Angiogenesis
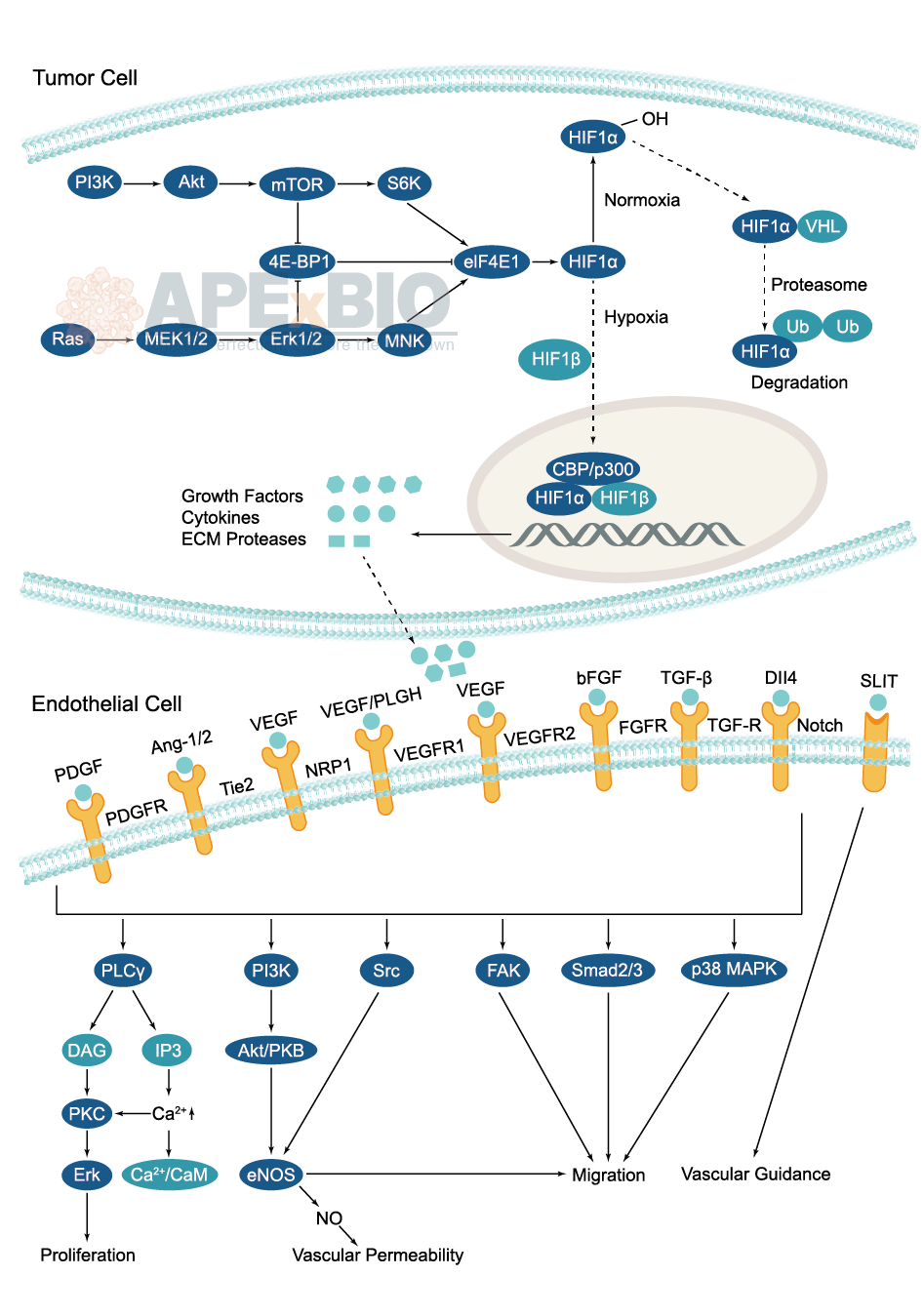
During tumor angiogenesis, cancer cells stimulate formation of new blood vessel for delivering oxygen and nutrients to a tumor. As the tumor grows, cells at the center of the mass become starved of oxygen, causing hypoxia. It stabilizes the expression of a transcription factor, HIF-1α (hypoxia inducible factor-1), which binds HIF-1β to upregulate the expression of several angiogenesis-promoting genes. Moreover, growth factor signaling also stimulates HIF-1 activity in order to maintain oxygen homeostasis for growing cells.
