Rifampin
Rifampin (CAS 13292-46-1) is an antibiotic belonging to the rifamycin family, characterized by bactericidal activity via selective inhibition of bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. This inhibition disrupts transcriptional initiation by preventing RNA synthesis, leading to impaired bacterial protein biosynthesis and subsequent cell death. In biomedical research, rifampin serves as an essential tool for investigations into bacterial resistance mechanisms, transcriptional regulation, and synthetic biology studies that rely on specific transcription inhibition.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 822.94 |
| Cas No. | 13292-46-1 |
| Formula | C43H58N4O12 |
| Solubility | ≥26.25 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in H2O; insoluble in EtOH |
| SDF | Download SDF |
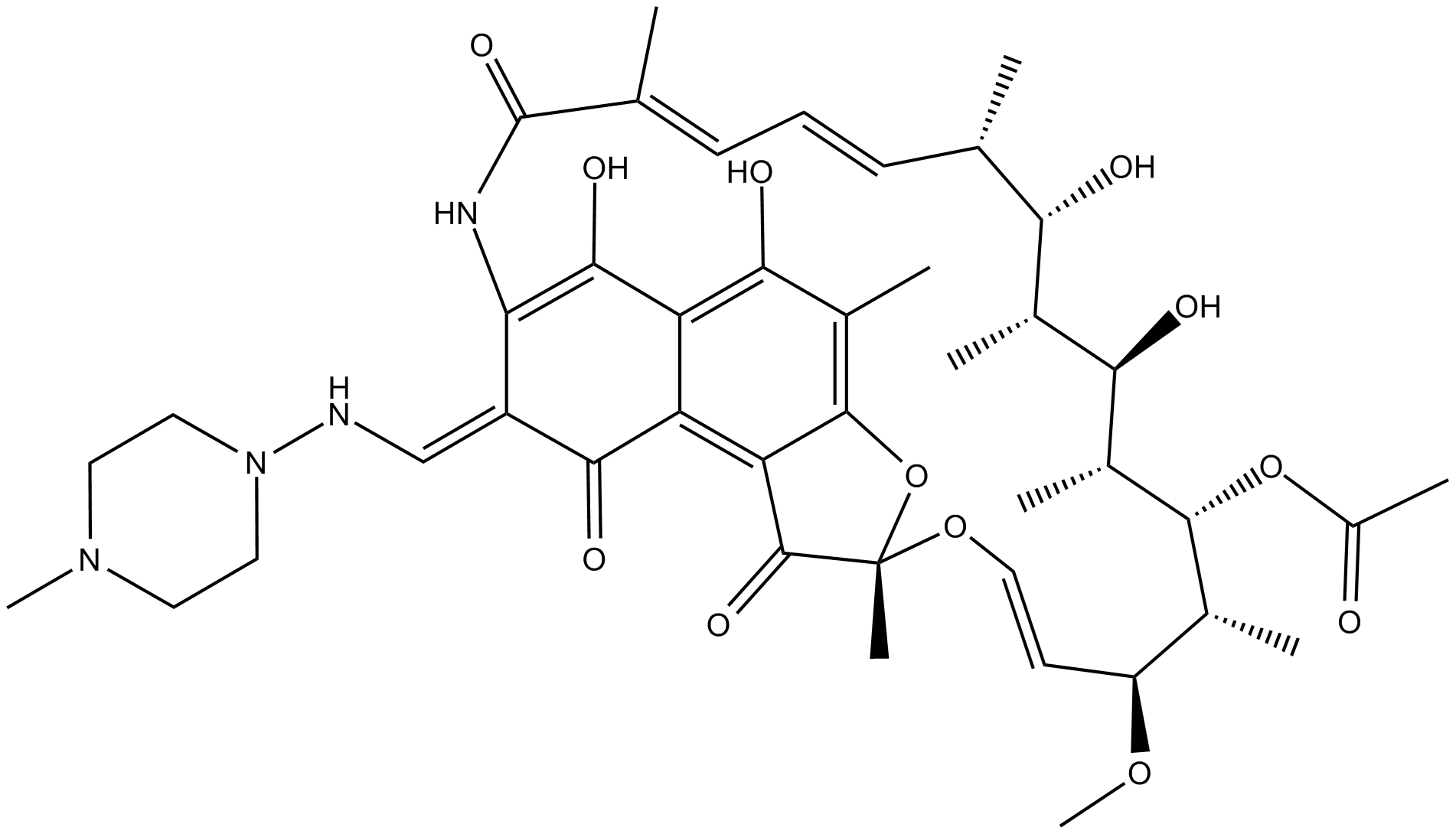
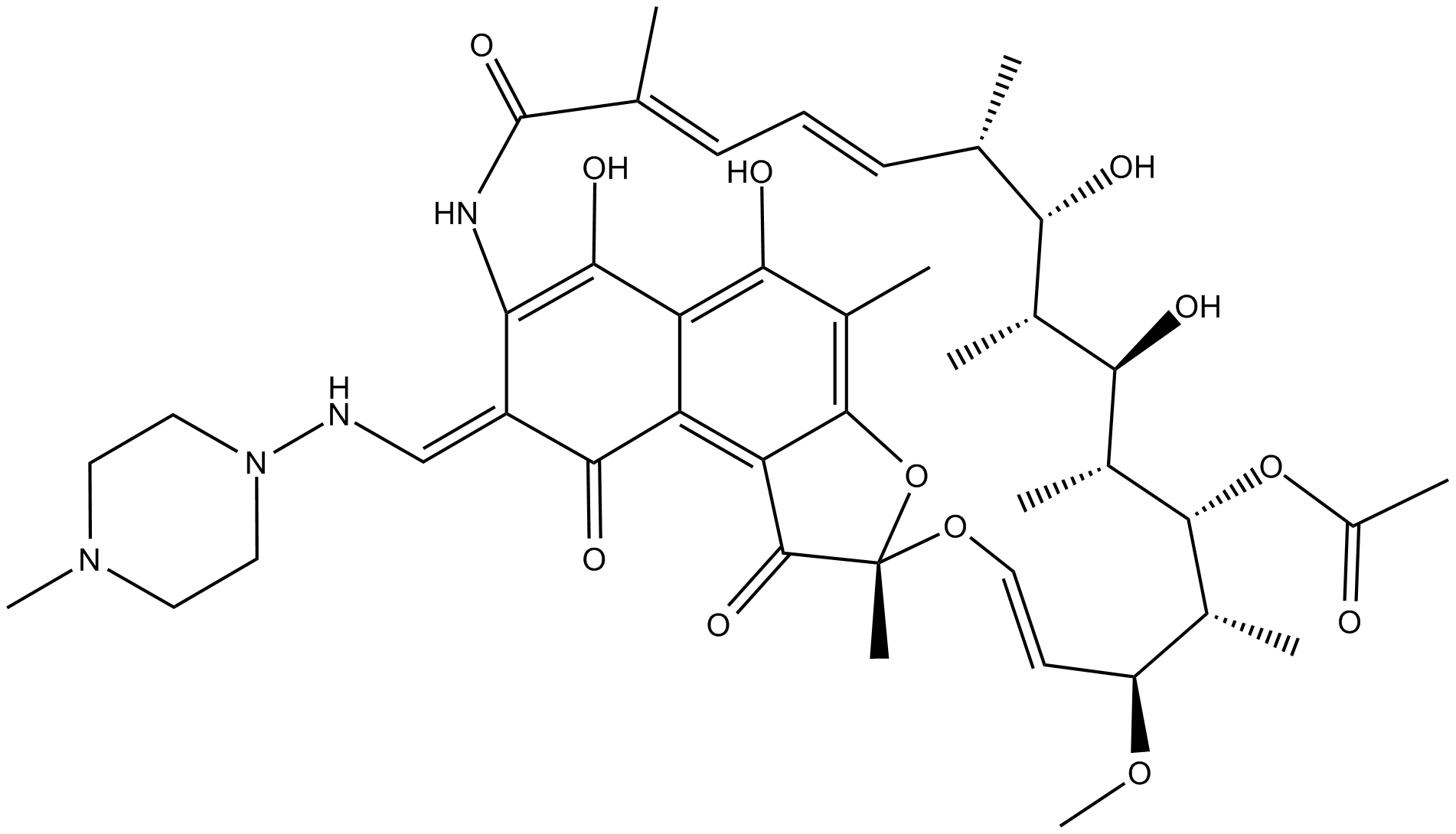
| Canonical SMILES | OC(C(/C=N/N1CCN(C)CC1)=C(NC(/C(C)=C\C=C\[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@@H](C)[C@H]2O)O)C)=O)C(O)=C3C(O)=C4C)=C3C5=C4O[C@](C)(O/C=C/[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@]([C@@H]2C)([H])OC(C)=O)C)OC)C5=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
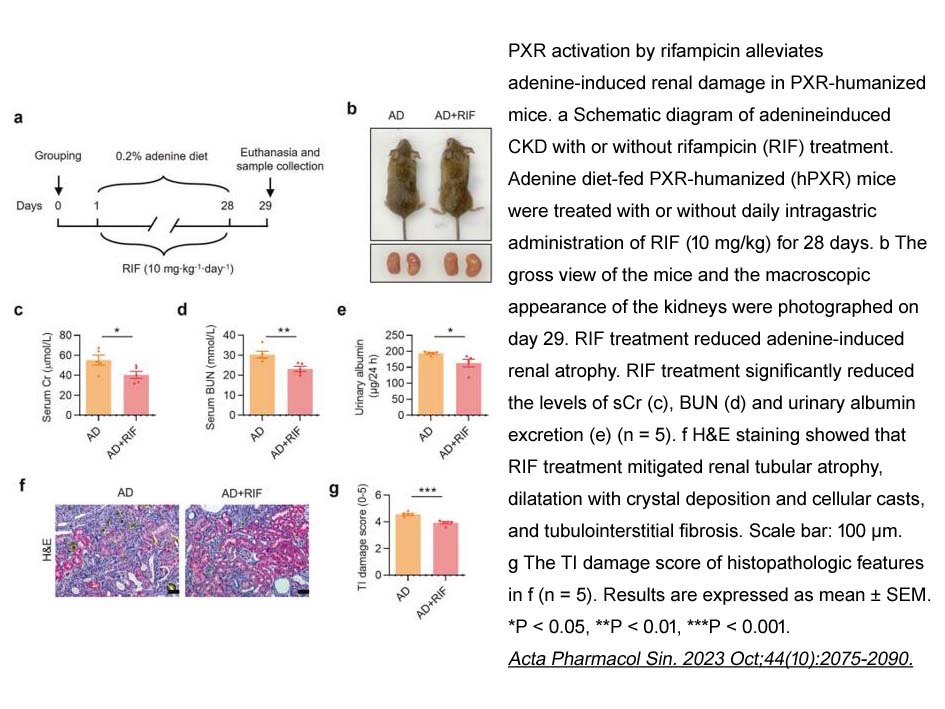
| Animal experiment:[1] | |
|
Animal models |
Male Parkes strain mice (20 ~ 25g) inoculated in the left hind footpad with 1 × 104 viable units of Mycobacterium marinum (M. marinum) |
|
Dosage form |
0.003%, 0.01%, 0.03% and 0.1% rifampin in the diet Administered by oral route |
|
Applications |
Rifampin at dosages of 0.003% and 0.01% in the diet was not suppressive to bacillary growth. A dosage of 0.03% resulted in a transient fall in viable bacillary count, which was followed by recovery of growth 10 days after inoculation. The highest dose (0.1%) was highly bactericidal, with the viable count of M. marinum reduced to, and maintained below, the detectable level of 2.0 × 102 organisms per foot pad after 7 days of treatment. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Banerjee DK, Holmes IB. In vitro and in vivo studies of the action of rifampicin, clofazimine and B1912 on Mycobacterium marinum. Chemotherapy, 1976, 22(3-4): 242-252. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data