Endocrinology and Hormones
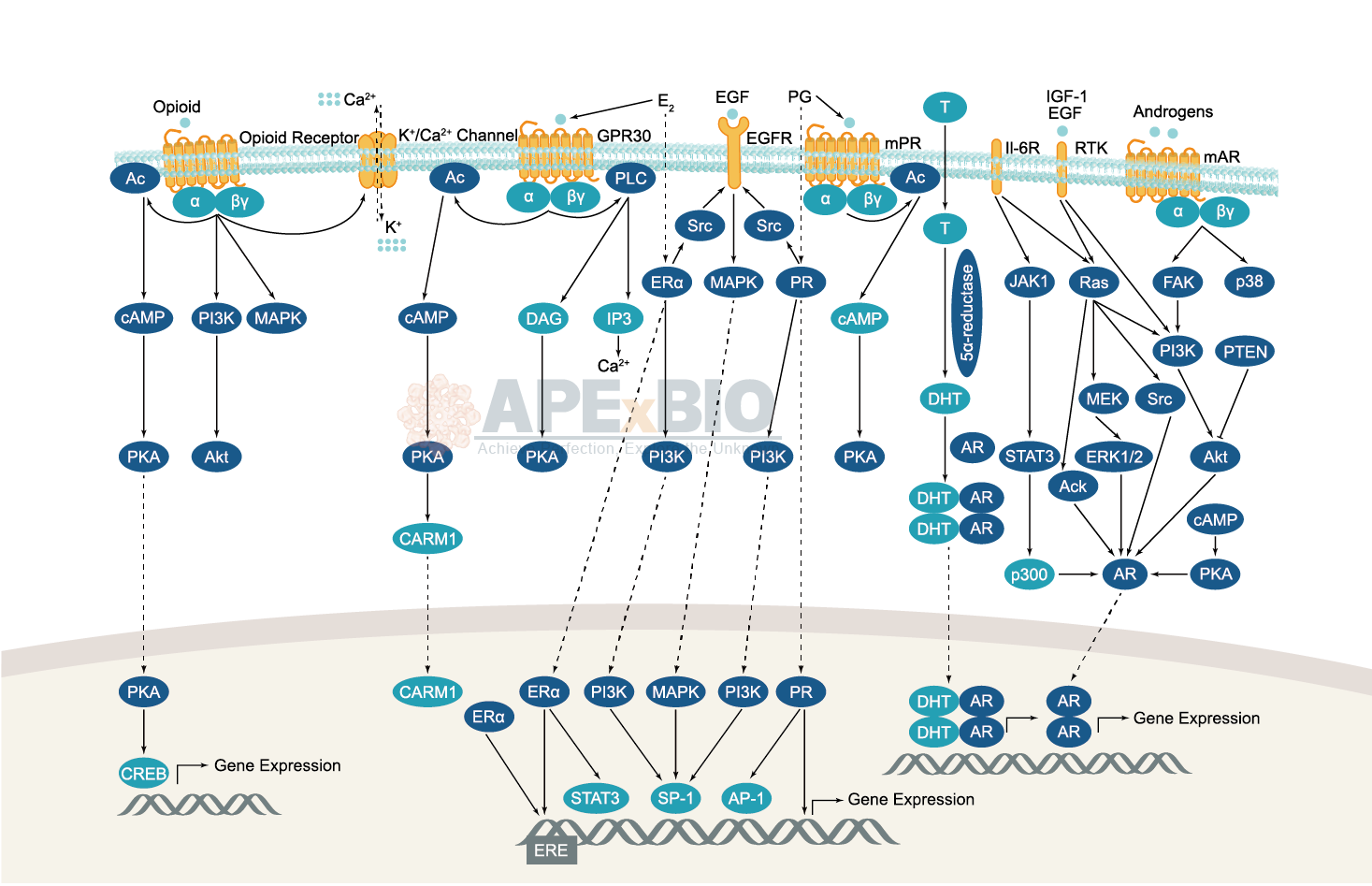
There are three types of hormones based on their chemical composition: Amines (e.g. dopamine, adrenalin and noradrenalin); Steroids (e.g. estrogen, testosterone and glucocorticoids); Peptides (e.g. the peptide hormones insulin, ghrelin and vasopressin). Peptide hormones produced by secretory nervous tissue are known as neuropeptides. For example, thyroid hormone plays important parts in development, homeostasis and metabolism, while cortisol is essential for growth, nutrient supply and immune function. Moreover, the regulation of blood glucose involves several pancreatic peptide insulin and its counter regulatory hormone, glucagon, as well as cortisol, growth hormone and epinephrine.
