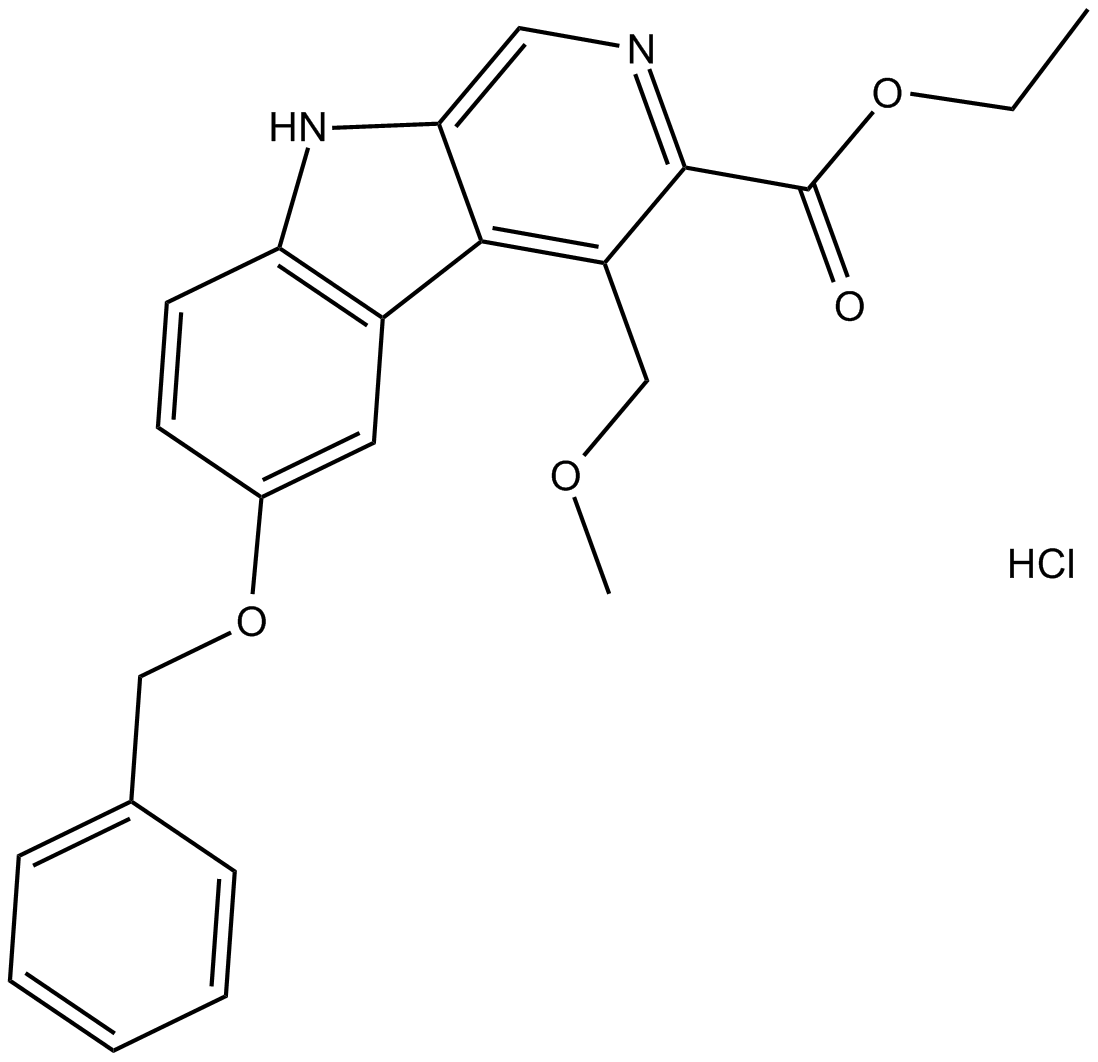 B6912 ZK 93423 hydrochlorideSummary: GABAA receptor agonist
B6912 ZK 93423 hydrochlorideSummary: GABAA receptor agonist -
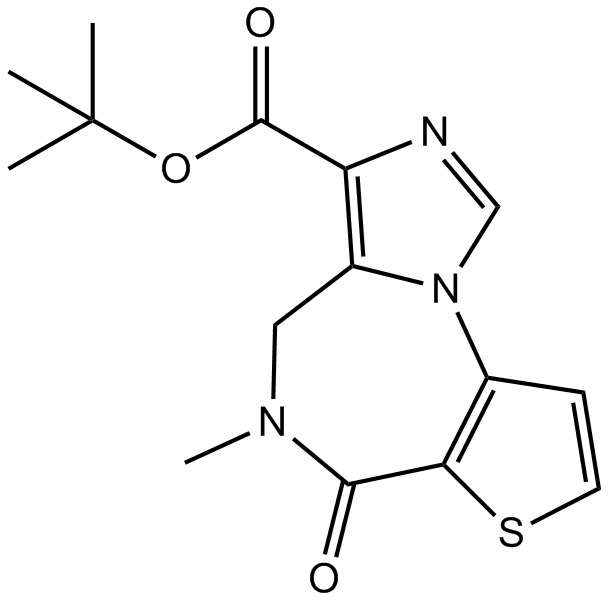 B6913 Ro 19-4603Summary: Benzodiazepine inverse agonist