-
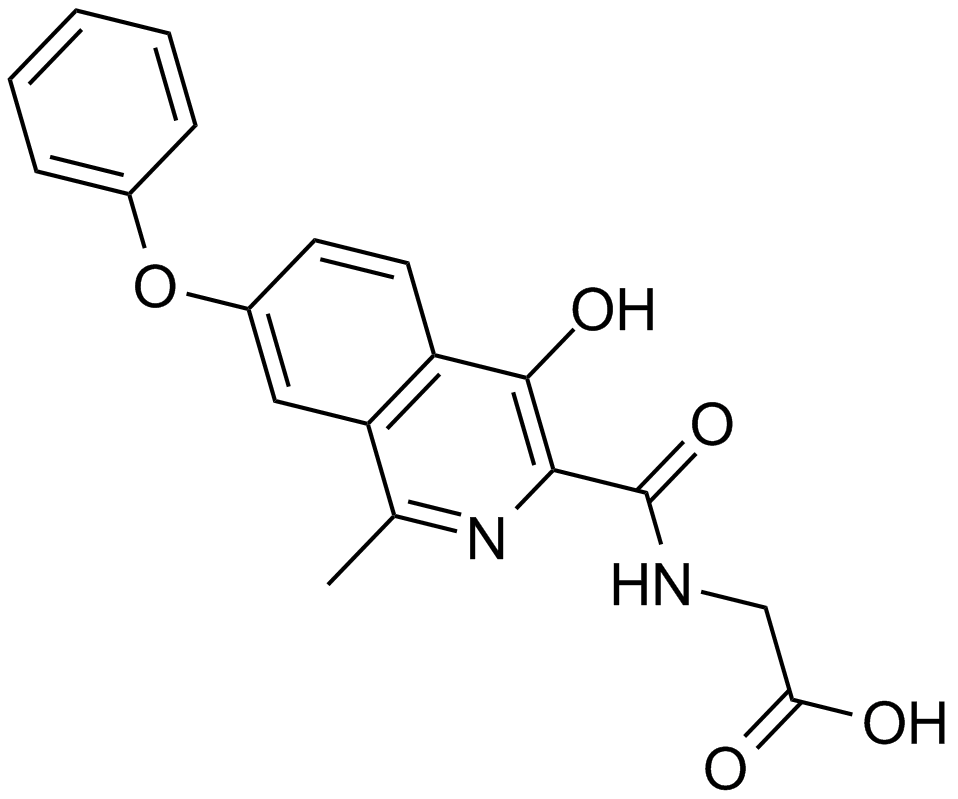 A4187 FG-4592 (ASP1517)1 CitationSummary: HIF prolyl-hydroxylase inhibitor
A4187 FG-4592 (ASP1517)1 CitationSummary: HIF prolyl-hydroxylase inhibitor -
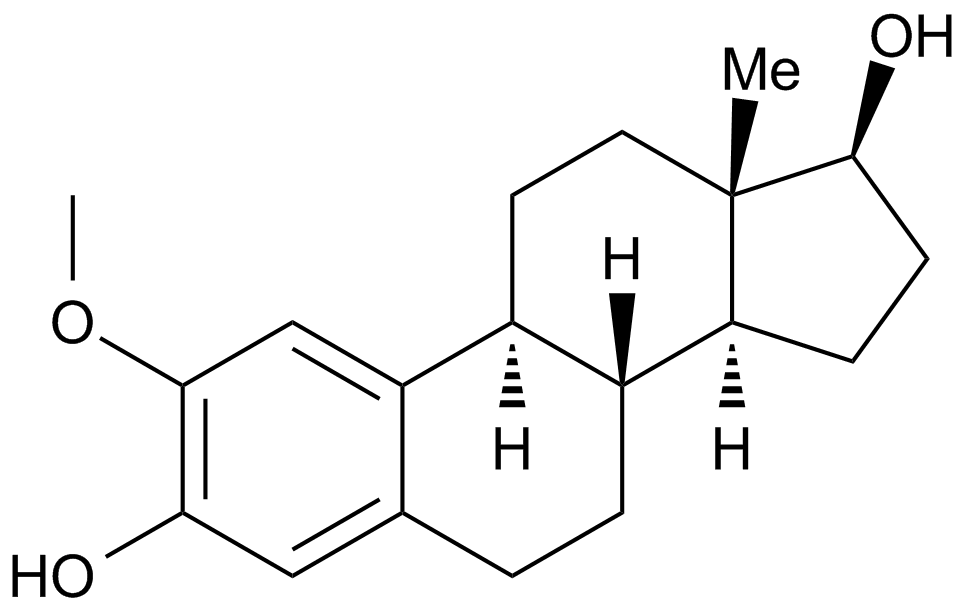 A4188 2-Methoxyestradiol (2-MeOE2)2 CitationSummary: Apoptotic, antiproliferative and antiangiogenic agent
