Endocrinology and Hormones
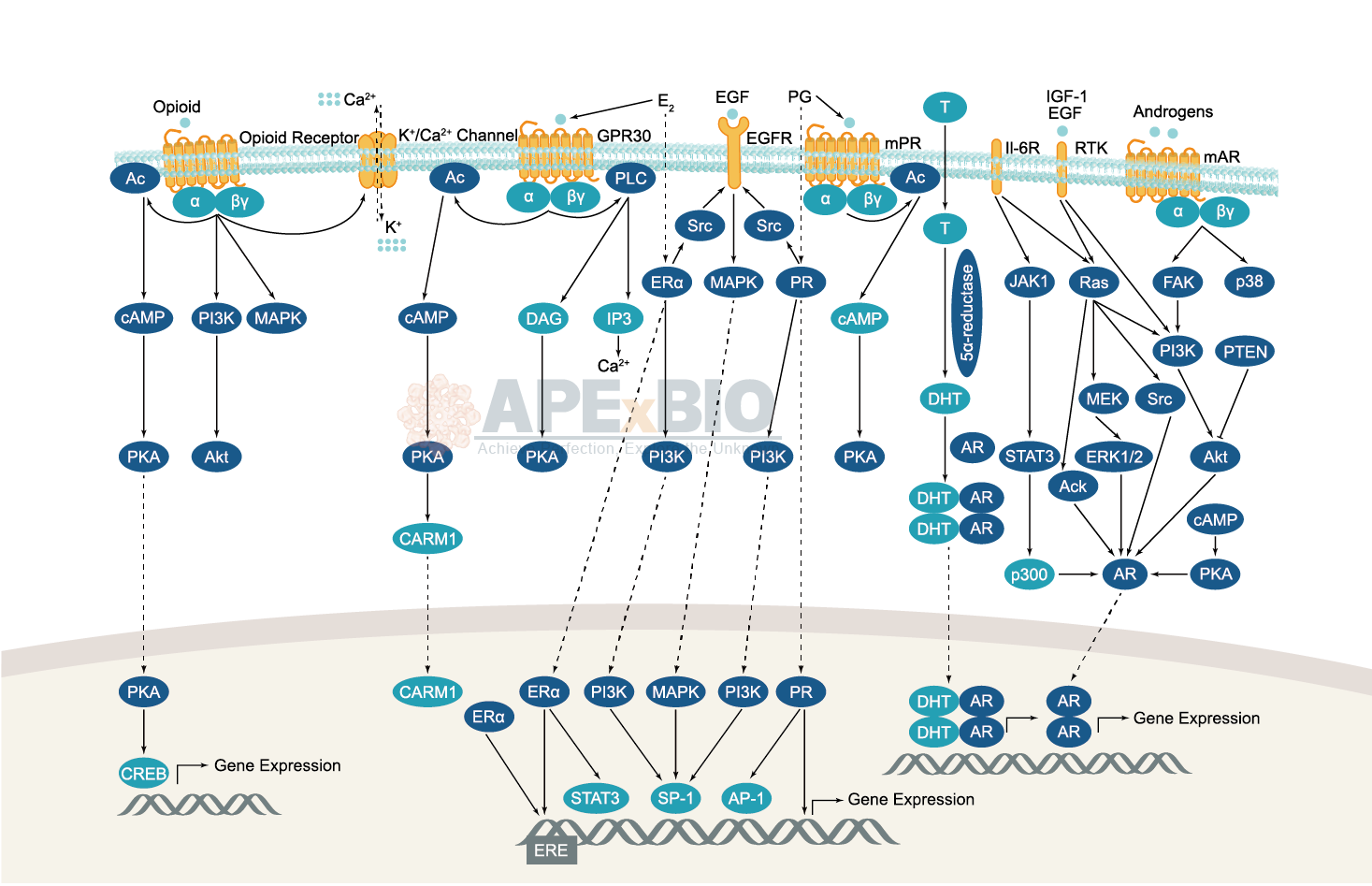
There are three types of hormones based on their chemical composition: Amines (e.g. dopamine, adrenalin and noradrenalin); Steroids (e.g. estrogen, testosterone and glucocorticoids); Peptides (e.g. the peptide hormones insulin, ghrelin and vasopressin). Peptide hormones produced by secretory nervous tissue are known as neuropeptides. For example, thyroid hormone plays important parts in development, homeostasis and metabolism, while cortisol is essential for growth, nutrient supply and immune function. Moreover, the regulation of blood glucose involves several pancreatic peptide insulin and its counter regulatory hormone, glucagon, as well as cortisol, growth hormone and epinephrine.