B6913 Ro 19-4603Summary: Benzodiazepine inverse agonist -
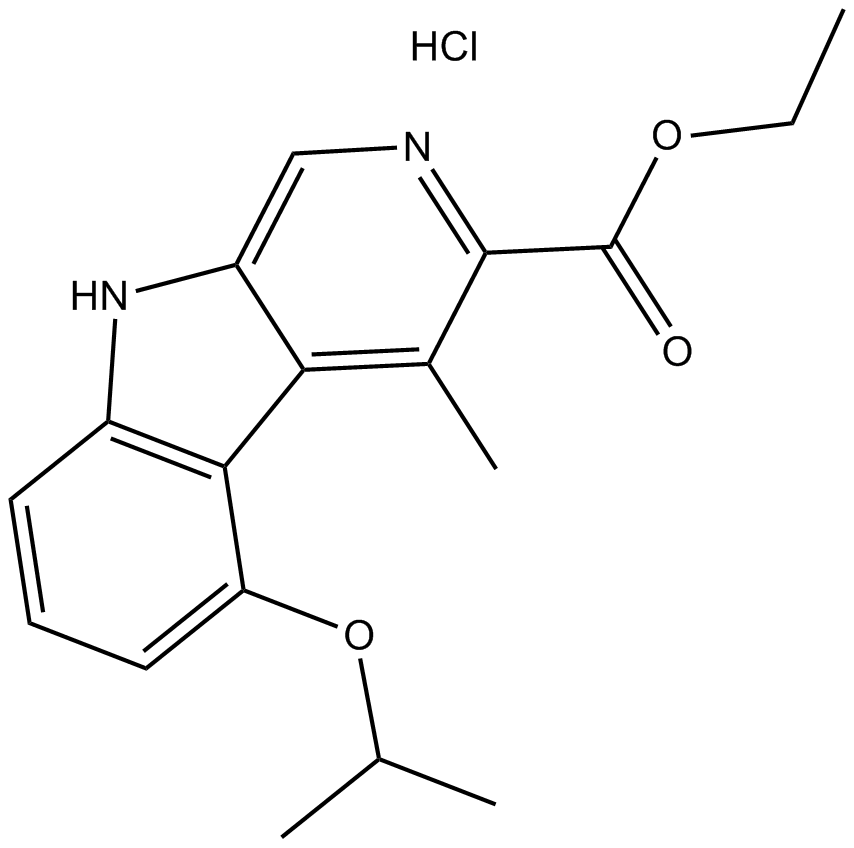 B6914 ZK 93426 hydrochlorideSummary: benzodiazepine receptor antagonist,competitive
B6914 ZK 93426 hydrochlorideSummary: benzodiazepine receptor antagonist,competitive -
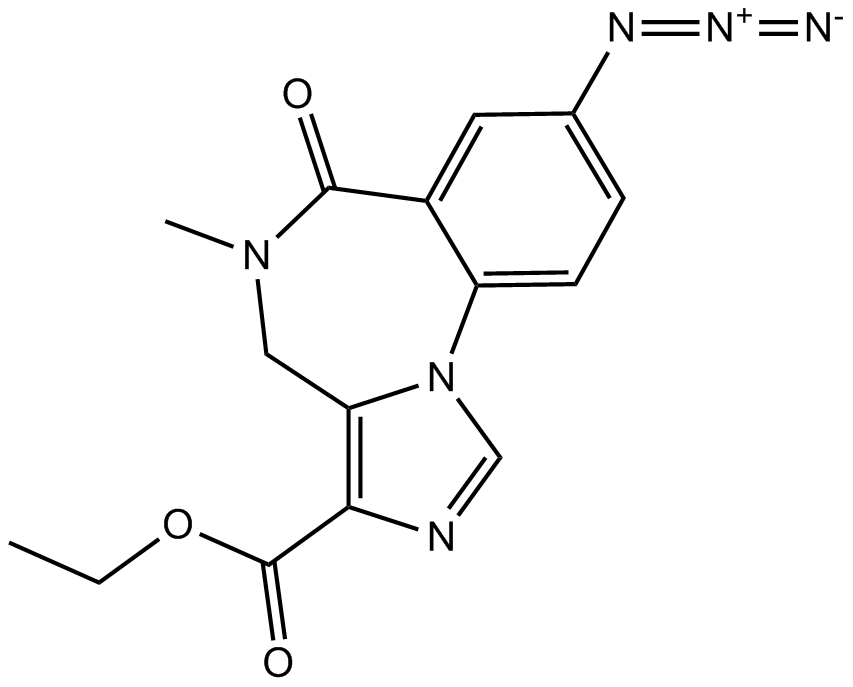 B6915 Ro 15-4513Summary: benzodiazepine ligand
