Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel

Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins which allow the flow of ions across the membrane. The ion channels can be broadly grouped into six families including calcium channels, chloride channels, potassium channels, sodium channels, gap junction proteins and porins. Not all ion channels are gated, such as certain type of K+ and Cl– channels, transient receptor potential superfamily of cation channels, the ryanodine receptors and the IP3 receptors, but most Na+, K+, Ca2+ and some Cl– channels are all gated by voltage. Ligand-gated channels are regulated in response to ligand binding (e.g. neurotransmitters signaling). These ligand-gated neurotransmitter receptors are known as ionotropic receptors. Various neurotransmitters couple to ionotropic receptors such as glutamate, acetylcholine, glycine, GABA, and serotonin.
-
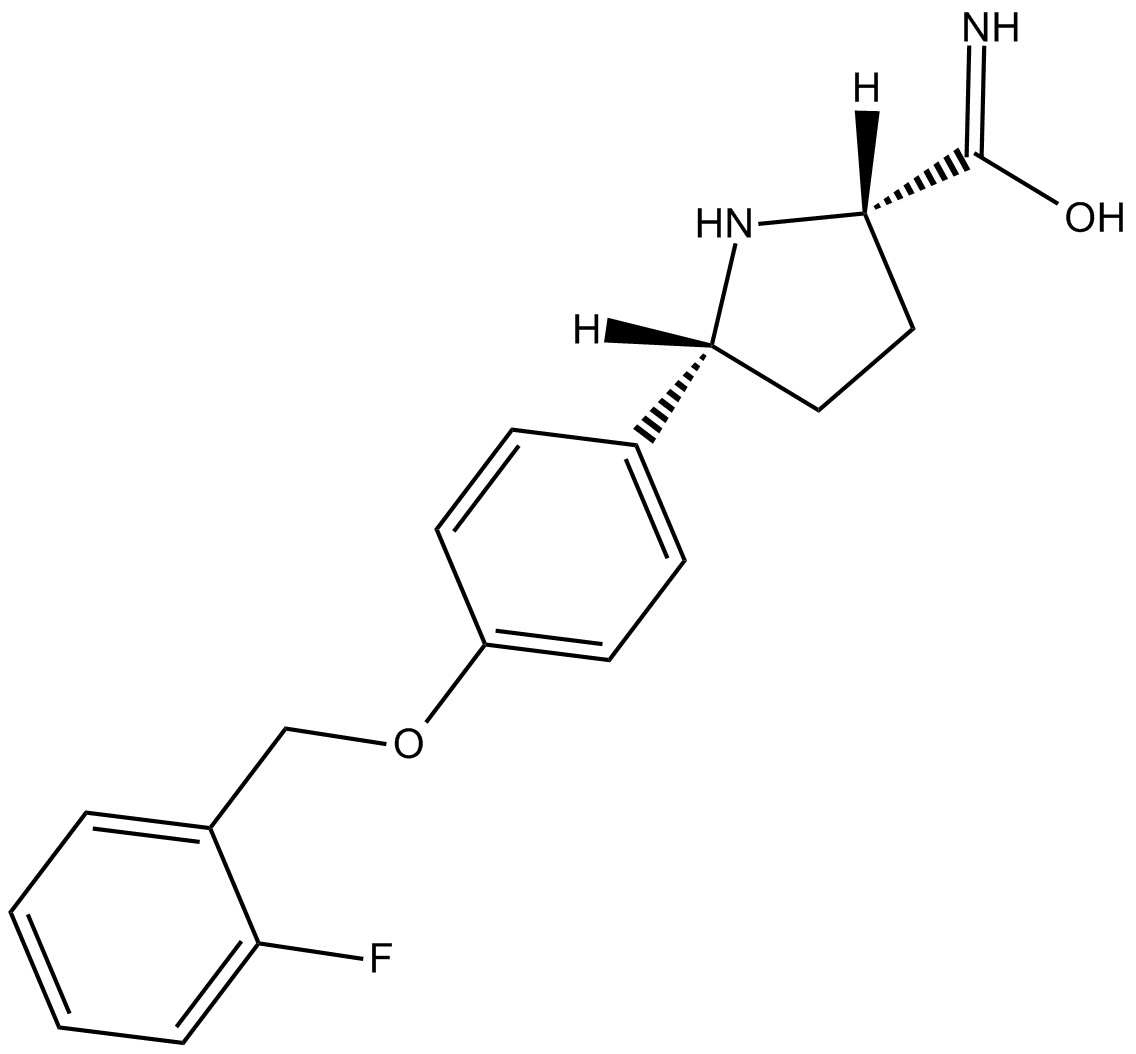 B5927 GSK1014802(CNV1014802)Summary: Novel sodium channel blocker
B5927 GSK1014802(CNV1014802)Summary: Novel sodium channel blocker -
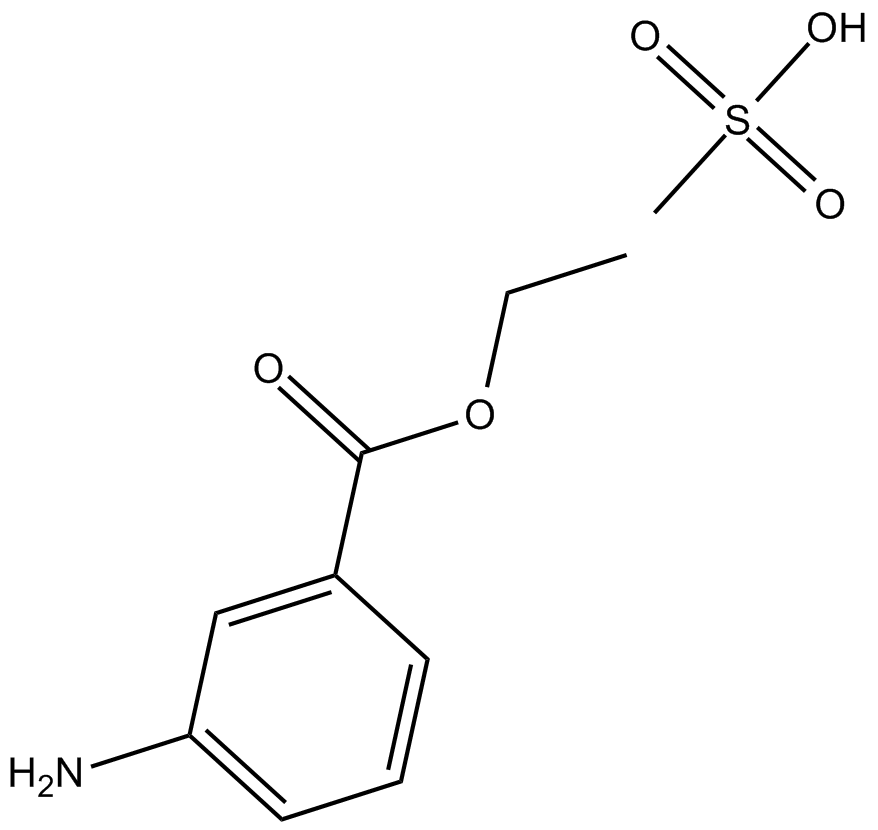 C3619 Ethyl 3-Aminobenzoate (methanesulfonate)Summary: block the generation of action potentials through voltage-dependent Na+-channels