Dysregulations in endocrine system are implicated in diseases such as Acromegaly, Cushing Syndrome, Diabetes, Dwarfism, Graves Disease, Hermaphroditism, Delayed and Precocious Puberty and Thyroid Diseases.
-
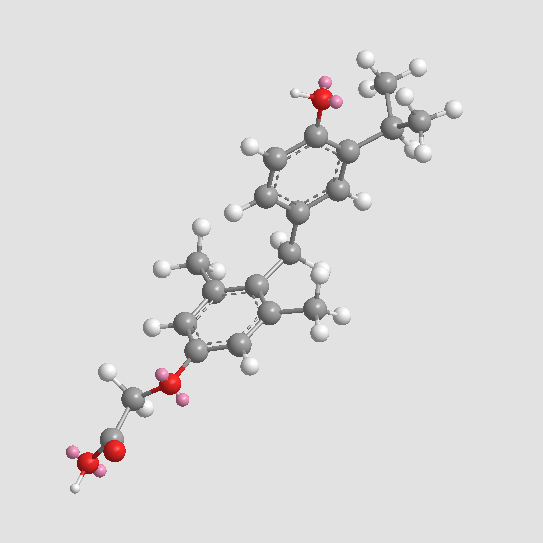 A3828 Sobetirome1 CitationSummary: Agonist of tyroid hormone receptor
A3828 Sobetirome1 CitationSummary: Agonist of tyroid hormone receptor -