B6915 Ro 15-4513Summary: benzodiazepine ligand -
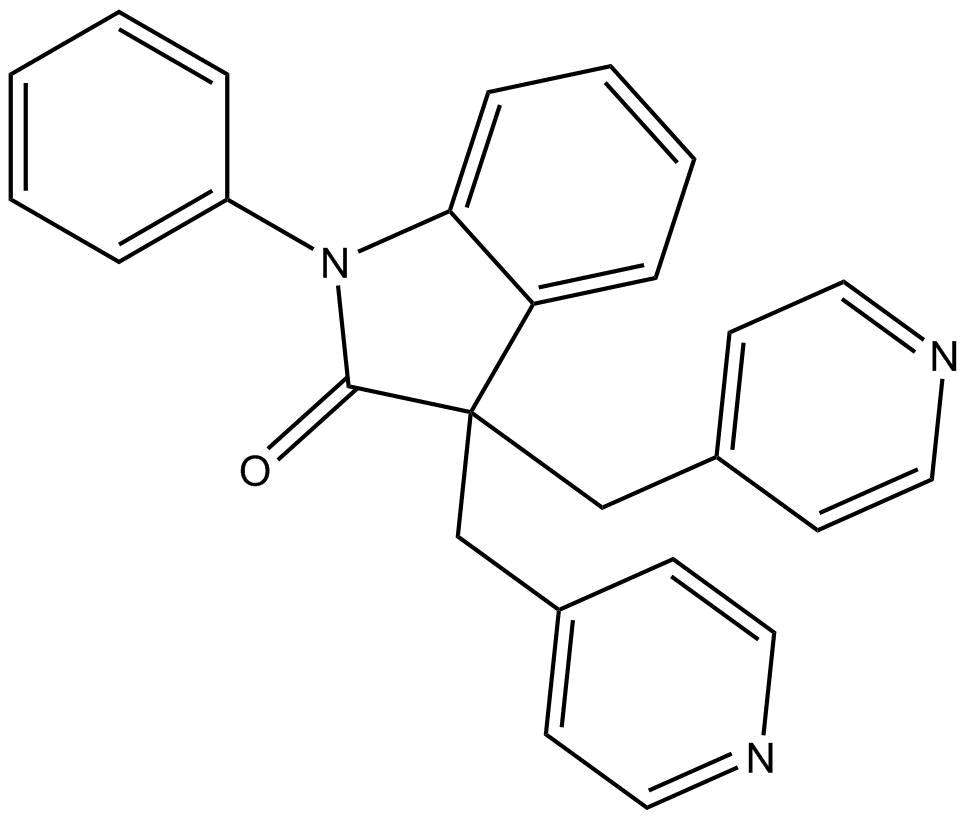 B6916 LinopirdineSummary: KV7 (KCNQ) voltage-gated potassium channels blocker
B6916 LinopirdineSummary: KV7 (KCNQ) voltage-gated potassium channels blocker