A4188 2-Methoxyestradiol (2-MeOE2)2 CitationSummary: Apoptotic, antiproliferative and antiangiogenic agent -
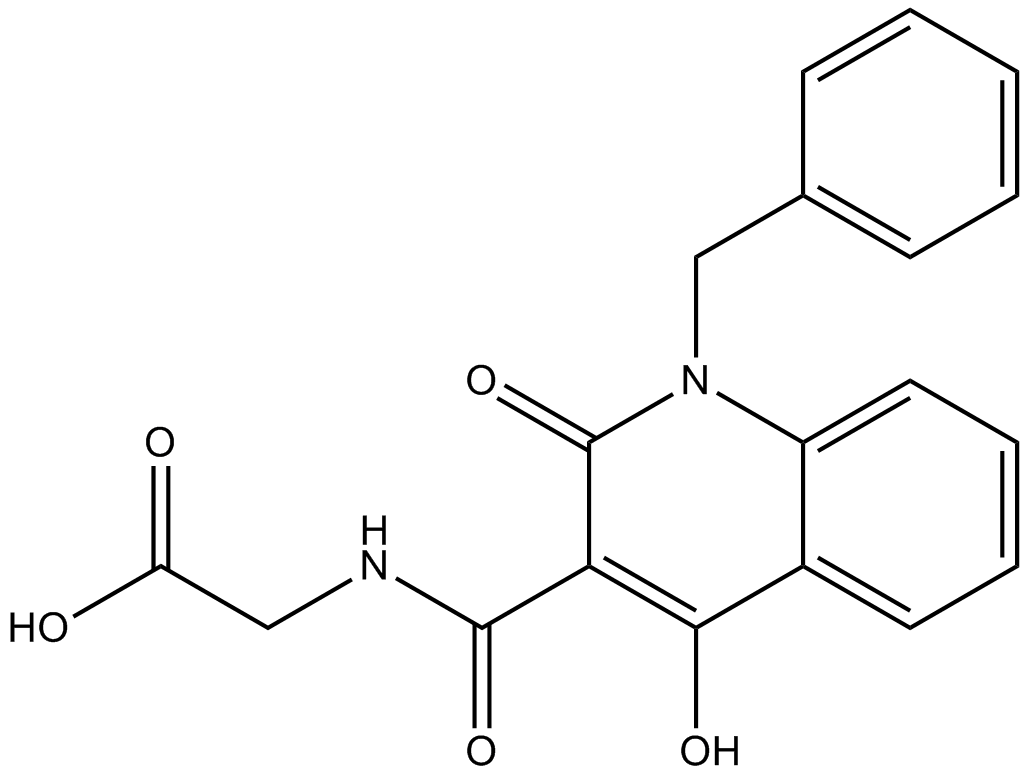 A4189 IOX2(Glycine)1 CitationSummary: HIF-1α prolyl hydroxylase-2 (PHD2) inhibitor
A4189 IOX2(Glycine)1 CitationSummary: HIF-1α prolyl hydroxylase-2 (PHD2) inhibitor -
