Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel

Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins which allow the flow of ions across the membrane. The ion channels can be broadly grouped into six families including calcium channels, chloride channels, potassium channels, sodium channels, gap junction proteins and porins. Not all ion channels are gated, such as certain type of K+ and Cl– channels, transient receptor potential superfamily of cation channels, the ryanodine receptors and the IP3 receptors, but most Na+, K+, Ca2+ and some Cl– channels are all gated by voltage. Ligand-gated channels are regulated in response to ligand binding (e.g. neurotransmitters signaling). These ligand-gated neurotransmitter receptors are known as ionotropic receptors. Various neurotransmitters couple to ionotropic receptors such as glutamate, acetylcholine, glycine, GABA, and serotonin.
-
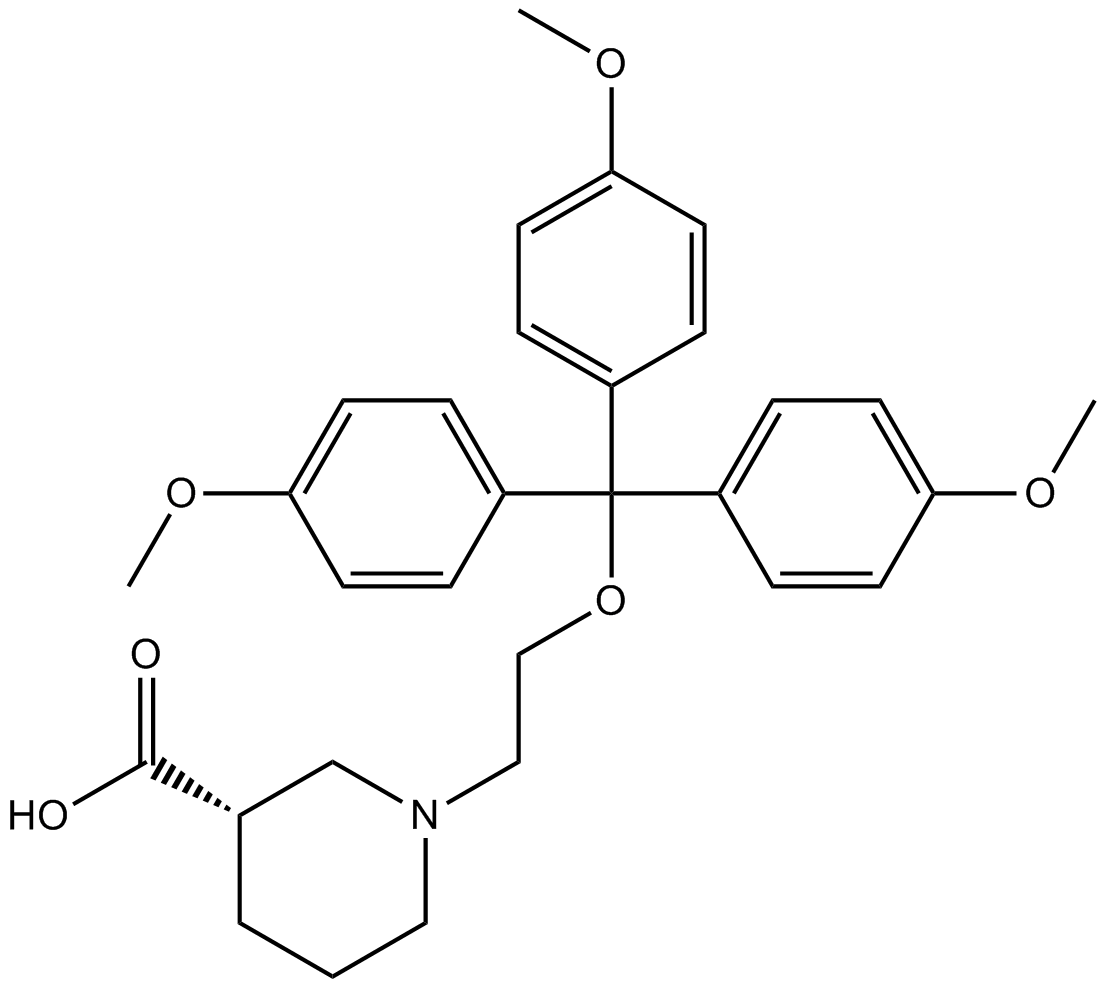 B6792 (S)-SNAP 5114Summary: GABA uptake inhibitor
B6792 (S)-SNAP 5114Summary: GABA uptake inhibitor -
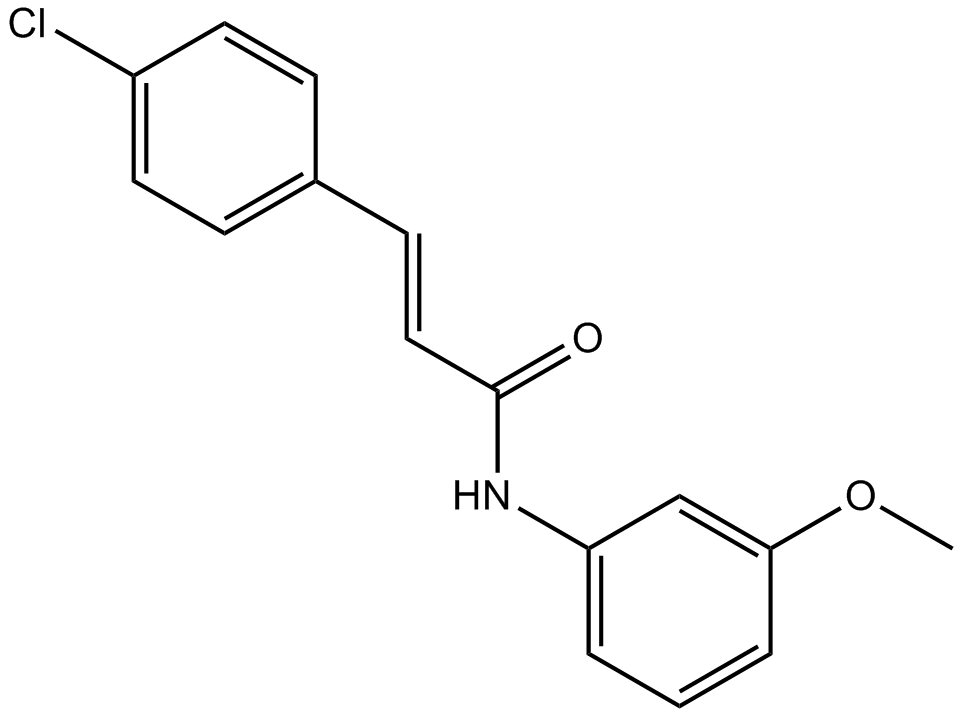 B6804 SB 366791Summary: vanilloid TRPV1 receptor antagonist
B6804 SB 366791Summary: vanilloid TRPV1 receptor antagonist -
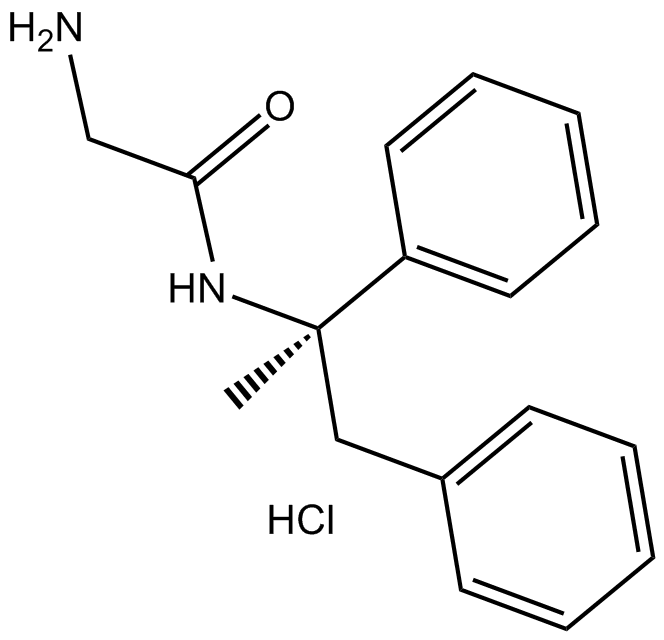 B6805 Remacemide hydrochlorideSummary: NMDA receptor antagonist
B6805 Remacemide hydrochlorideSummary: NMDA receptor antagonist -
 B6811 IEM 1460Summary: AMPA receptors blocker
