CUDA
IC50: 11.1 and 112 nM for the mouse and human soluble epoxide hydrolase, respectively
CUDA is a soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) inhibitor.
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid metabolites of arachidonic acid, such as 11(12)-EET and 14(15)-EET, have been identified as endothelium derived hyperpolarizing factors with vasodilator activity. Soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) can catalyze the conversion of EETs to the corresponding dihydroxy eicosatrienoic acids thereby diminishing their activity.
In vitro: In a previous study, in order to test if the CUDA’s mechanism of action is retained upon structural modification, the dissociation constants of CUDA was evaluated for mouse sEH. Results showed that for CUDA, competitive a tight-binding inhibition kinetic was obtained with r2 > 0.99. Moreover, the KI value of 3.8 nM was obtained for CUDA. In addition, it was found that CUDA was an inhibitor of sEH exhibiting IC50 values of 11.1 nM and 112 nM for the mouse and human enzymes, respectively [1].
In vivo: Currently, there is no animal in vivo data reported.
Clinical trial: So far, no clinical study has been conducted.
Reference:
[1] C. Morisseau, M. H. Goodrow, J. W. Newman, et al. Structural refinement of inhibitors of urea-based soluble epoxide hydrolases. Biochemical Pharmacology 63, 1599-1608 (2002).
| Physical Appearance | A crystalline solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 340.5 |
| Cas No. | 479413-68-8 |
| Formula | C19H36N2O3 |
| Solubility | ≤1mg/ml in ethanol;5mg/ml in DMSO;10mg/ml in dimethyl formamide |
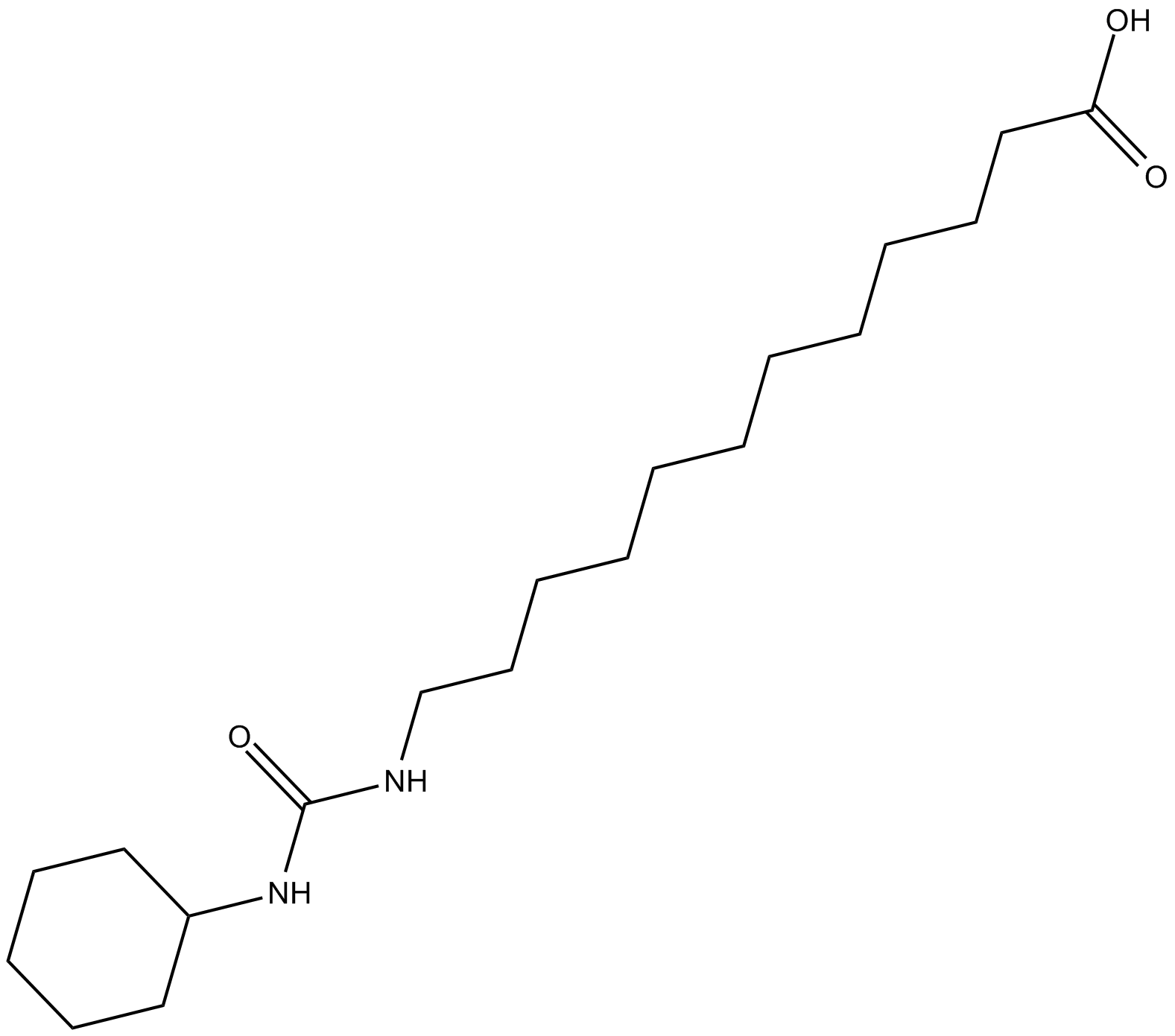
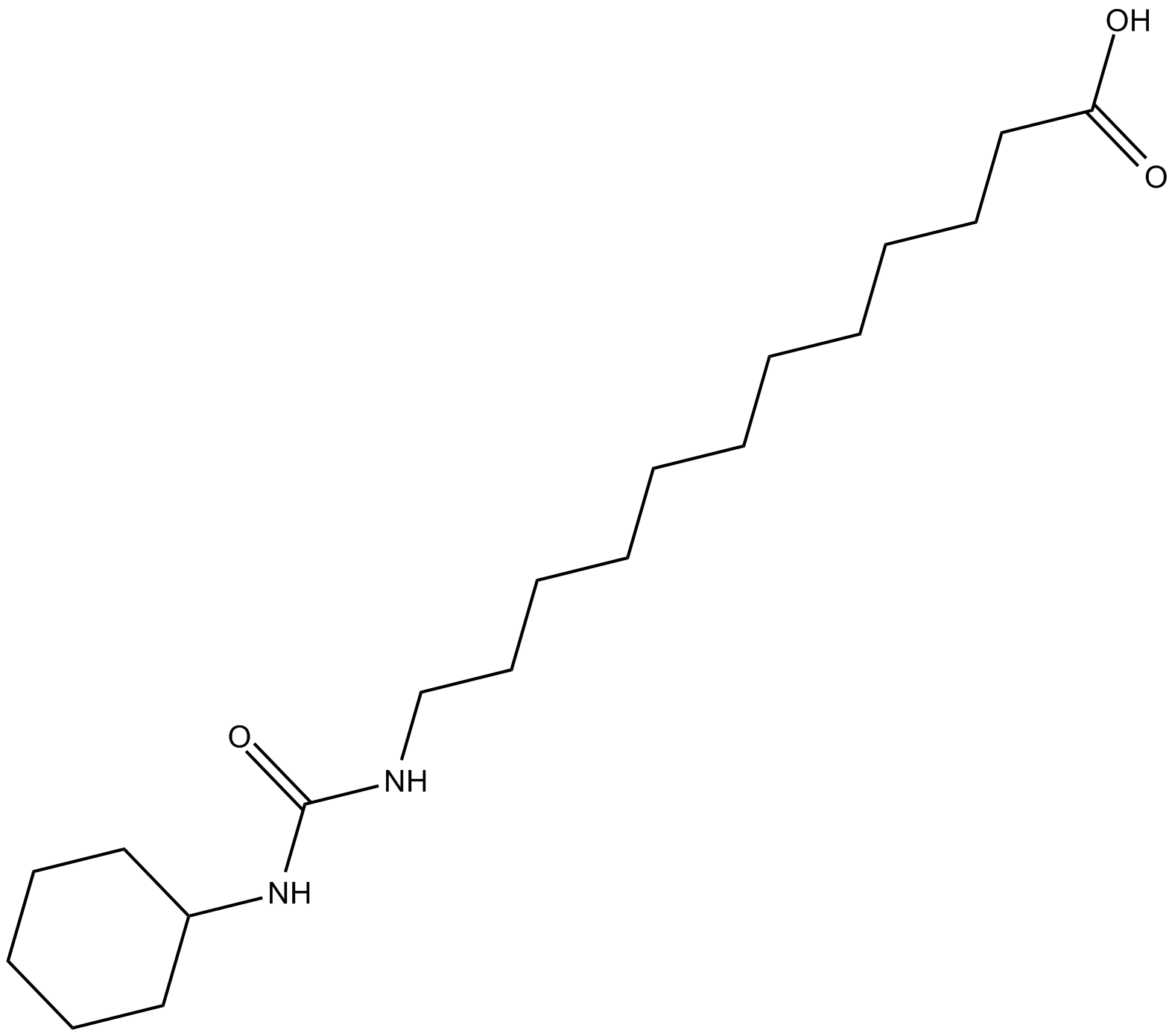
| Chemical Name | 12-[[(cyclohexylamino)carbonyl]amino]-dodecanoic acid |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | O=C(NCCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O)NC1CCCCC1 |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity = 98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
- Datasheet
Chemical structure