Dysregulations in endocrine system are implicated in diseases such as Acromegaly, Cushing Syndrome, Diabetes, Dwarfism, Graves Disease, Hermaphroditism, Delayed and Precocious Puberty and Thyroid Diseases.
-
 A8518 Rosuvastatin CalciumSummary: HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor
A8518 Rosuvastatin CalciumSummary: HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor -
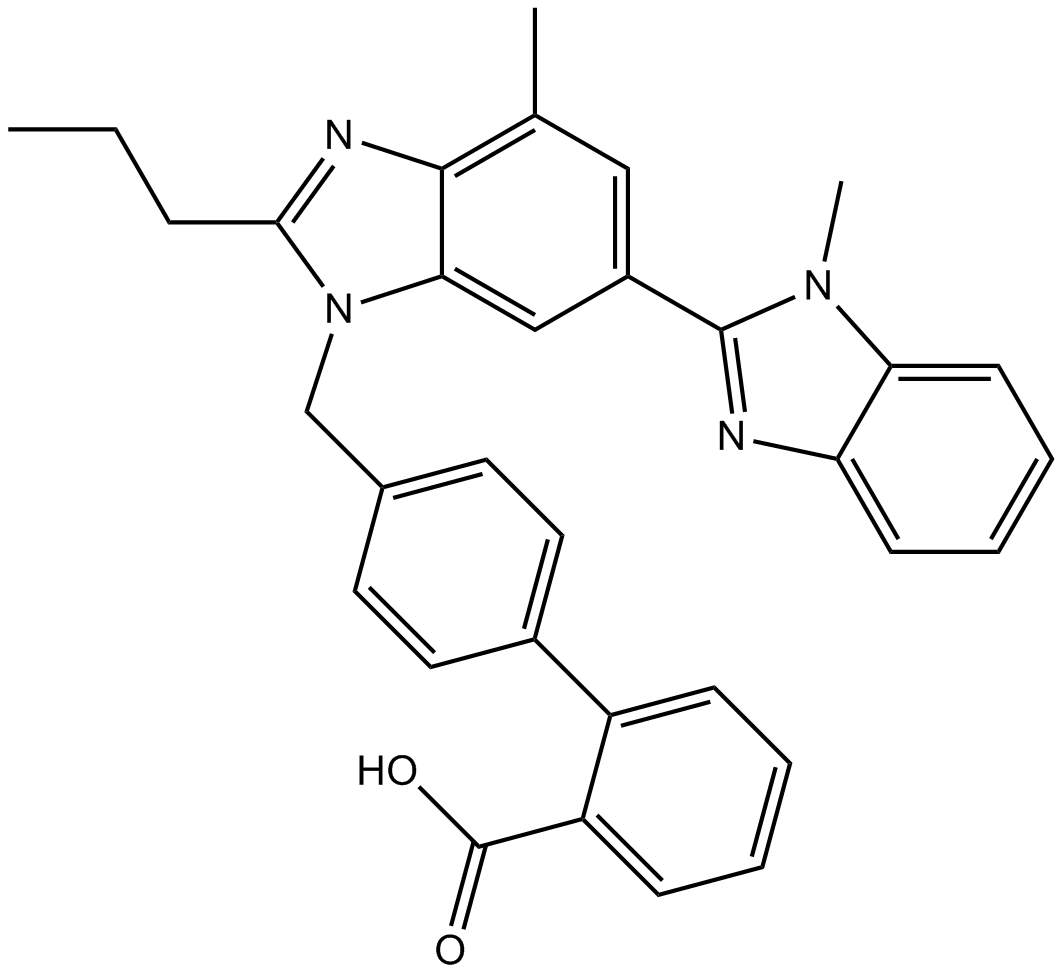 A8531 TelmisattanSummary: Angiotensin II receptor antagonist
A8531 TelmisattanSummary: Angiotensin II receptor antagonist -
 A8426 EstroneSummary: Estrogenic hormone
A8426 EstroneSummary: Estrogenic hormone -