B6811 IEM 1460Summary: AMPA receptors blocker -
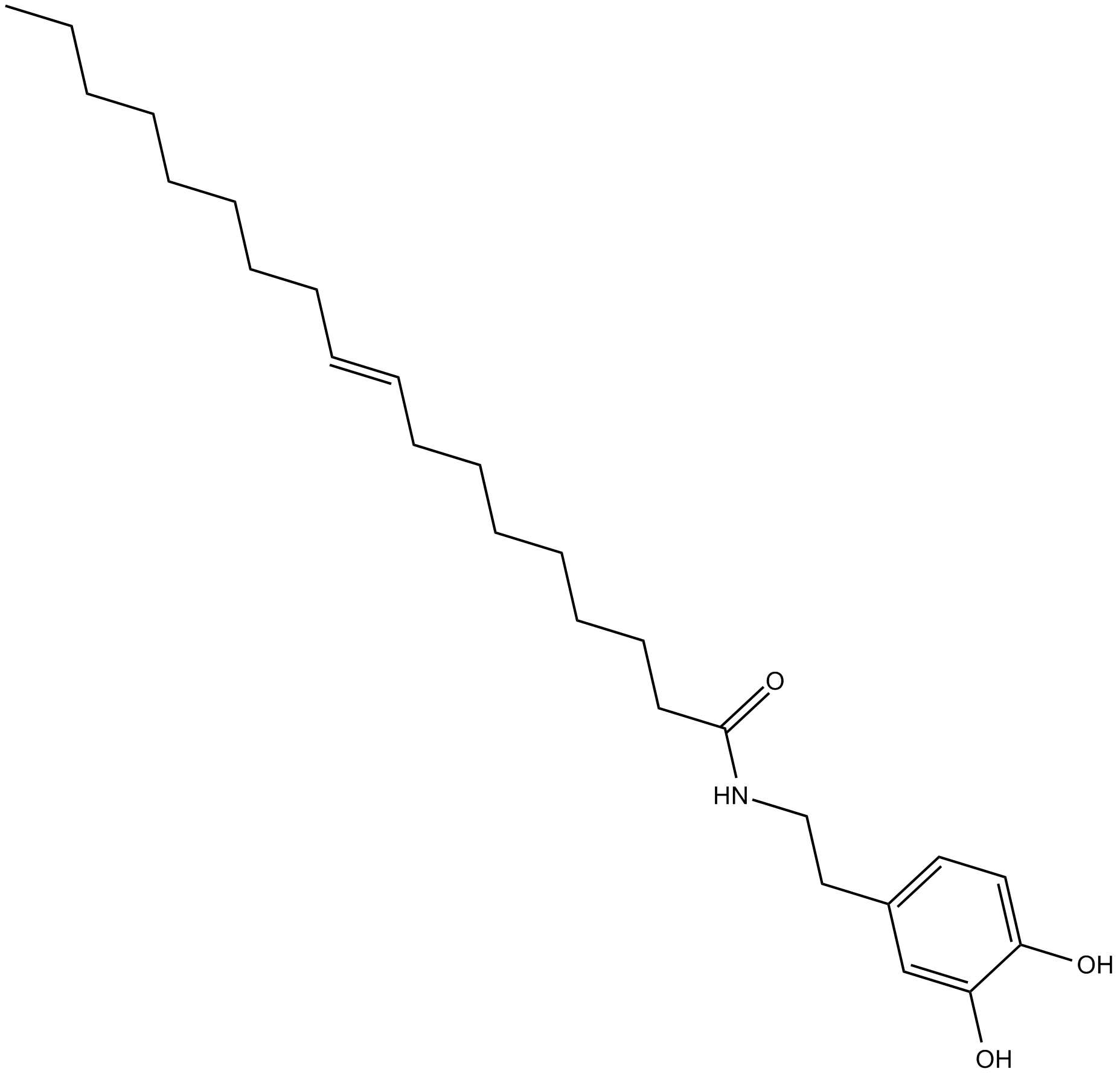 B6814 OLDASummary: endogenous vanilloid TRPV1 (VR1) receptor agonist
B6814 OLDASummary: endogenous vanilloid TRPV1 (VR1) receptor agonist -
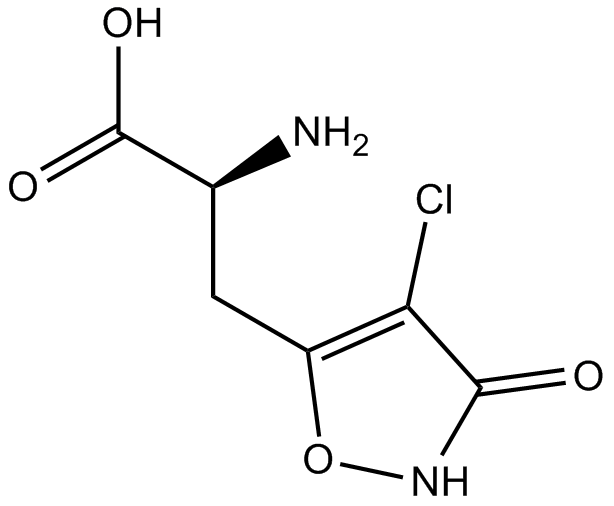 B6823 Cl-HIBOSummary: desensitising AMPA receptor agonist
B6823 Cl-HIBOSummary: desensitising AMPA receptor agonist -
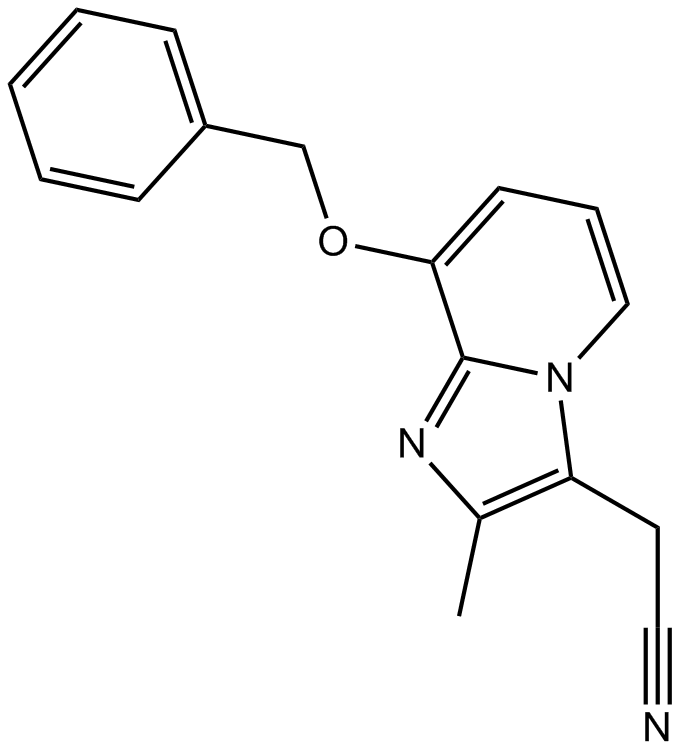 B6832 SCH 28080Summary: H+,K+-ATPase inhibitor