C3619 Ethyl 3-Aminobenzoate (methanesulfonate)Summary: block the generation of action potentials through voltage-dependent Na+-channels -
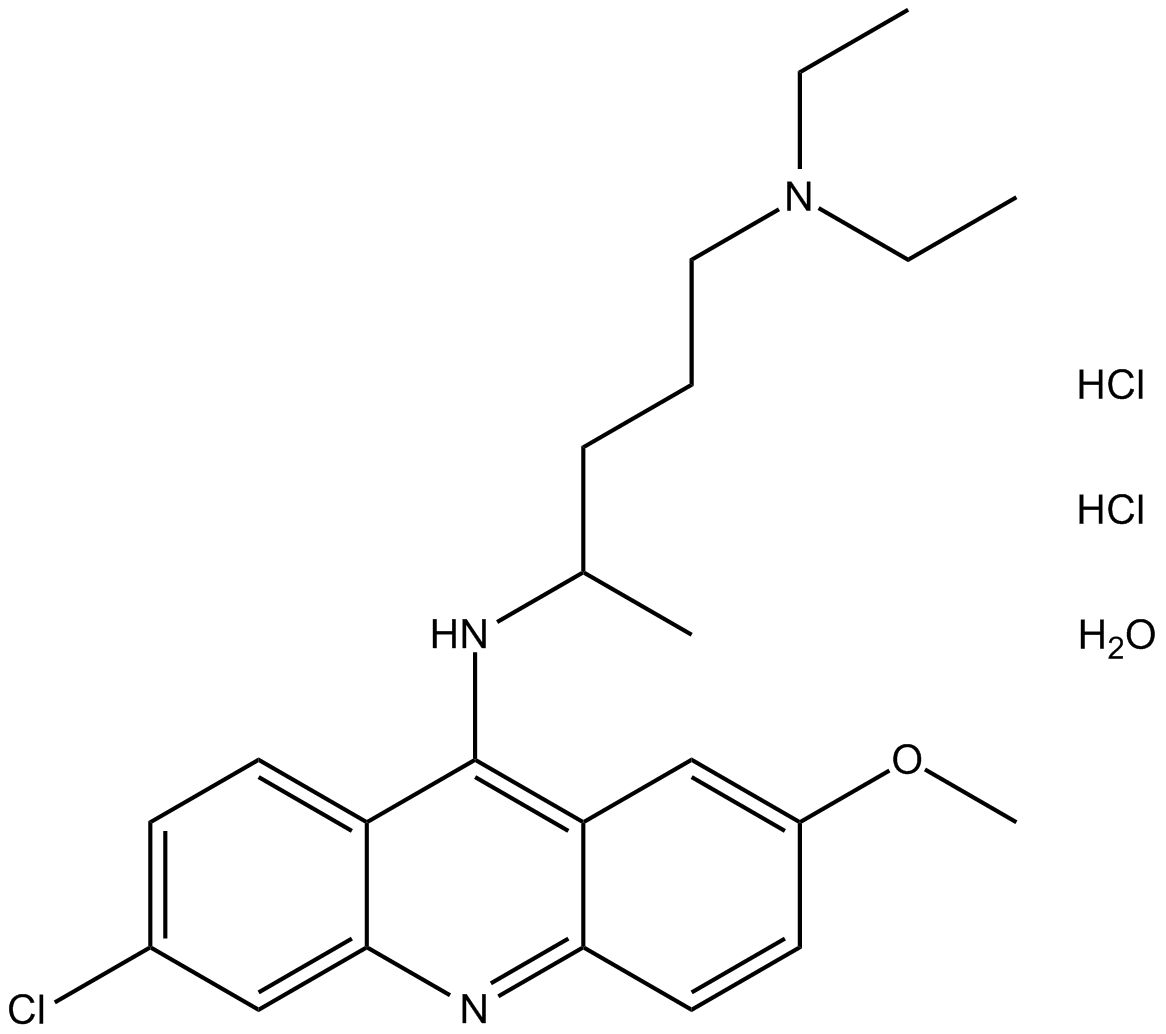 C5039 Quinacrine (hydrochloride hydrate)Summary: voltage-dependent sodium channels blocker
C5039 Quinacrine (hydrochloride hydrate)Summary: voltage-dependent sodium channels blocker -
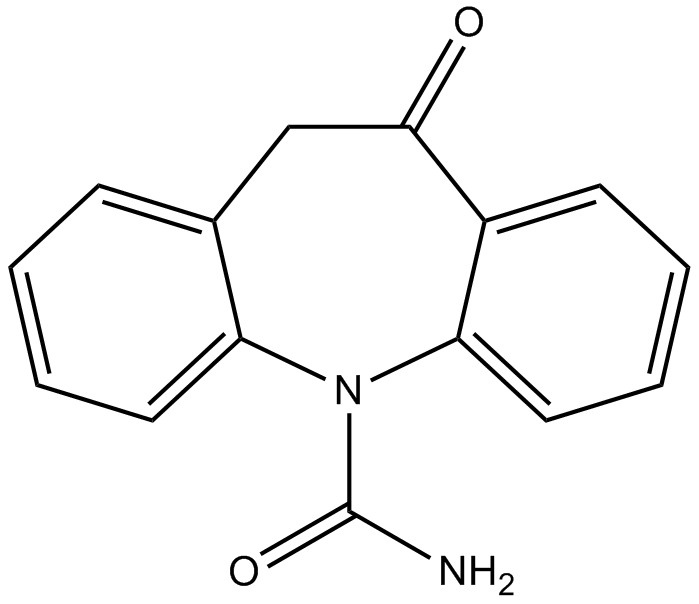 B2279 OxcarbazepineSummary: BTX inhibitor
