Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel

Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins which allow the flow of ions across the membrane. The ion channels can be broadly grouped into six families including calcium channels, chloride channels, potassium channels, sodium channels, gap junction proteins and porins. Not all ion channels are gated, such as certain type of K+ and Cl– channels, transient receptor potential superfamily of cation channels, the ryanodine receptors and the IP3 receptors, but most Na+, K+, Ca2+ and some Cl– channels are all gated by voltage. Ligand-gated channels are regulated in response to ligand binding (e.g. neurotransmitters signaling). These ligand-gated neurotransmitter receptors are known as ionotropic receptors. Various neurotransmitters couple to ionotropic receptors such as glutamate, acetylcholine, glycine, GABA, and serotonin.
-
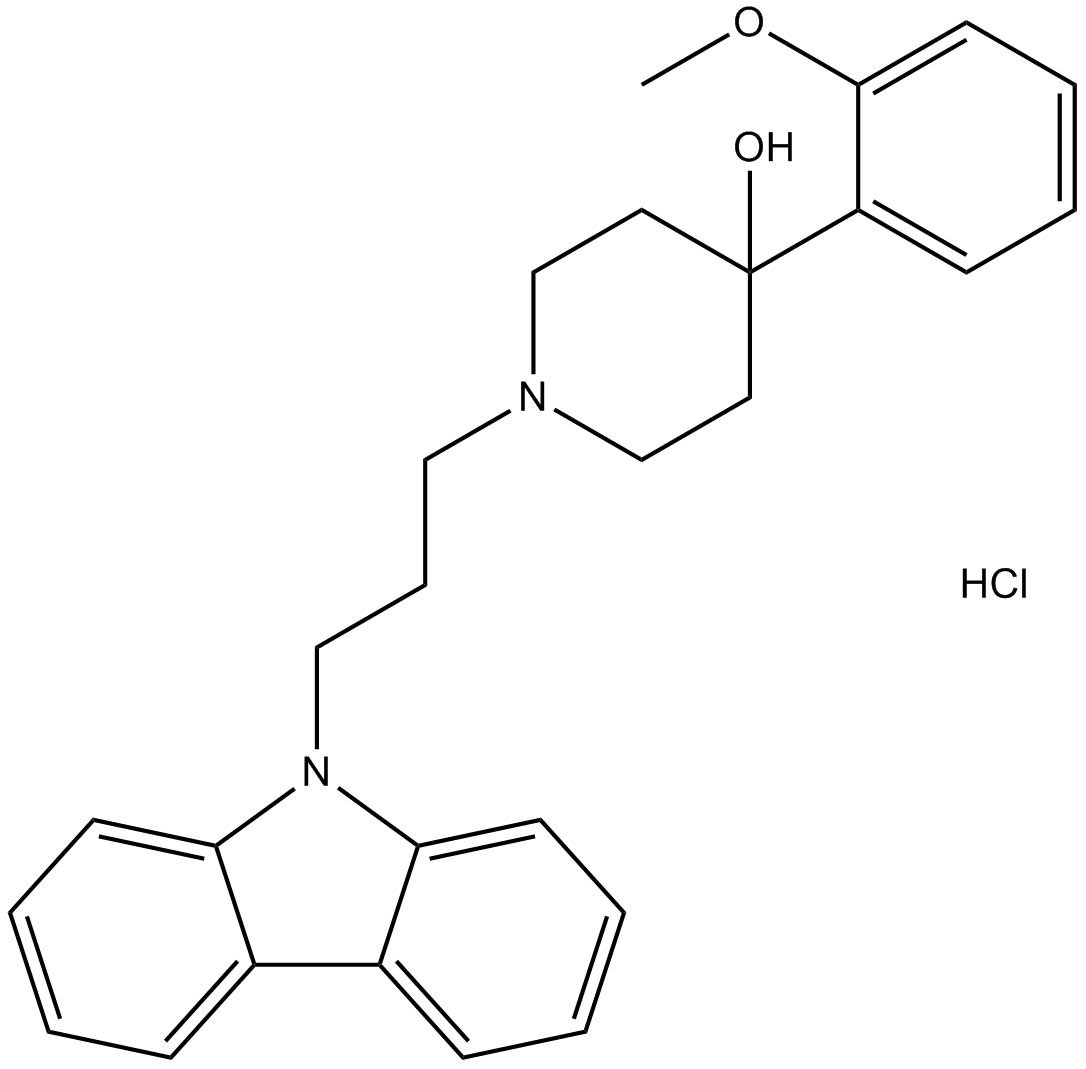 B7172 NNC 05-2090 hydrochlorideSummary: GABA uptake inhibitor