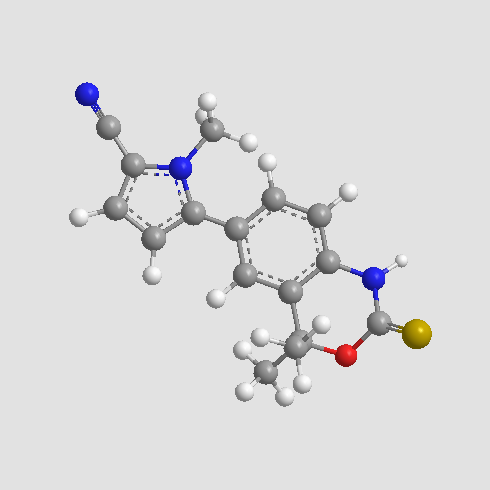 A3857 Tanaproget1 CitationSummary: Progesterone receptor agonist
A3857 Tanaproget1 CitationSummary: Progesterone receptor agonist -
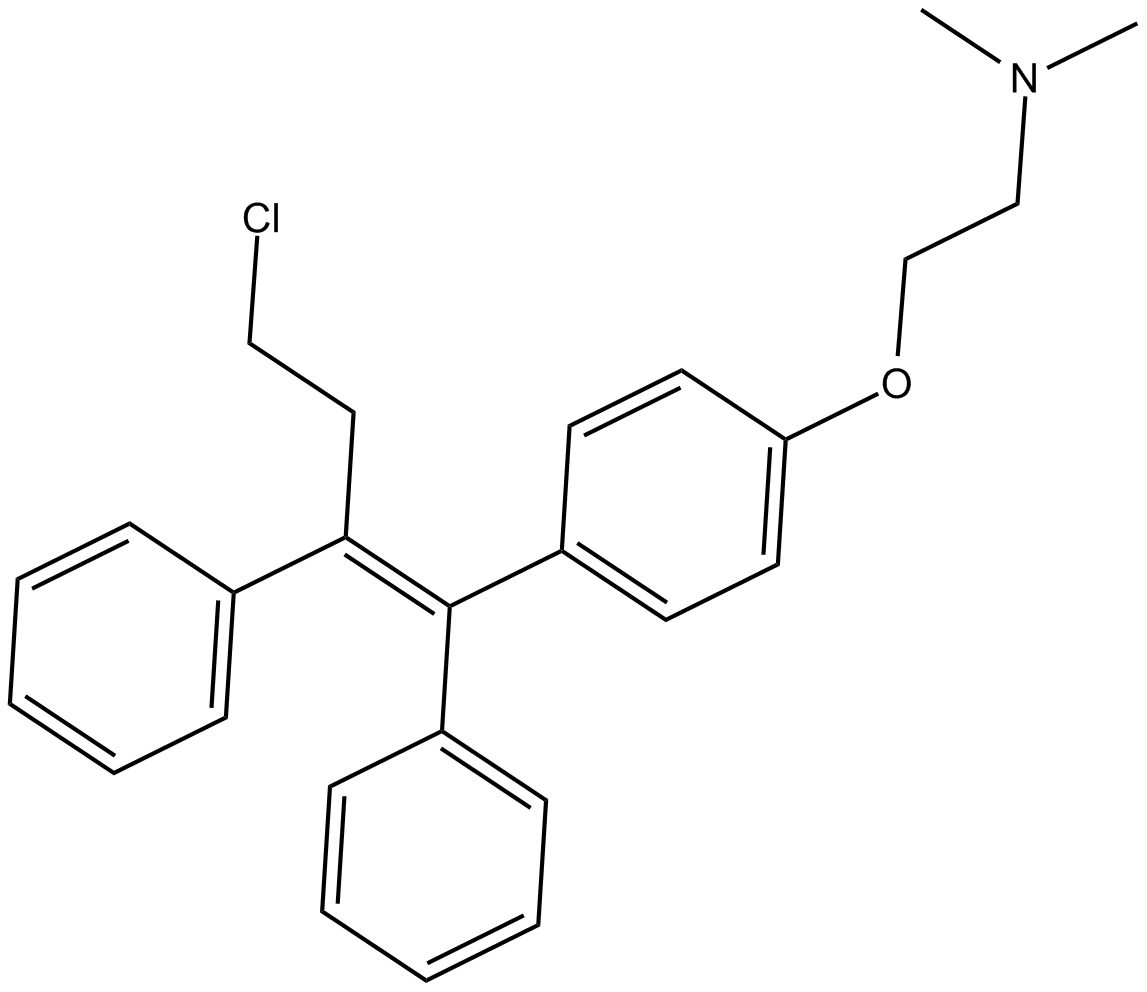 A3884 ToremifeneSummary: Estrogen-receptor modulator
A3884 ToremifeneSummary: Estrogen-receptor modulator -