B2279 OxcarbazepineSummary: BTX inhibitor -
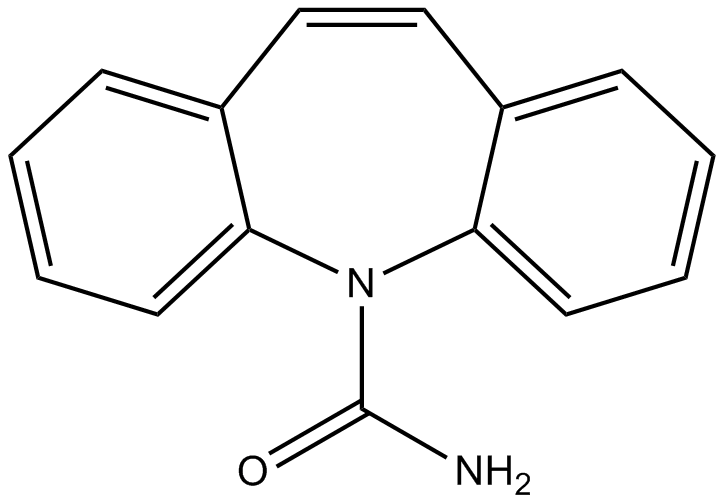 B1390 CarbamazepineSummary: Inhibitor of neuronal voltage-gated Na+ channels
B1390 CarbamazepineSummary: Inhibitor of neuronal voltage-gated Na+ channels -
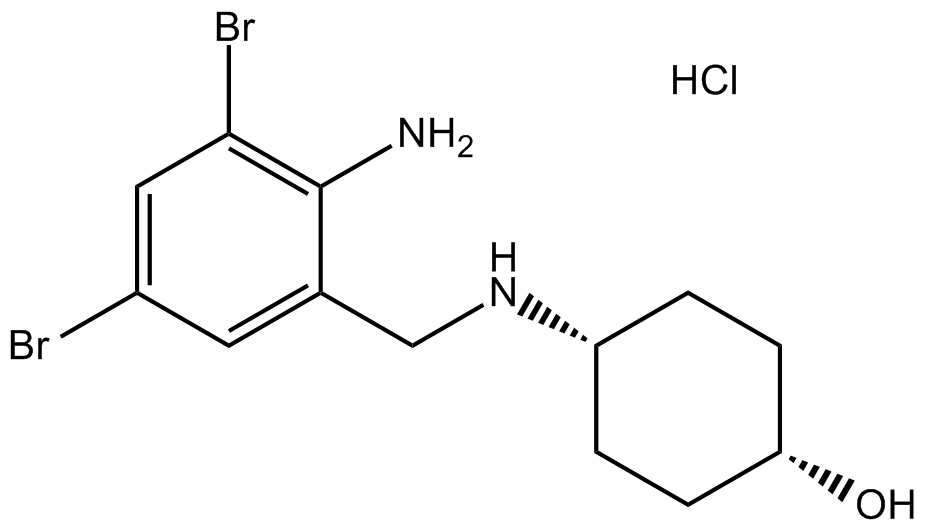 B2267 Ambroxol HClSummary: TTX-resistant Na+ currents inhibitor
B2267 Ambroxol HClSummary: TTX-resistant Na+ currents inhibitor -