B7172 NNC 05-2090 hydrochlorideSummary: GABA uptake inhibitor -
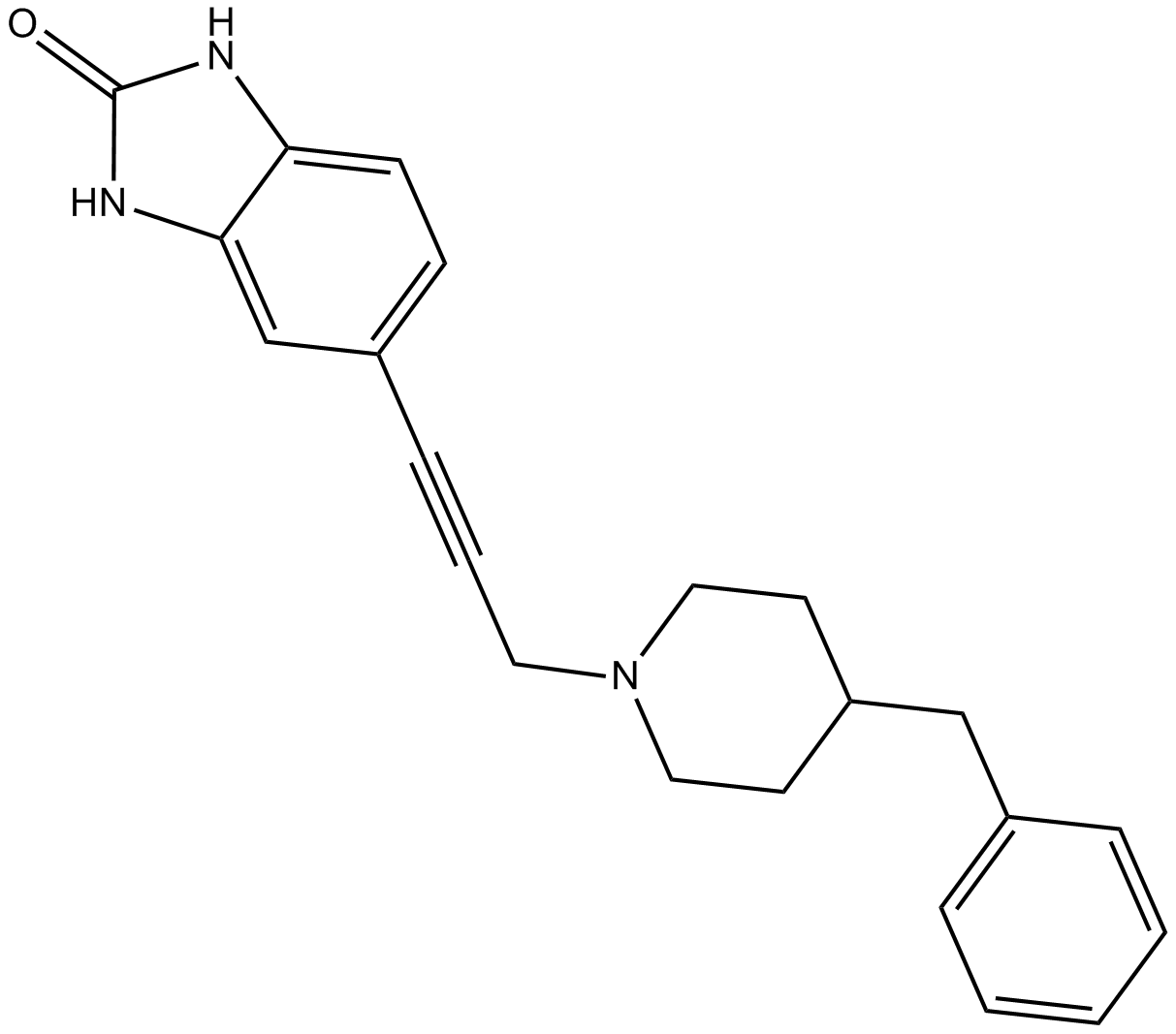 B7186 TCS 46bSummary: NR1A/NR2B NMDA receptor antagonist,orally active
B7186 TCS 46bSummary: NR1A/NR2B NMDA receptor antagonist,orally active -
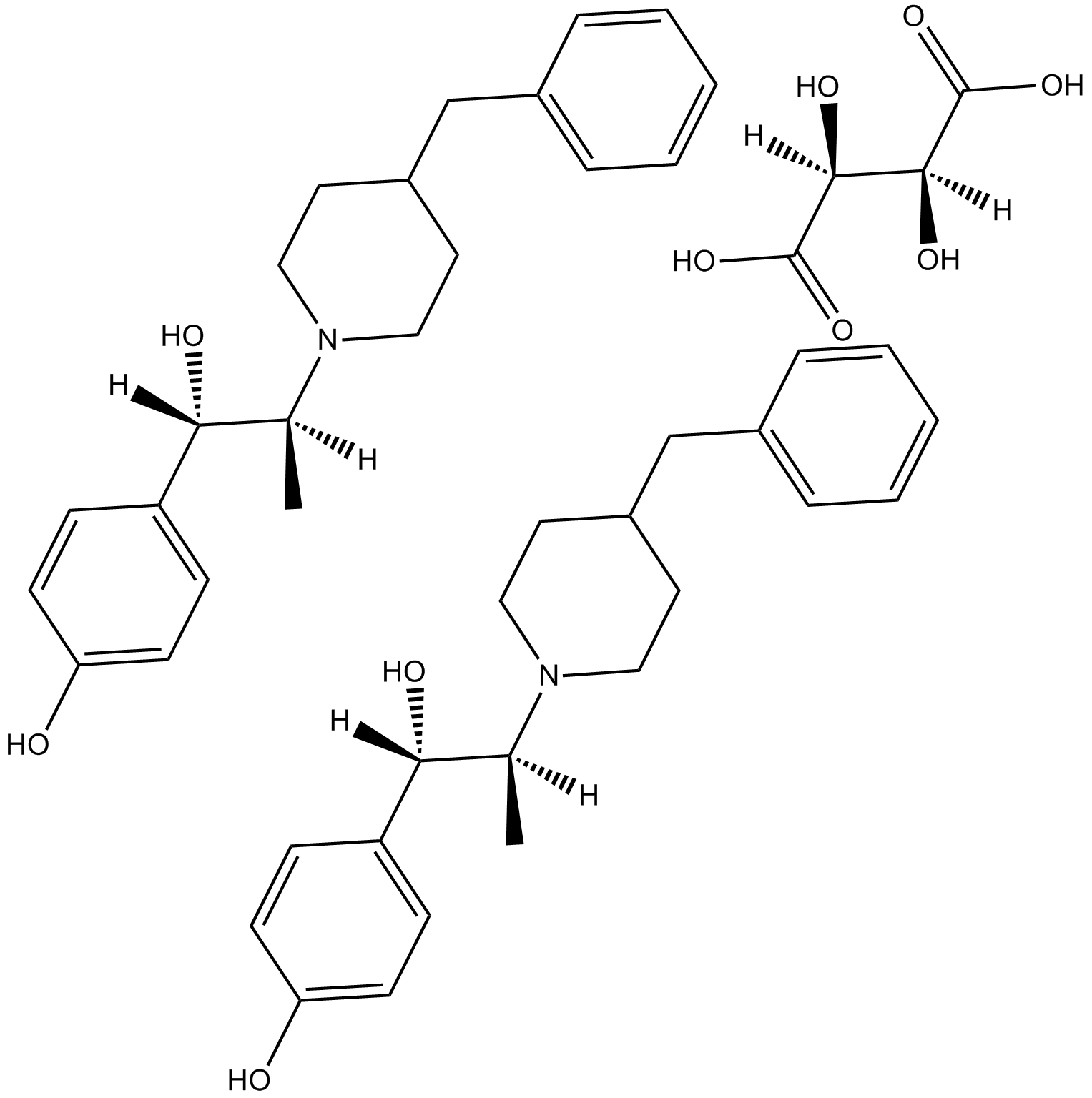 B7212 threo Ifenprodil hemitartrateSummary: σ receptor agonist and NR2B subunit-selective NMDA receptor antagonist
B7212 threo Ifenprodil hemitartrateSummary: σ receptor agonist and NR2B subunit-selective NMDA receptor antagonist -
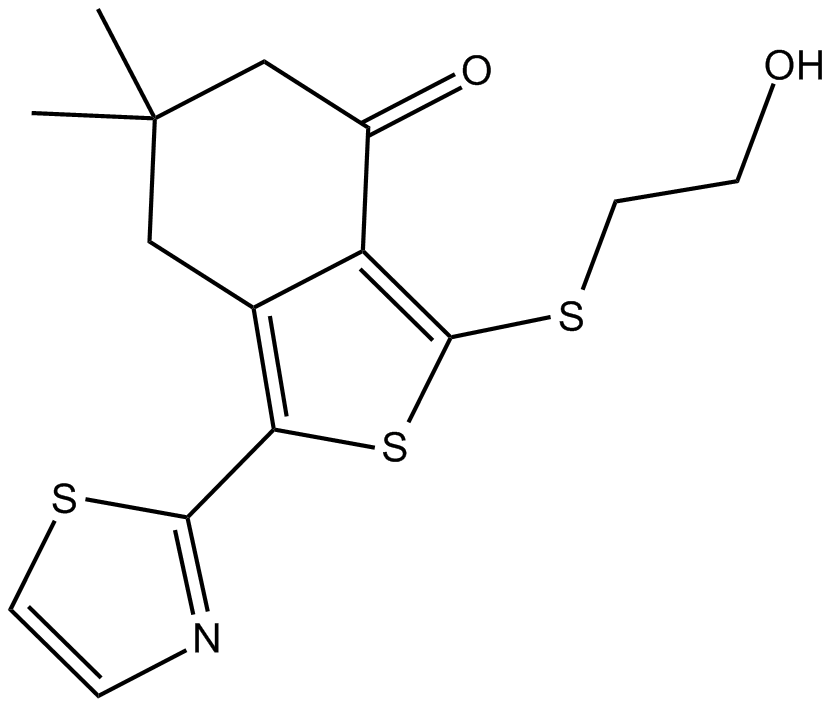 B7214 TB 21007Summary: GABAA receptor inverse agonist
B7214 TB 21007Summary: GABAA receptor inverse agonist -