B6832 SCH 28080Summary: H+,K+-ATPase inhibitor -
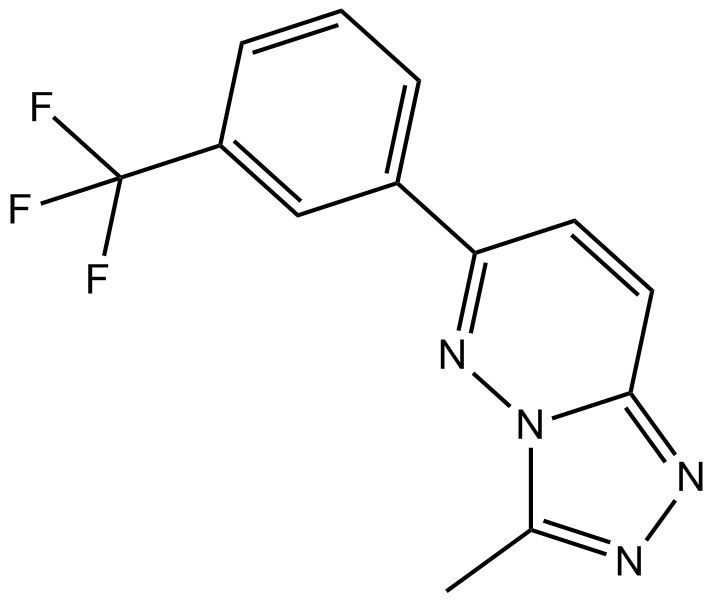 B6840 CL 218872Summary: Benzodiazepine agonist
B6840 CL 218872Summary: Benzodiazepine agonist -
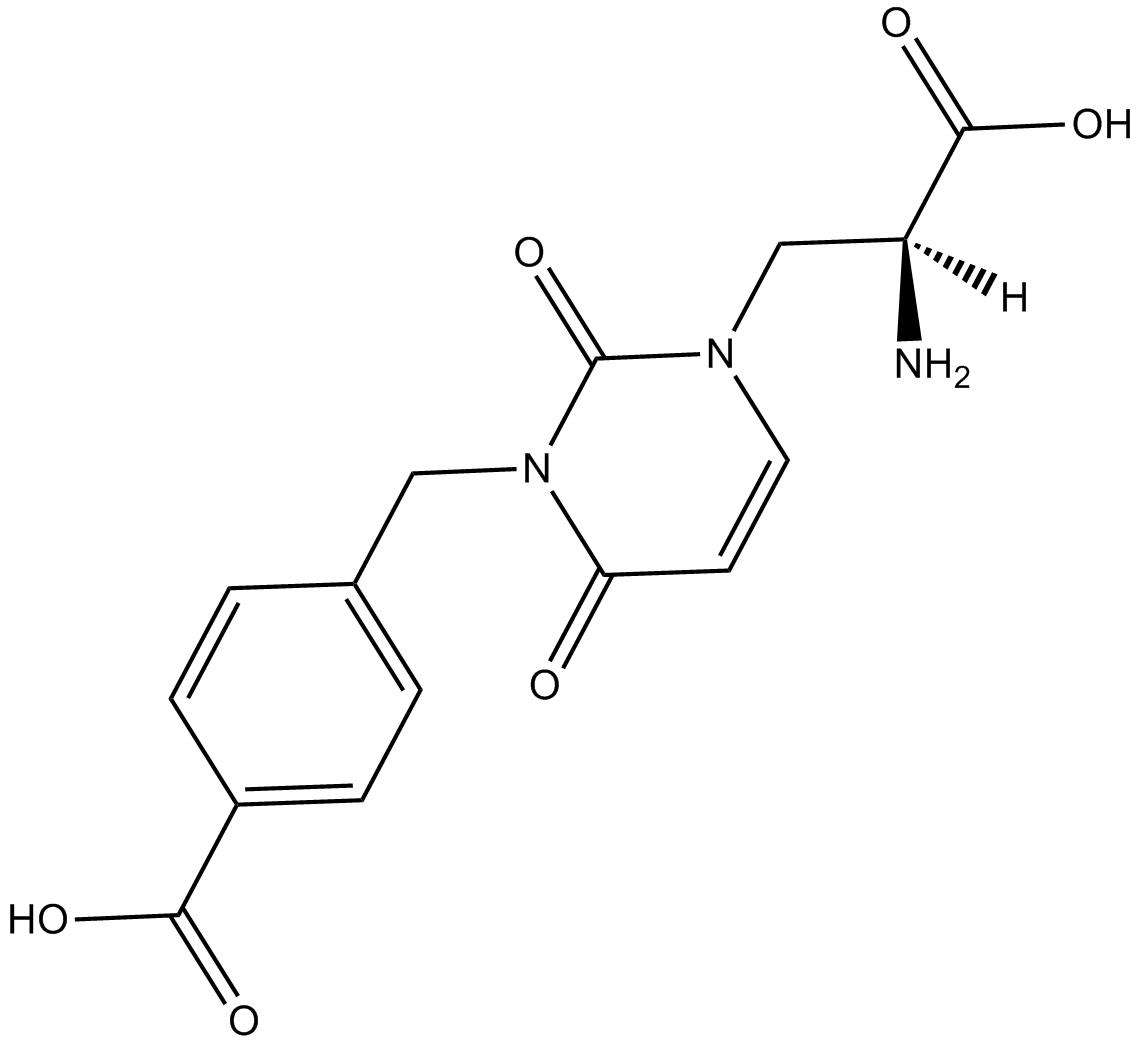 B6849 UBP 282Summary: AMPA and kainate receptor antagonist
B6849 UBP 282Summary: AMPA and kainate receptor antagonist -
 B6850 UBP 301Summary: kainate receptor antagonist
B6850 UBP 301Summary: kainate receptor antagonist