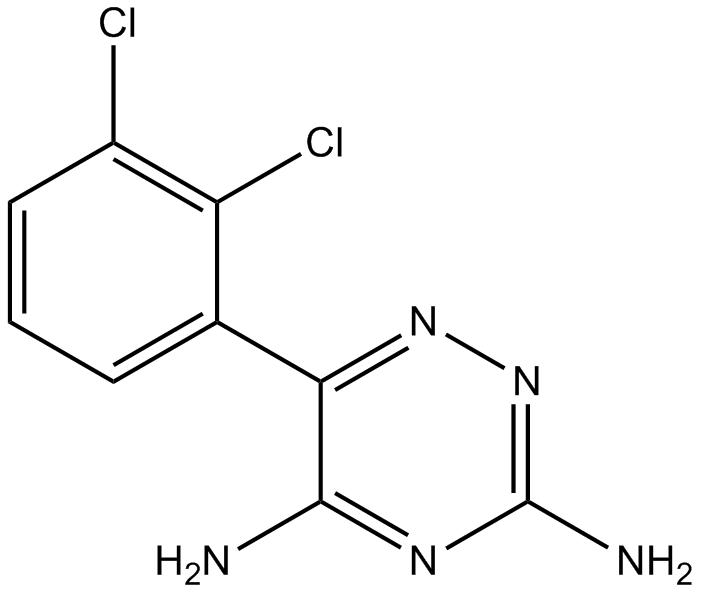 B2249 Lamotrigine1 CitationTarget: 5-HT receptors|sodium channelSummary: 5-HT inhibitor, sodium channel blocker
B2249 Lamotrigine1 CitationTarget: 5-HT receptors|sodium channelSummary: 5-HT inhibitor, sodium channel blocker -
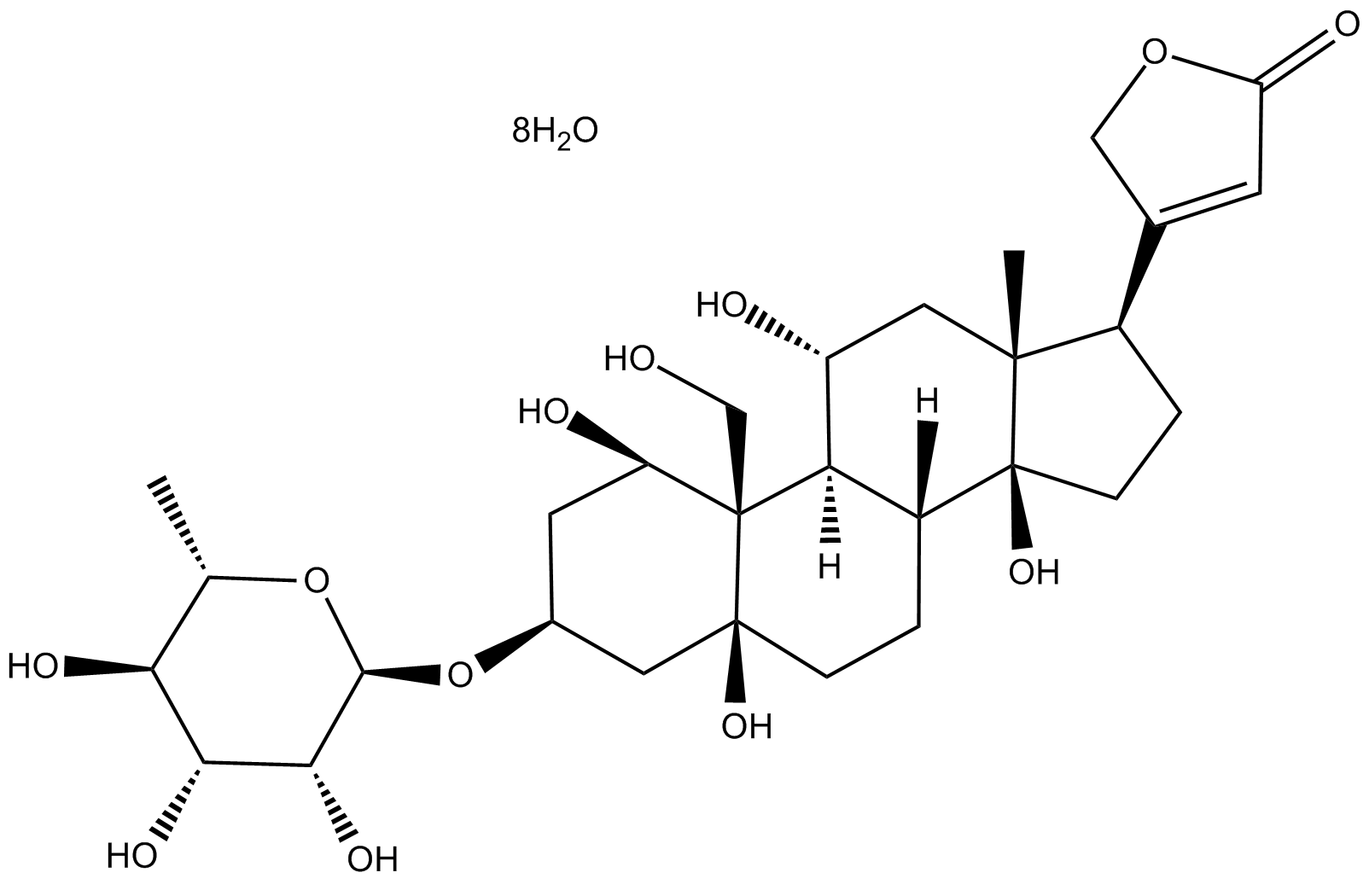 B2270 OuabainSummary: selective Na+/K+-ATPase inhibitor
B2270 OuabainSummary: selective Na+/K+-ATPase inhibitor -