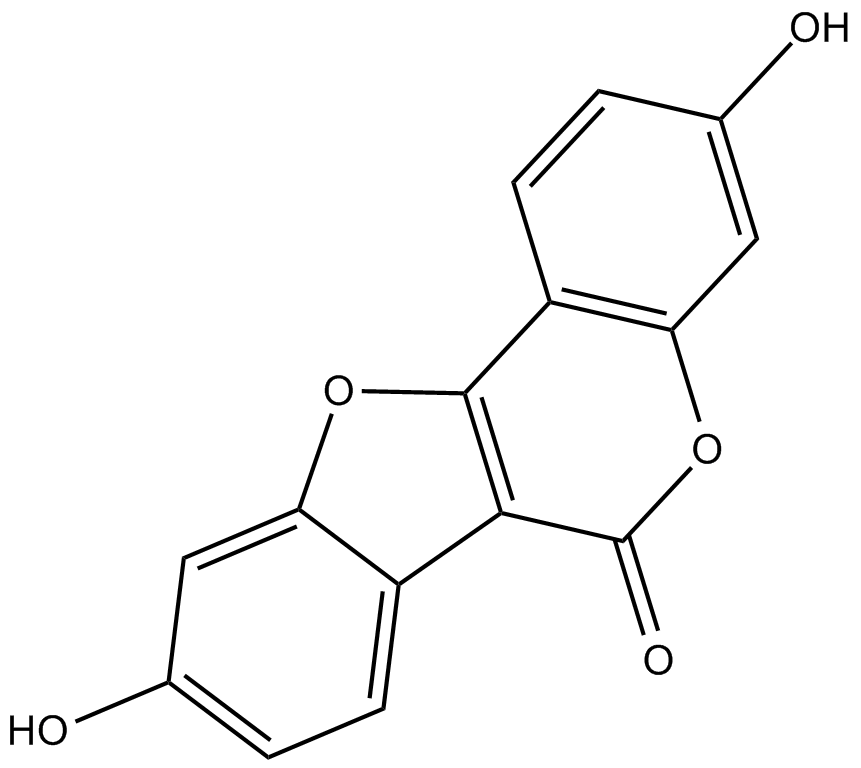 C5832 CoumestrolSummary: competitive binder of the estrogen receptors ERα
C5832 CoumestrolSummary: competitive binder of the estrogen receptors ERα -
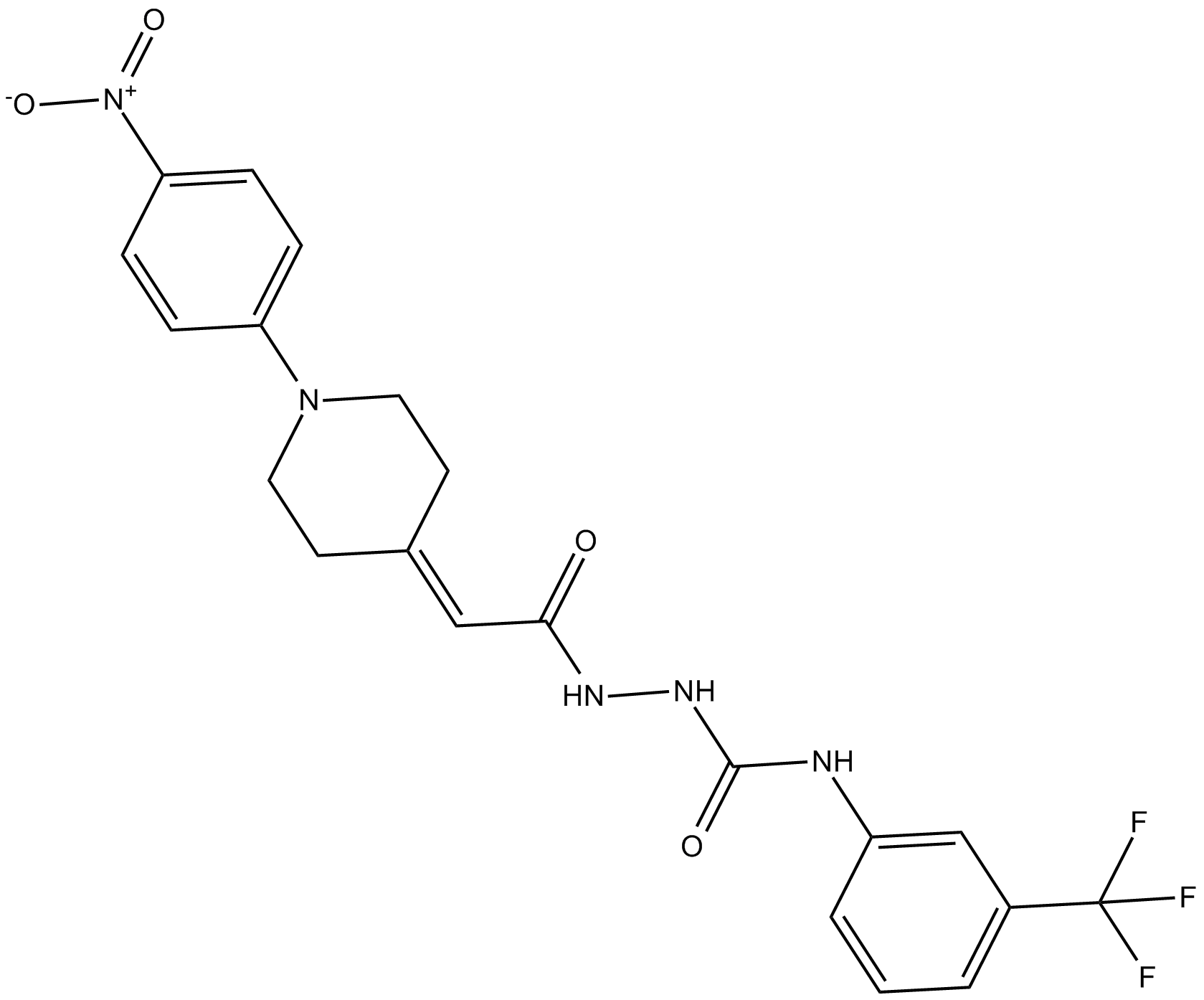 C3006 Thyroid Hormone Receptor Antagonist (1-850)Summary: Thyroid hormone receptor antagonist
C3006 Thyroid Hormone Receptor Antagonist (1-850)Summary: Thyroid hormone receptor antagonist -