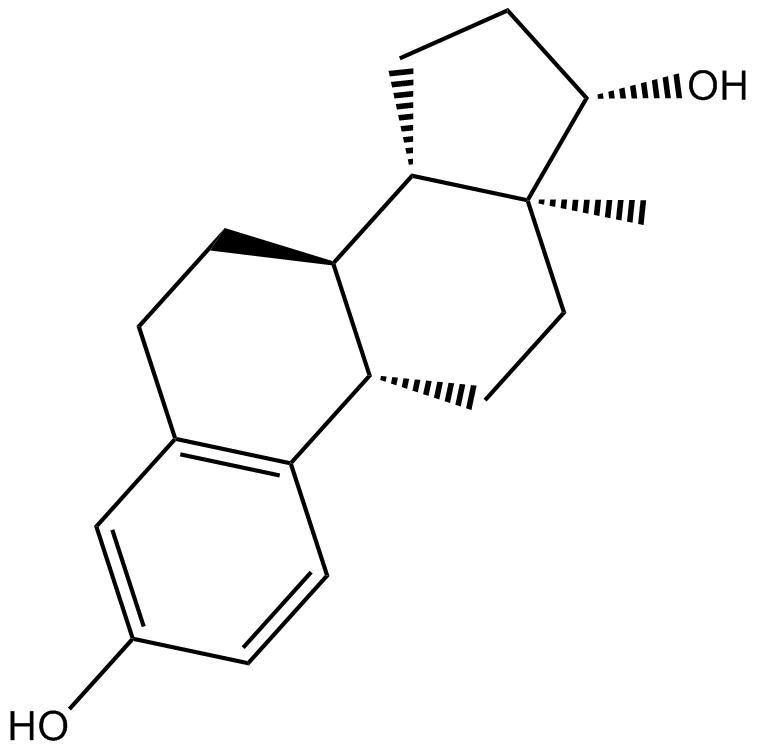 A8425 EstradiolTarget: Estrogen and Related ReceptorsSummary: Sex hormone
A8425 EstradiolTarget: Estrogen and Related ReceptorsSummary: Sex hormone -
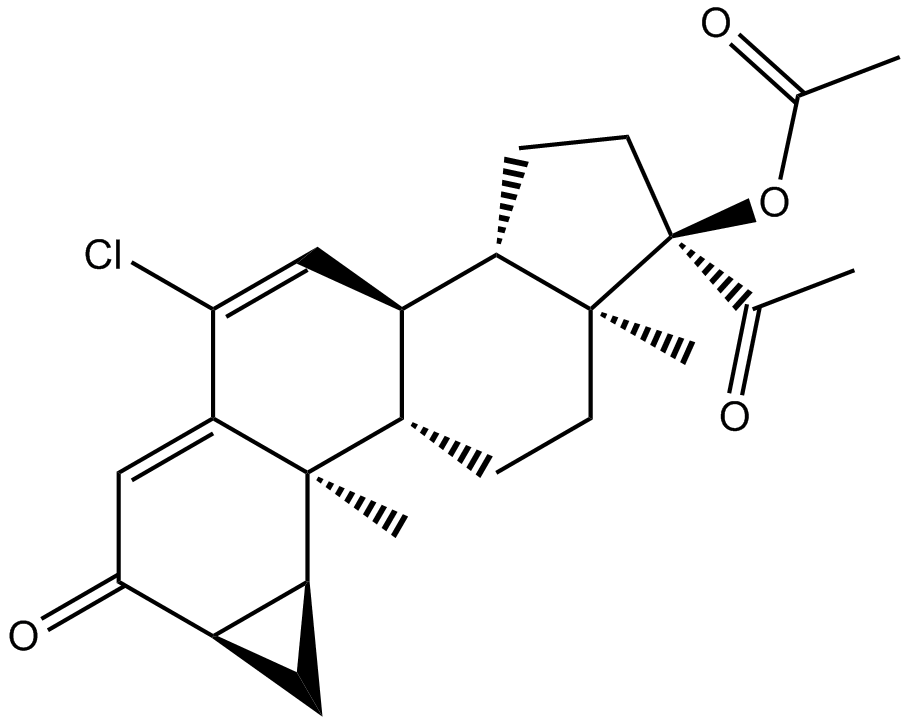 A8404 Cyproterone AcetateSummary: Androgen receptor antagonist
A8404 Cyproterone AcetateSummary: Androgen receptor antagonist -
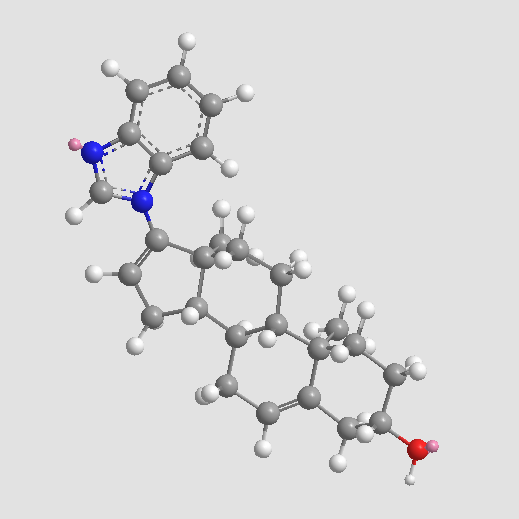 A8623 TOK-001Target: Androgen Receptors|Cytochrome P450 (CYP450)Summary: CYP17 inhibitor and androgen receptor (AR) antagonist
A8623 TOK-001Target: Androgen Receptors|Cytochrome P450 (CYP450)Summary: CYP17 inhibitor and androgen receptor (AR) antagonist -