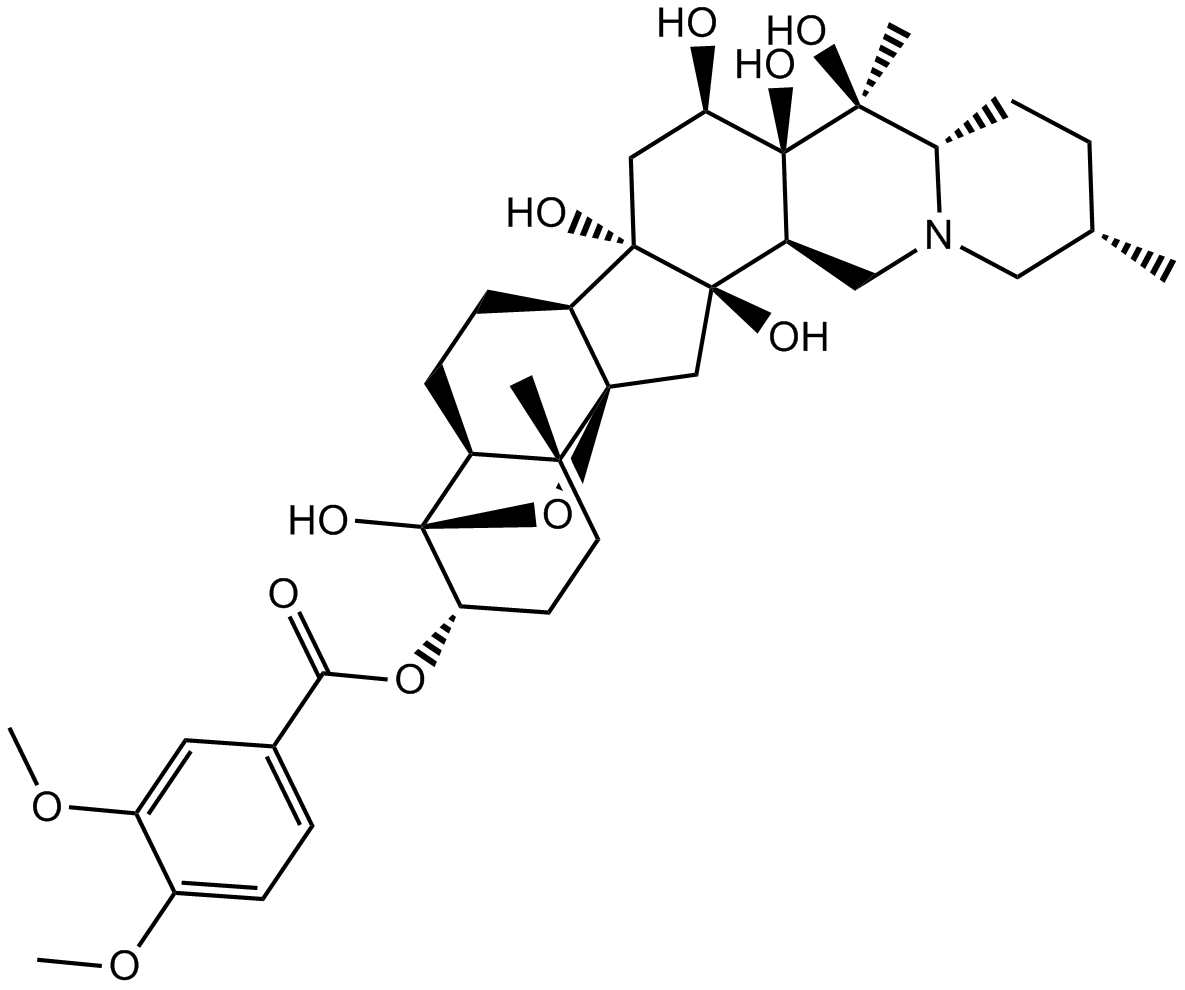 B7219 VeratridineSummary: Voltage-gated Na+ channel opener
B7219 VeratridineSummary: Voltage-gated Na+ channel opener -
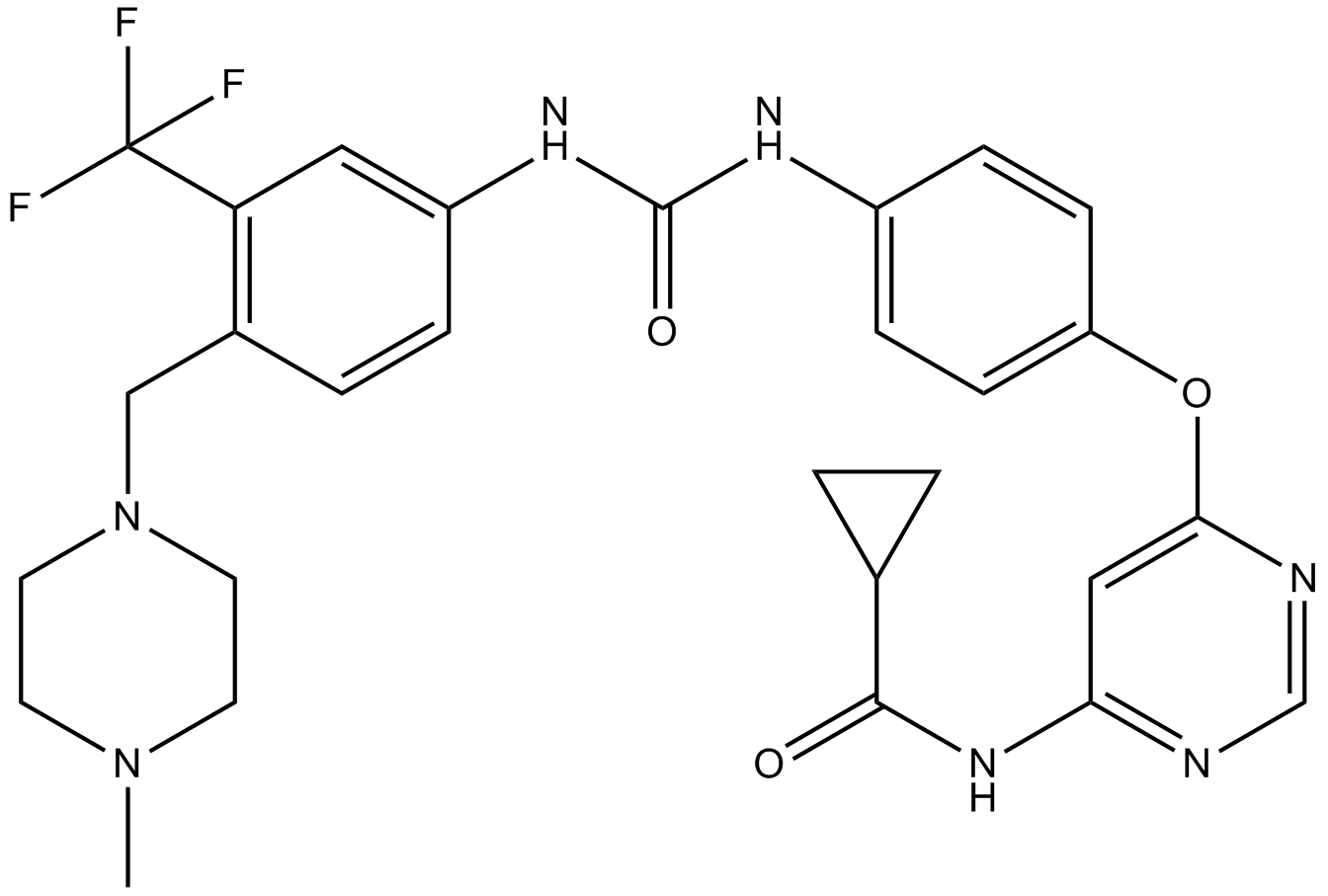 B7223 WS 3Summary: TRPM8 receptor agonist
B7223 WS 3Summary: TRPM8 receptor agonist -