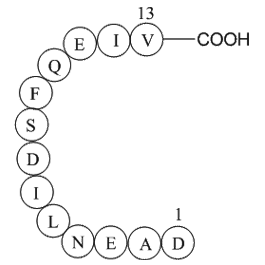 A1020 GnRH Associated Peptide (GAP) (1-13), humanTarget: prolactin secretion|gonadotropin releaseSummary: Inhibitor of prolactin secretion
A1020 GnRH Associated Peptide (GAP) (1-13), humanTarget: prolactin secretion|gonadotropin releaseSummary: Inhibitor of prolactin secretion -
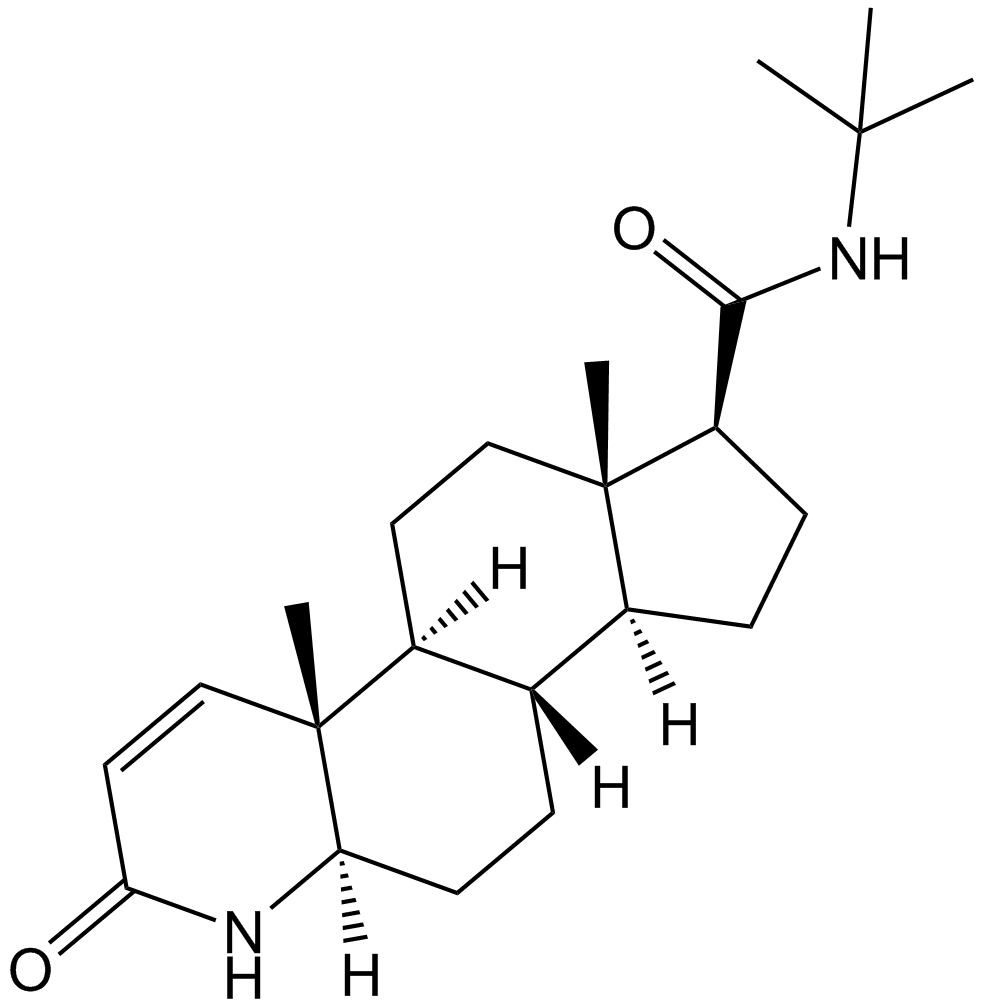 A5143 FinasterideSummary: Inhibitor of Type II 5α-reductase
