Search results for: 'signaling pathways endocrinology and hormones'
-
 L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research. -
 L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch. -
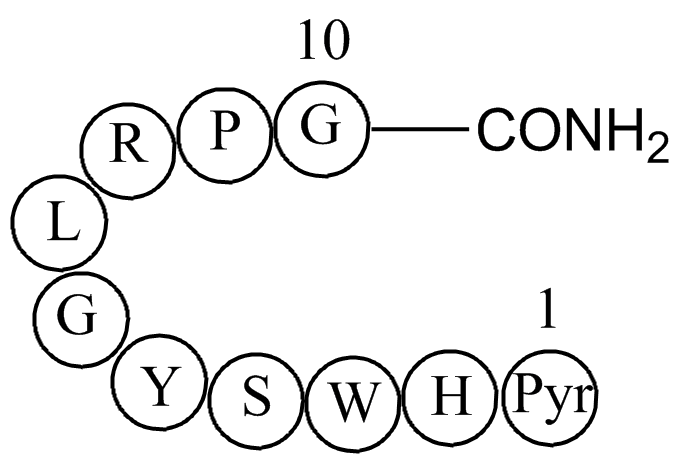 A1147 Luteinizing hormone releasing hormone human acetate salt (LHRH)Target: MMPSummary: acitivator of MMP-2 and MMP-9, selective
A1147 Luteinizing hormone releasing hormone human acetate salt (LHRH)Target: MMPSummary: acitivator of MMP-2 and MMP-9, selective -
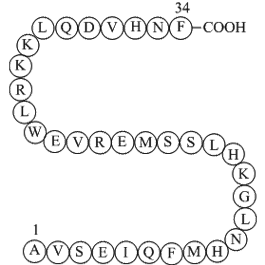 A1114 Parathyroid Hormone (1-34), bovineSummary: Enhancer of blood calcium level
A1114 Parathyroid Hormone (1-34), bovineSummary: Enhancer of blood calcium level -
 L1044P DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 178 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044P DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 178 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research. -