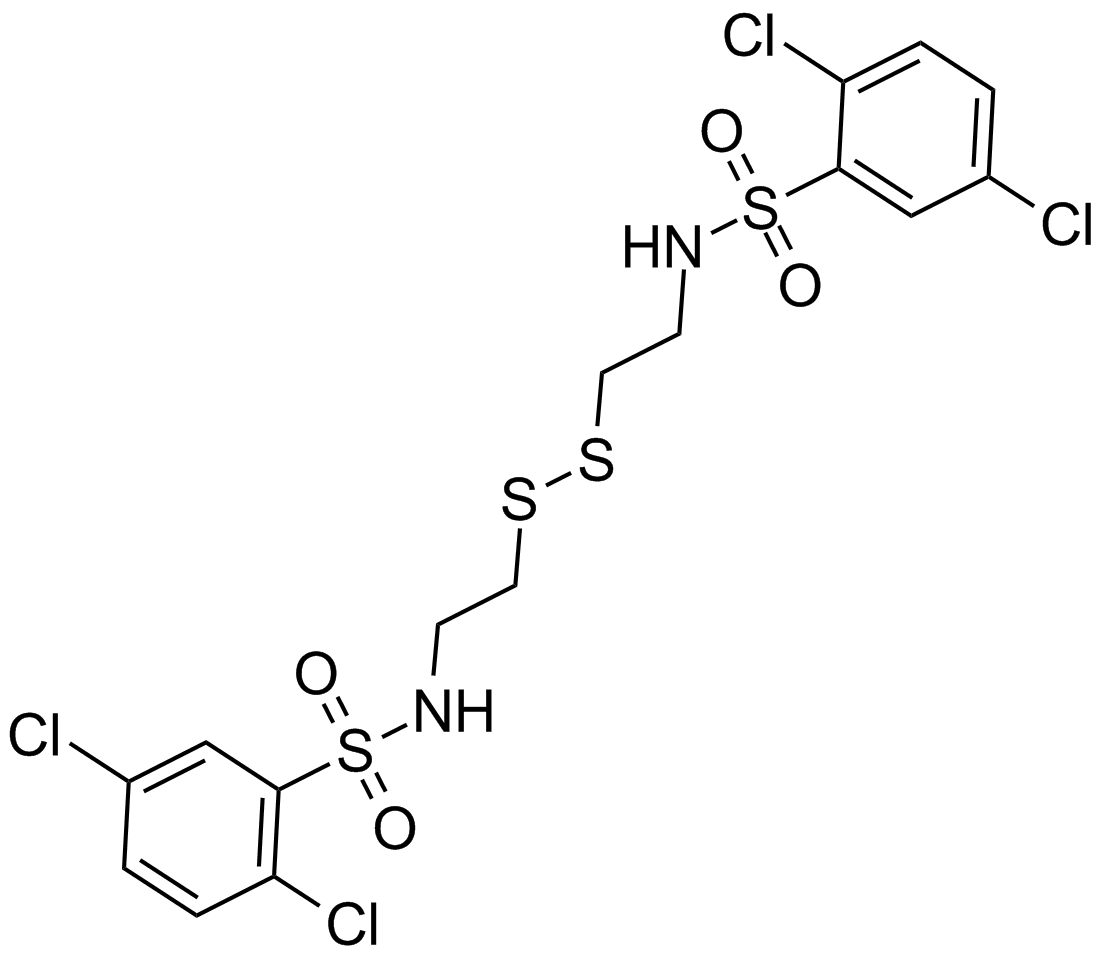 A4507 KC7F2Summary: HIF-1α inhibitor
A4507 KC7F2Summary: HIF-1α inhibitor -
 A4509 PX 12Target: TrxSummary: Trx-1 inhibitor
A4509 PX 12Target: TrxSummary: Trx-1 inhibitor -
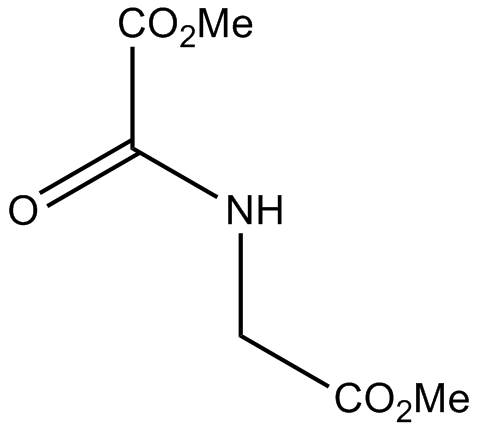 A4506 DMOGTarget: Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors (HIF-PHIs)Summary: Competitive HIF-PH inhibitor, cell-permeable