A5143 FinasterideSummary: Inhibitor of Type II 5α-reductase -
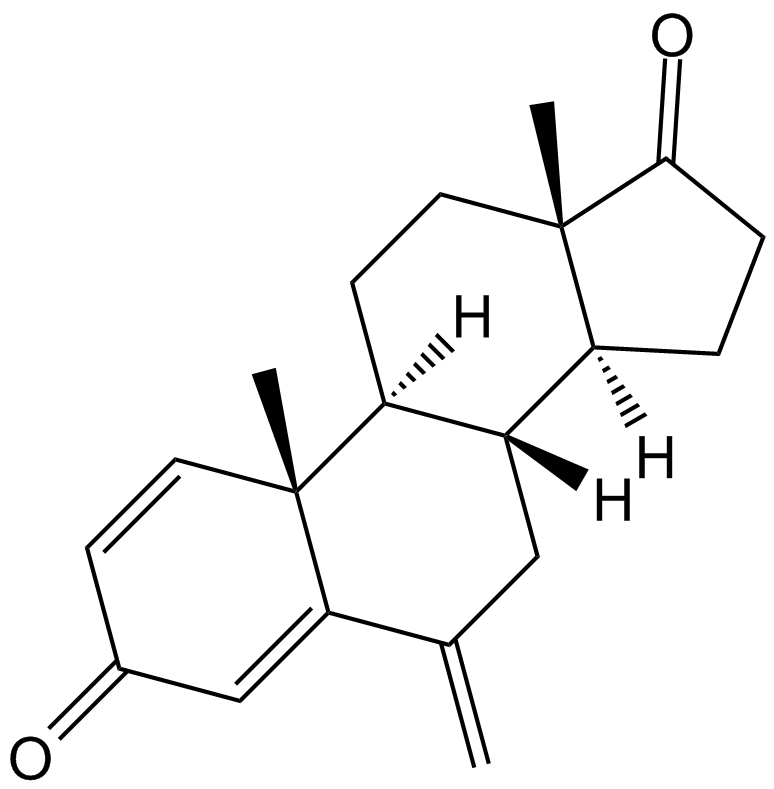 A1296 ExemestaneSummary: Steroidal aromatase inhibitor,selective and irreversible
A1296 ExemestaneSummary: Steroidal aromatase inhibitor,selective and irreversible -
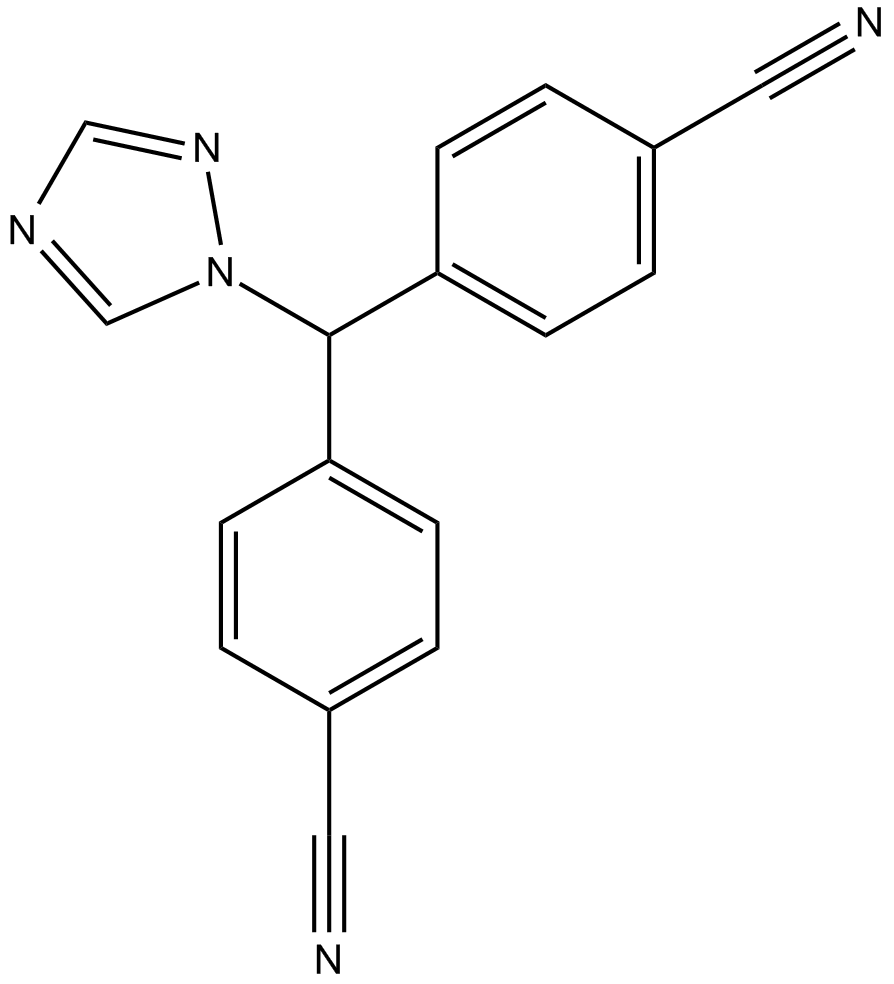 A1307 LetrozoleTarget: AromatasesSummary: Non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor
A1307 LetrozoleTarget: AromatasesSummary: Non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor -
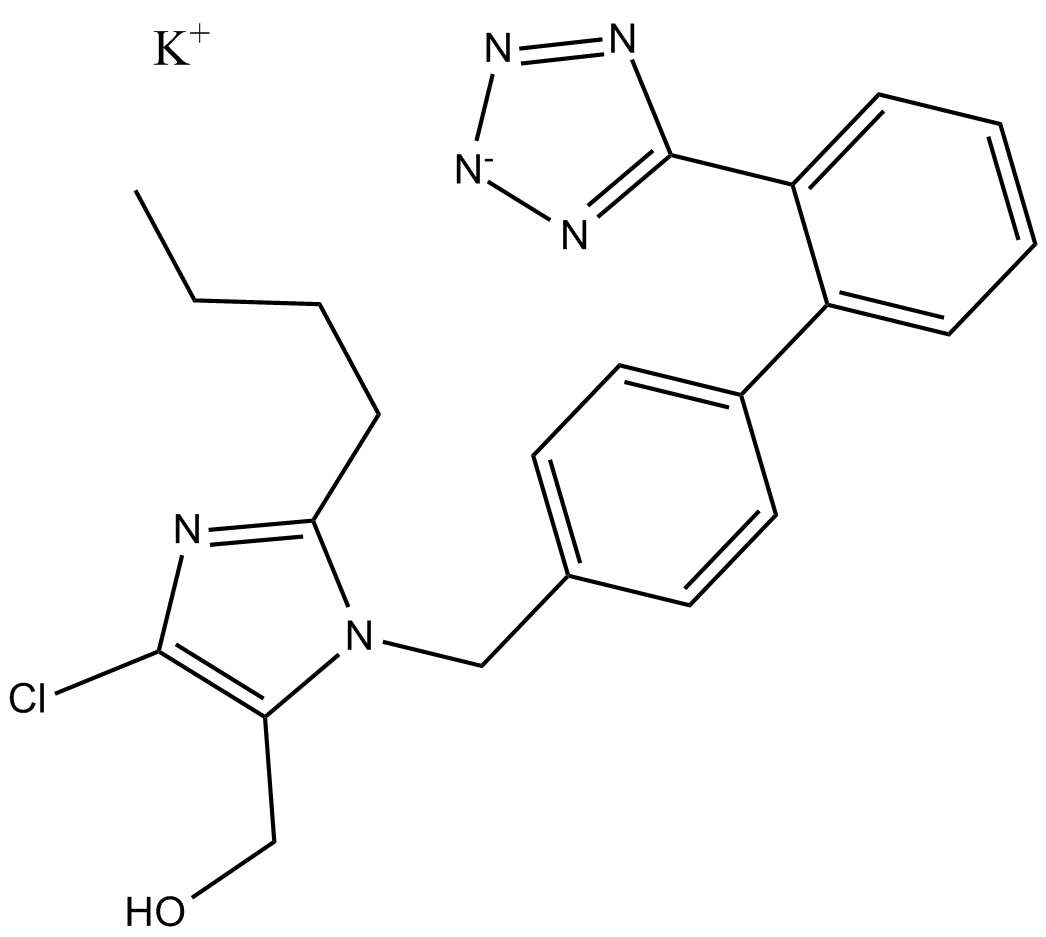 A1425 Losartan Potassium (DuP 753)Summary: Angiotensin AT1 receptor antagonist
A1425 Losartan Potassium (DuP 753)Summary: Angiotensin AT1 receptor antagonist