 L1026P DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 948 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026P DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 948 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch. -
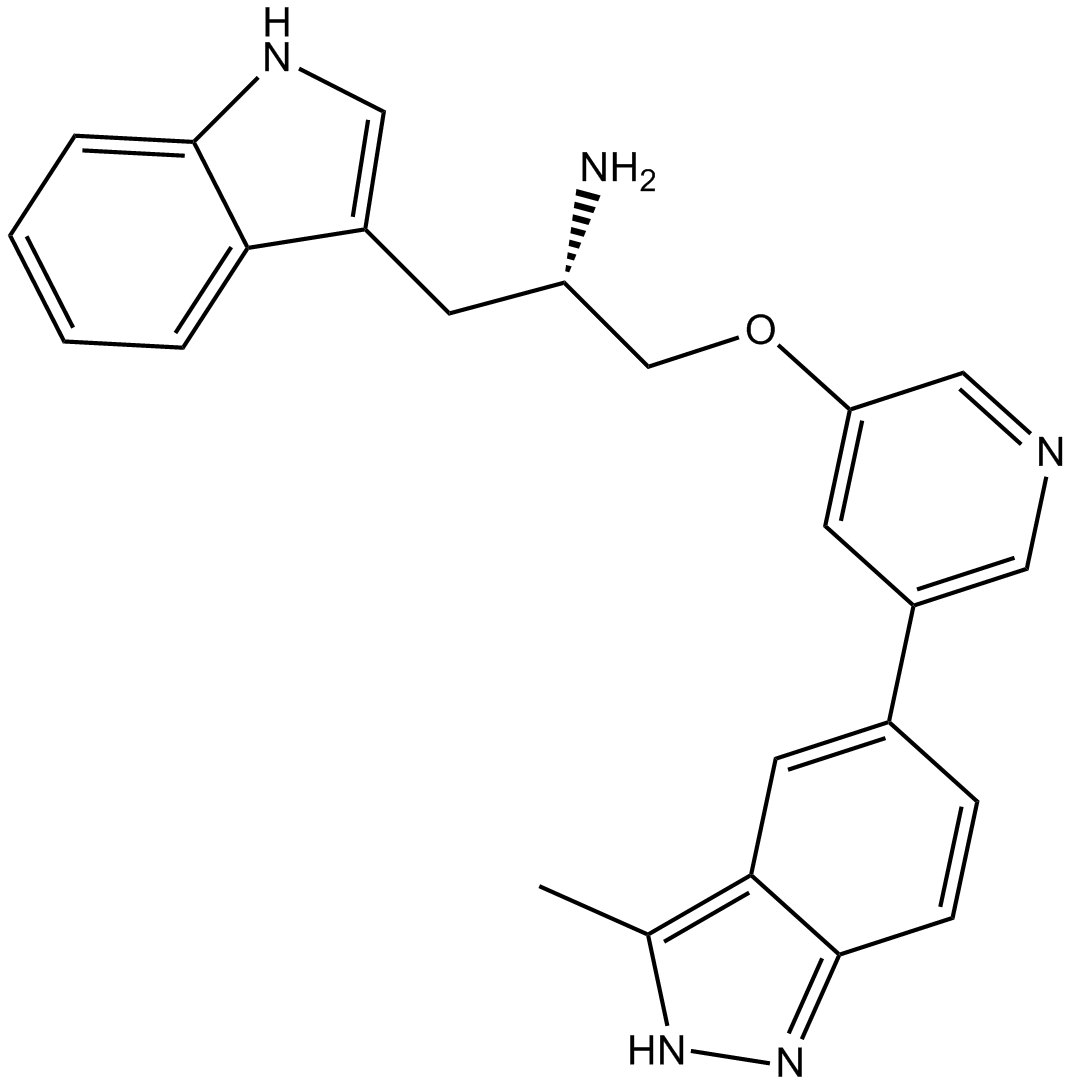 A3135 A-443654Summary: Akt inhibitor,potent and selective
A3135 A-443654Summary: Akt inhibitor,potent and selective -
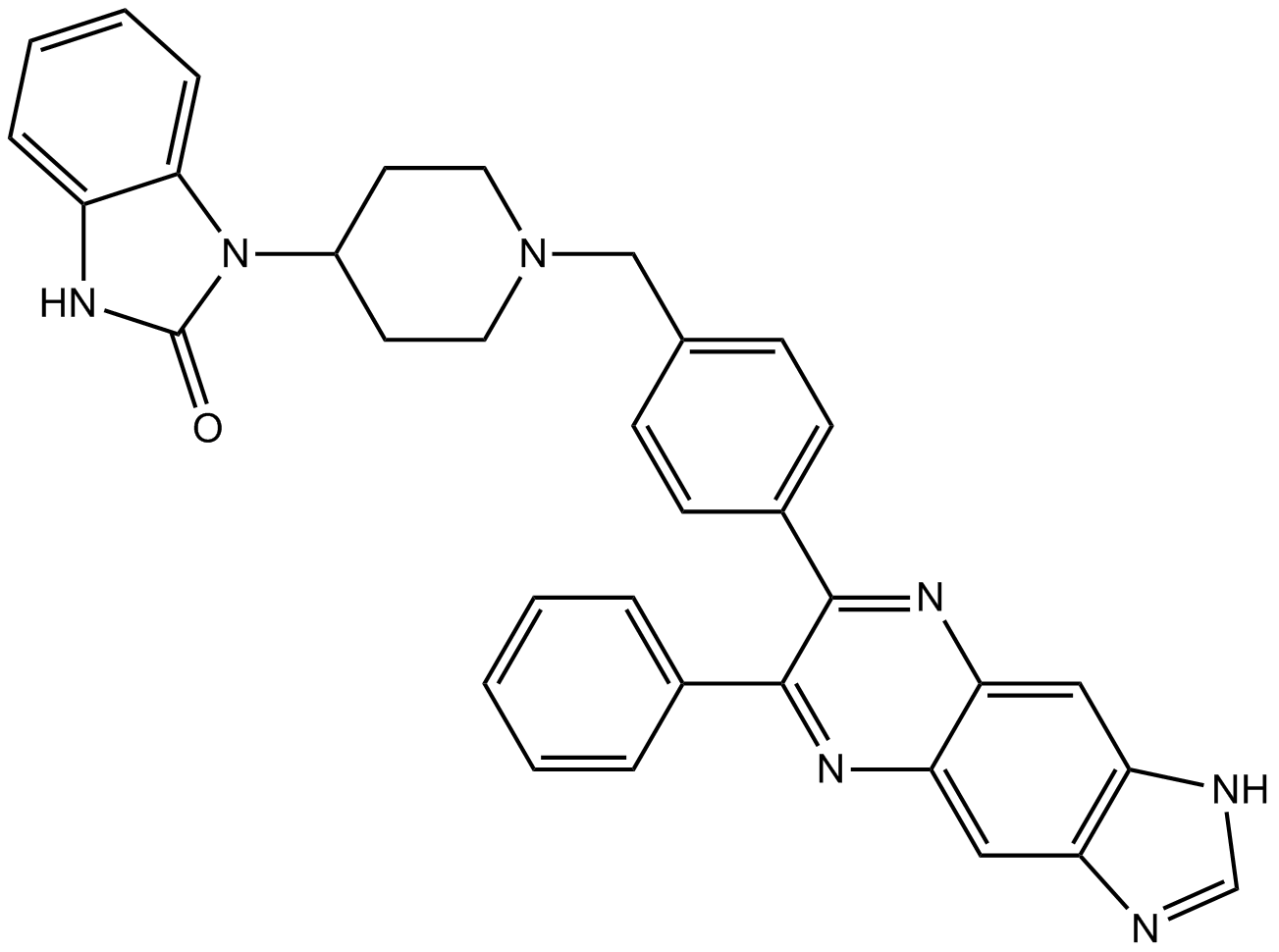 A3149 AKT inhibitor VIII2 CitationTarget: AktSummary: Allosteric Akt kinase inhibitor
A3149 AKT inhibitor VIII2 CitationTarget: AktSummary: Allosteric Akt kinase inhibitor -
 A3199 AT7867 dihydrochlorideSummary: Akt1 and p70S6K/PKA inhibitor
A3199 AT7867 dihydrochlorideSummary: Akt1 and p70S6K/PKA inhibitor -
 A3238 BEZ235 Tosylate1 CitationSummary: MTOR/P13K inhibitor
A3238 BEZ235 Tosylate1 CitationSummary: MTOR/P13K inhibitor