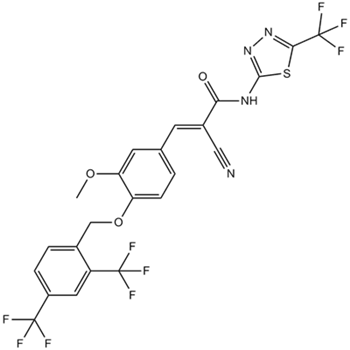 B3238 XCT790Target: Estrogen and Related ReceptorsSummary: ERRα agonist
B3238 XCT790Target: Estrogen and Related ReceptorsSummary: ERRα agonist -
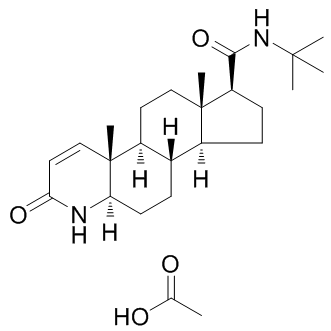 B1195 Finasteride acetateSummary: 5α-reductase inhibitor
B1195 Finasteride acetateSummary: 5α-reductase inhibitor -
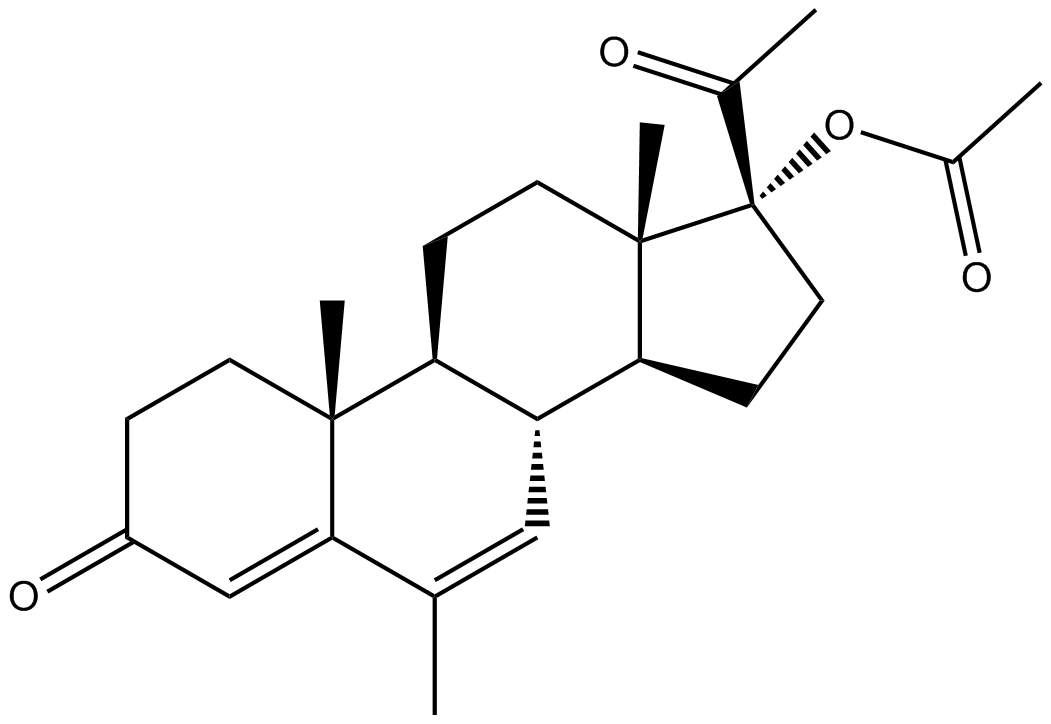 B1377 Megestrol AcetateSummary: Anti-estrogen agent
B1377 Megestrol AcetateSummary: Anti-estrogen agent -
 B1515 Raloxifene HClTarget: Estrogen and Related ReceptorsSummary: Estrogen receptor (ER)
B1515 Raloxifene HClTarget: Estrogen and Related ReceptorsSummary: Estrogen receptor (ER)