A4506 DMOGTarget: Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors (HIF-PHIs)Summary: Competitive HIF-PH inhibitor, cell-permeable -
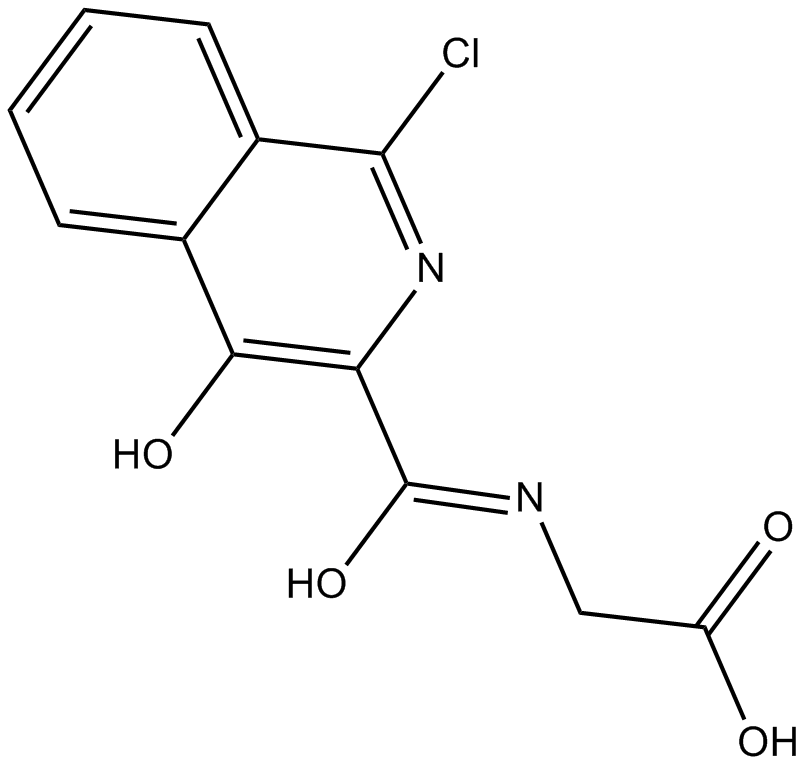 B5851 FG2216Target: Pyruvate dehydrogenases (PDH)Summary: HIF-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor
B5851 FG2216Target: Pyruvate dehydrogenases (PDH)Summary: HIF-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor -
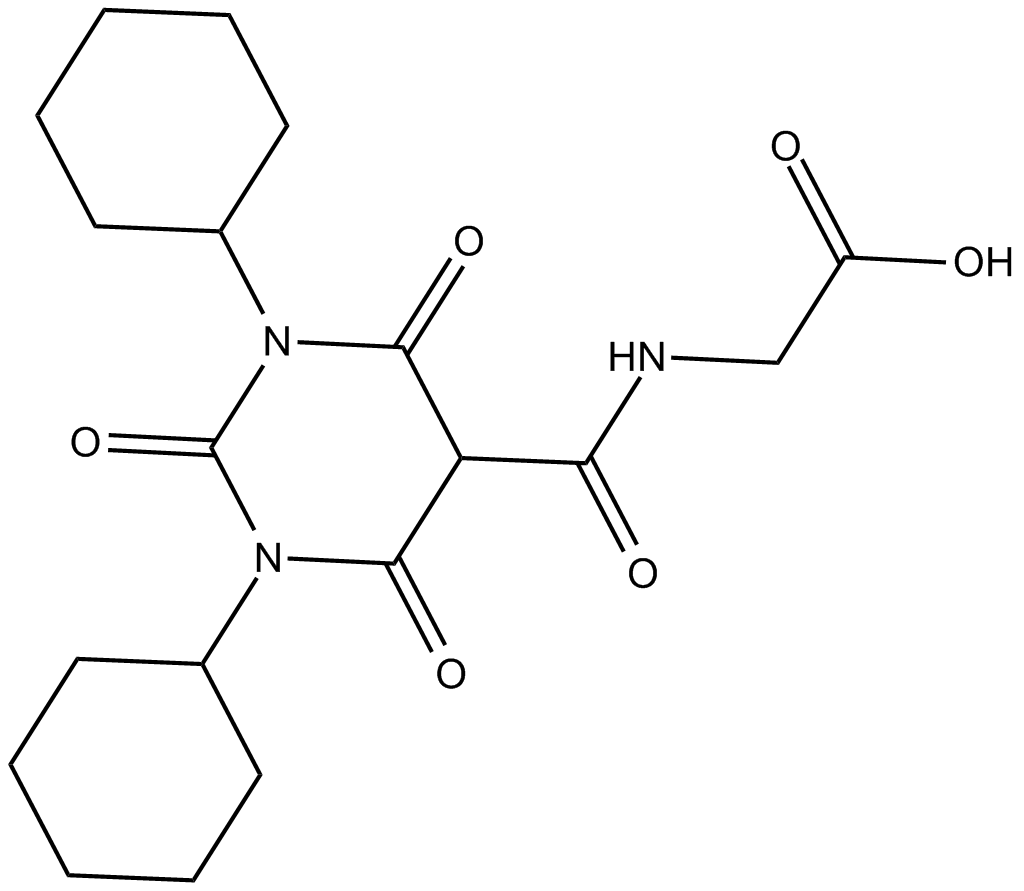 B6106 Daprodustat(GSK1278863)Summary: HIF-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor
B6106 Daprodustat(GSK1278863)Summary: HIF-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor -