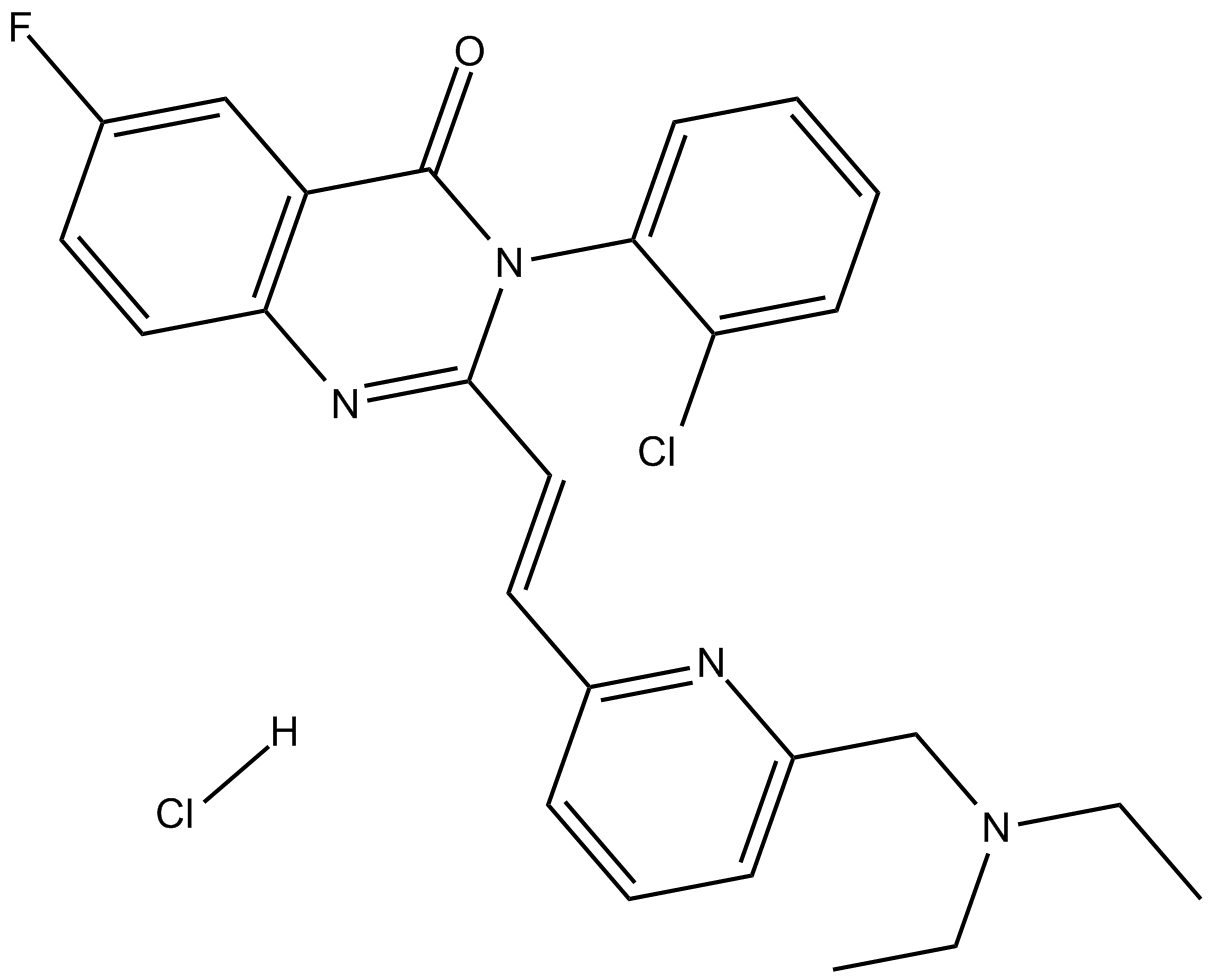 B7225 CP 465022 hydrochlorideSummary: AMPA receptor antagonist, non-competitive and selective
B7225 CP 465022 hydrochlorideSummary: AMPA receptor antagonist, non-competitive and selective -
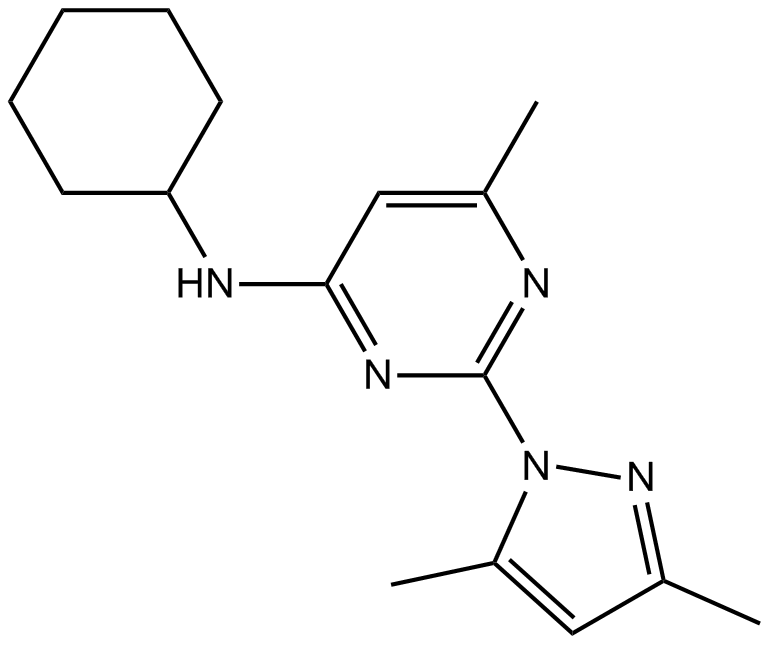 B7231 CyPPASummary: Activator of small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels
B7231 CyPPASummary: Activator of small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels -
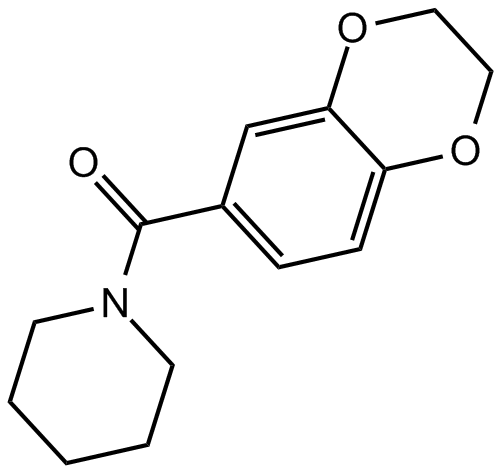 B7240 CX 546Summary: AMPA receptor potentiator
B7240 CX 546Summary: AMPA receptor potentiator -
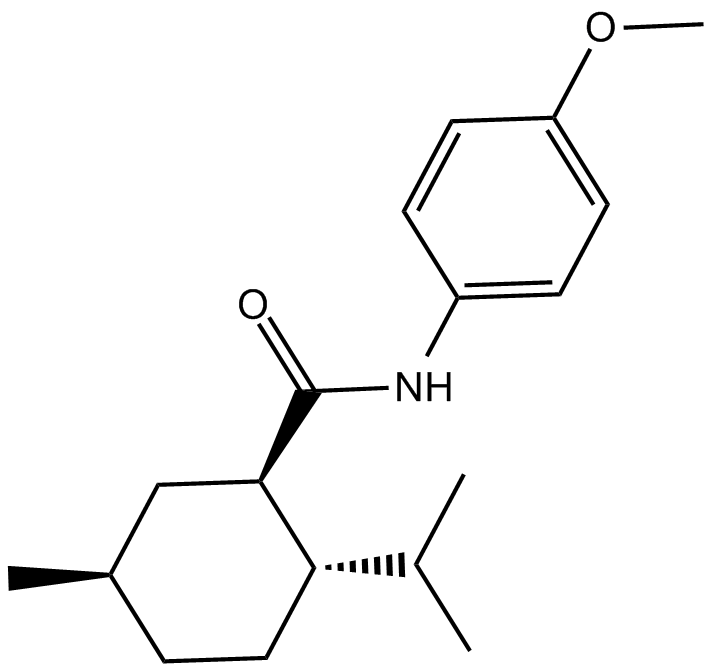 B7251 WS 12Summary: TRPM8 agonist
B7251 WS 12Summary: TRPM8 agonist