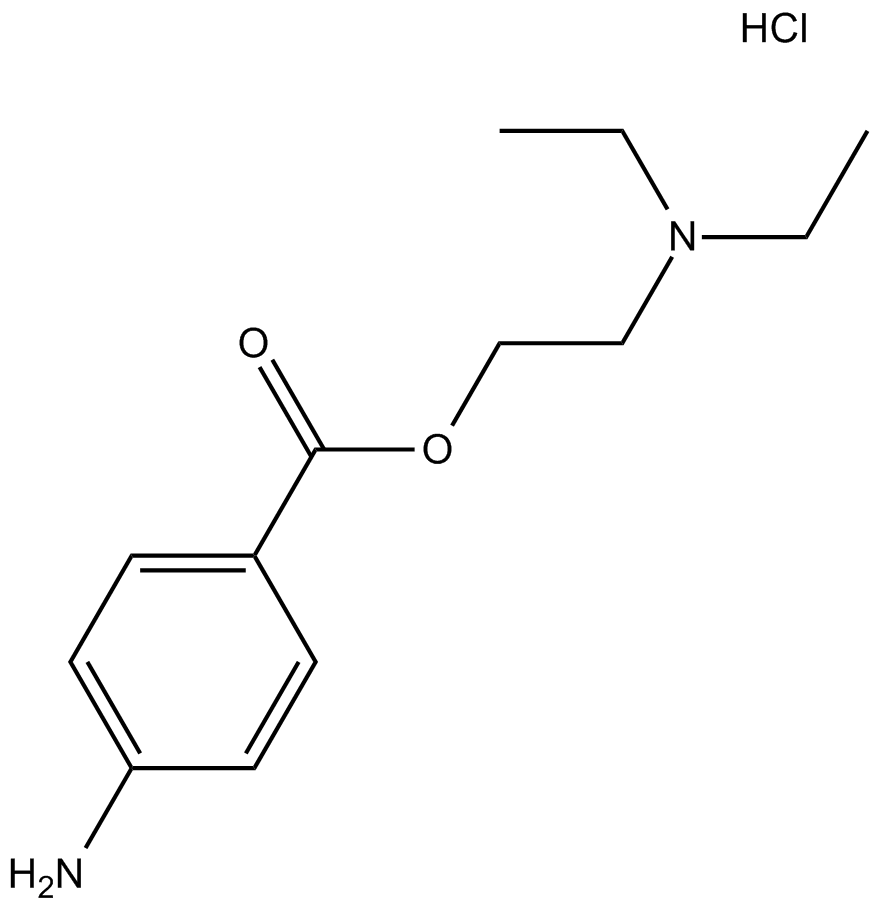 B2273 Procaine HClSummary: inhibitor of sodium channel, NMDA receptor and nAChR
B2273 Procaine HClSummary: inhibitor of sodium channel, NMDA receptor and nAChR -
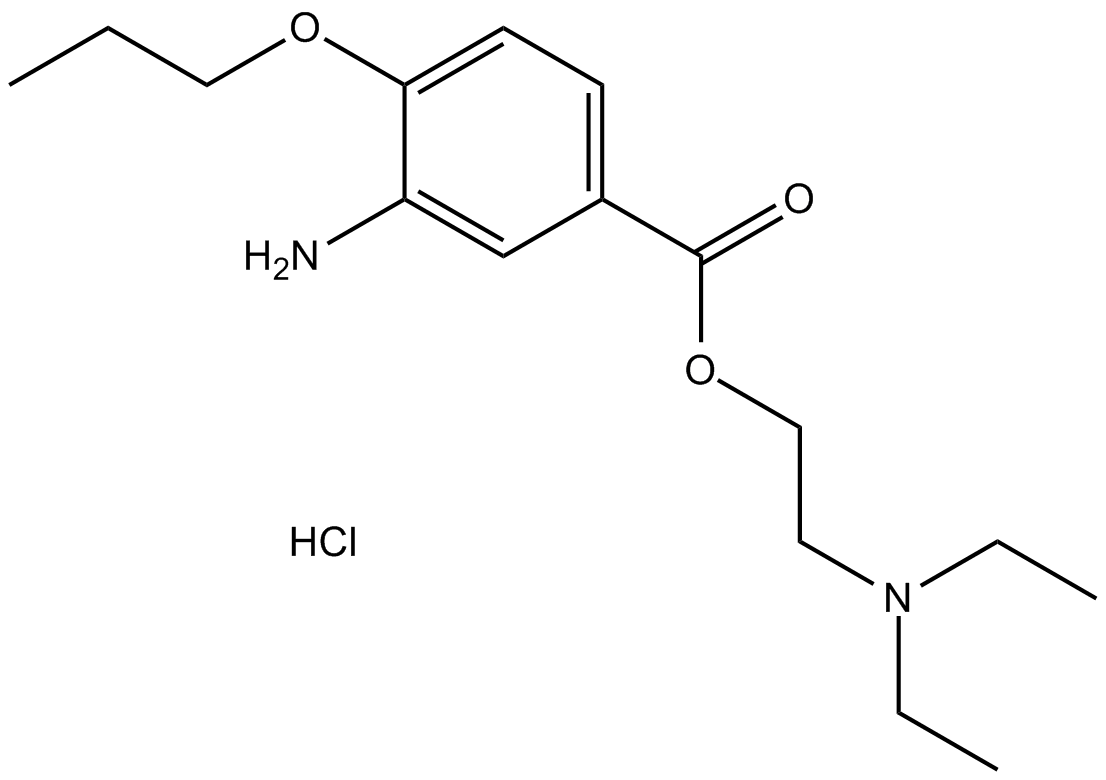 B2274 Proparacaine HClTarget: Voltage-gated Sodium (NaV) ChannelsSummary: voltage-gated sodium channels antagonist
B2274 Proparacaine HClTarget: Voltage-gated Sodium (NaV) ChannelsSummary: voltage-gated sodium channels antagonist