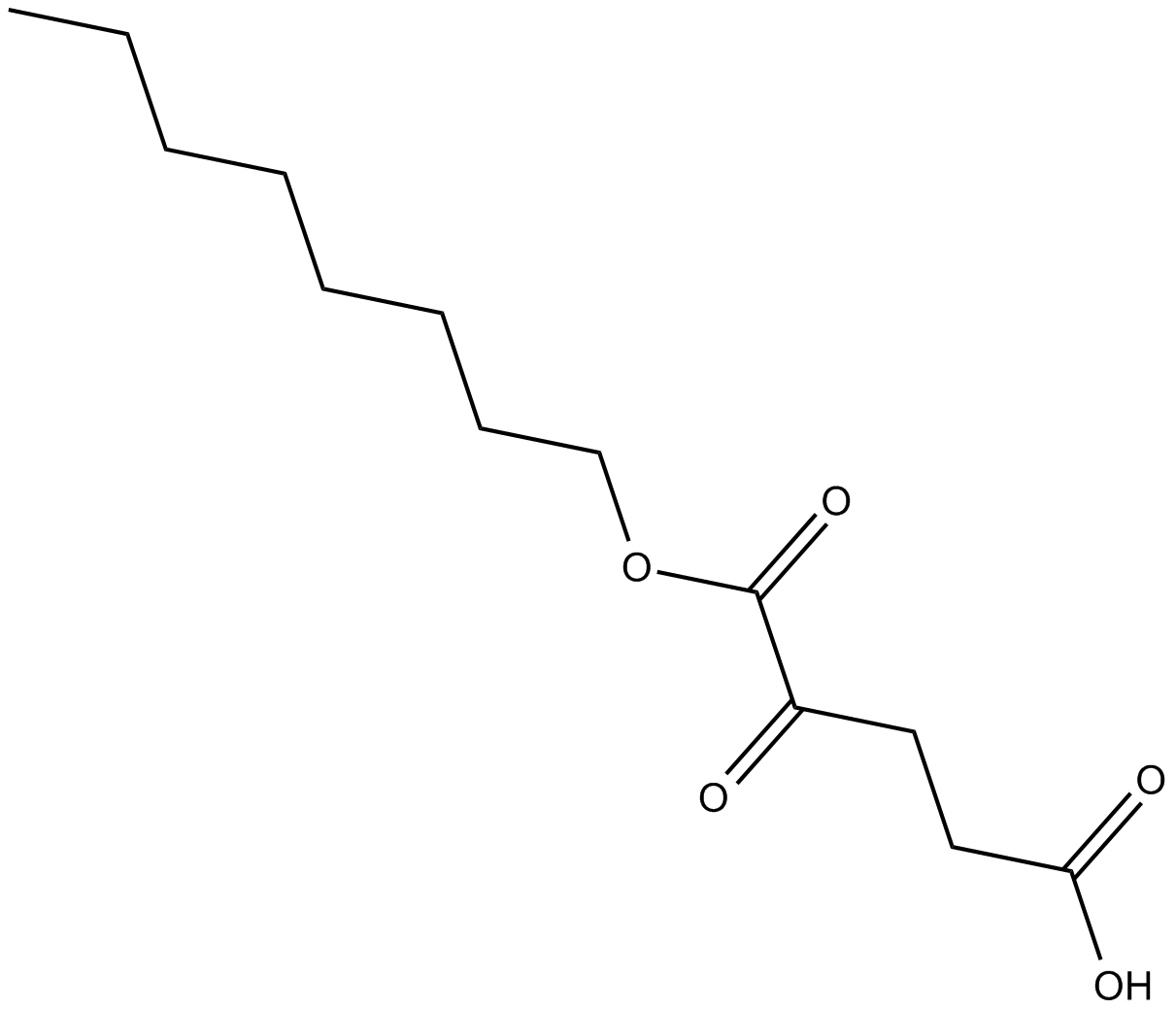 C4321 Octyl-α-ketoglutarateSummary: prolyl hydroxylases (PHD) activator
C4321 Octyl-α-ketoglutarateSummary: prolyl hydroxylases (PHD) activator -
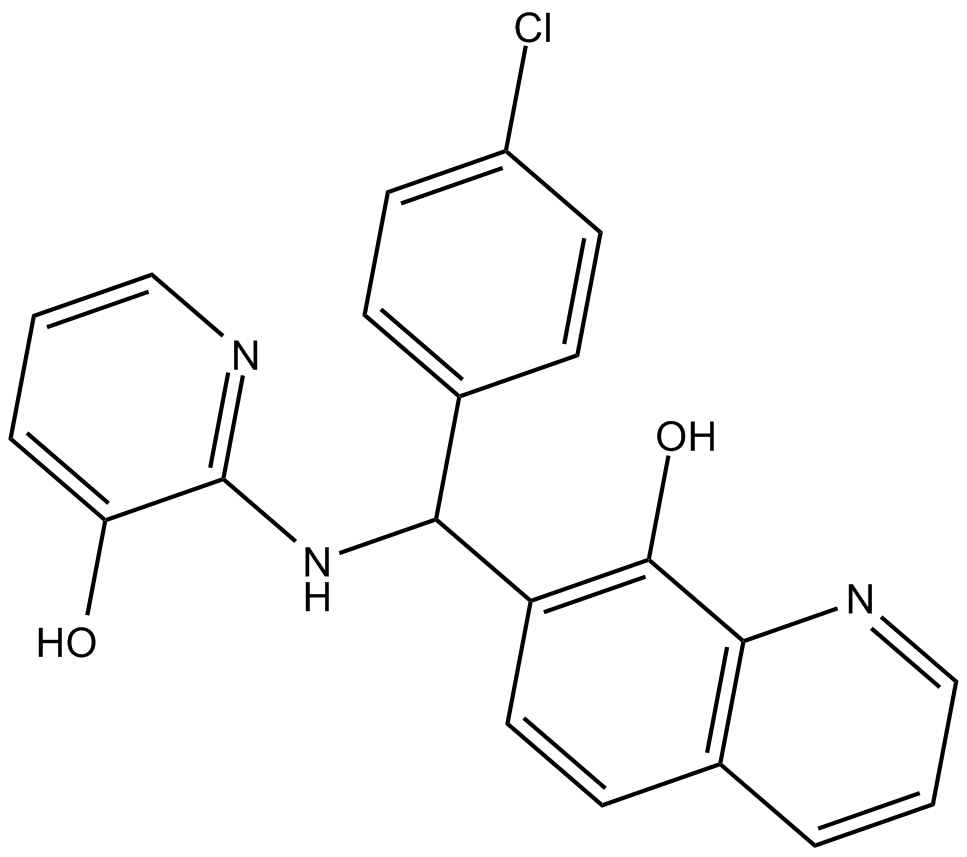 C4377 AdaptaquinSummary: HIF-prolyl hydroxylase-2 (PHD2) inhibitor
C4377 AdaptaquinSummary: HIF-prolyl hydroxylase-2 (PHD2) inhibitor

