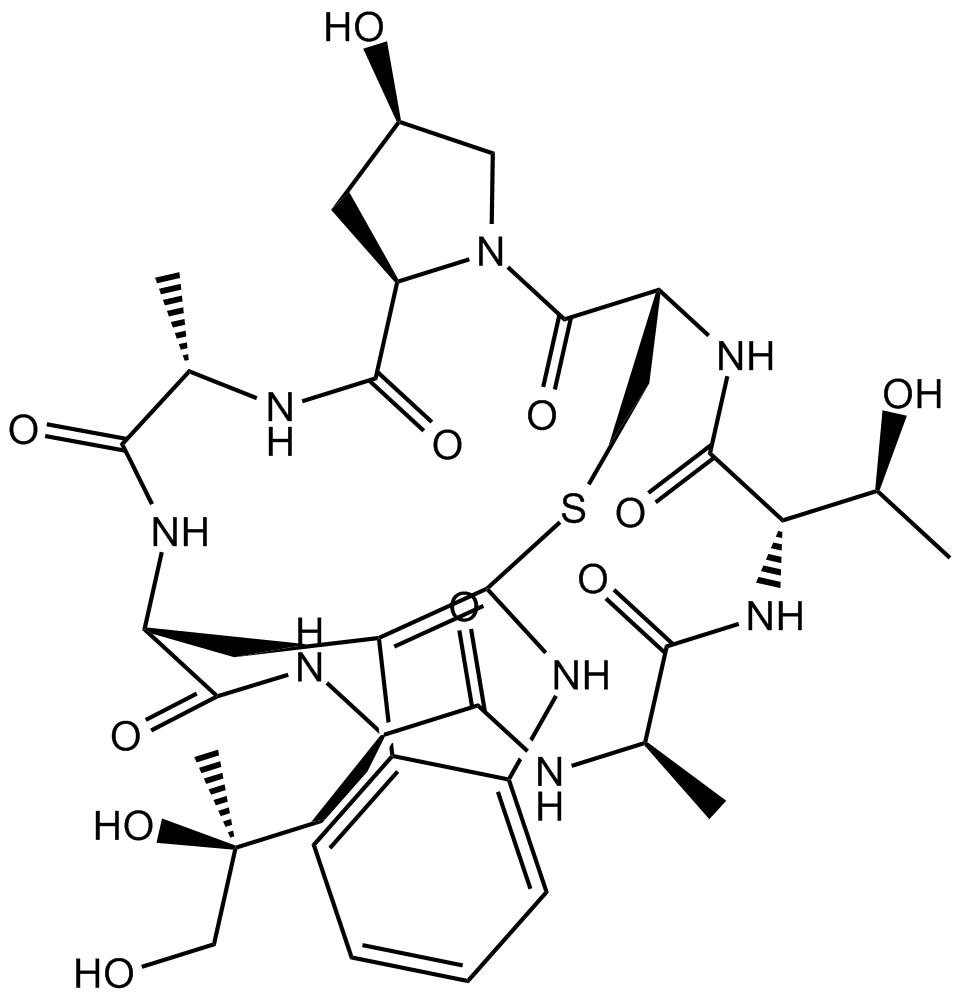
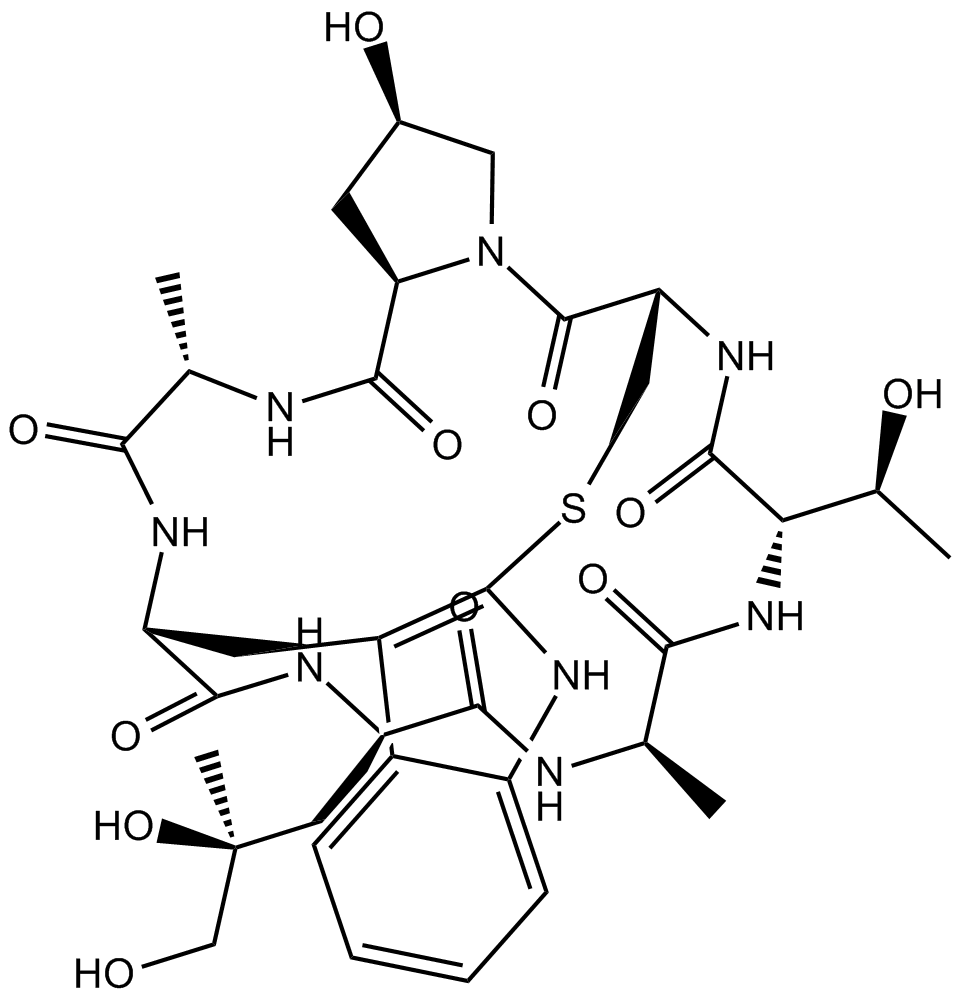
Phalloidin
Phalloidin (CAS 17466-45-4) is a cyclic heptapeptide toxin originally isolated from the Amanita phalloides mushroom, which specifically binds filamentous actin (F-actin) with high affinity (Kd approximately 20 nM), without binding to monomeric actin (G-actin). By binding directly to F-actin, phalloidin stabilizes these filaments and prevents their depolymerization, thereby disrupting the dynamic equilibrium essential for normal cytoskeletal processes. Conjugates of phalloidin with fluorophores such as FITC or Cy dyes are widely utilized in microscopy-based applications, enabling selective and species-independent visualization of F-actin organization in fixed cells, permeabilized samples, tissue sections, and cell-free assays.
- 1. Guanlin Zhou, Chao Wang, et al. "Alternating magnetic field pretreatment promotes cellular endocytosis to enhance the efficacy of magnetic hyperthermia." Volume 114, Part A, December 2025, 107429
- 2. Mei Liu, et al. "Shear Bond Strength to Enamel, Mechanical Properties and Cellular Studies of Fiber-Reinforced Composites Modified by Depositing SiO2 Nanofilms on Quartz Fibers via Atomic Layer Deposition." Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Mar 5:19:2113-2136. PMID: 38476282
- 3. Mengliu Luo, MD, et al. "Yo-Yo Dieting Delays Male Drosophila melanogaster Aging Through Enhanced Mitochondrial Function, Relative to Sustained High-Calorie Diet Feeding." J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2024 Apr 1;79(4):glae014. PMID: 38198696
- 4. Wang X, Cai Y, et al. "Effect of Biodentine on Odonto/Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells." Bioengineering (Basel) 2022 Dec 21;10(1). PMID: 36671584
| Physical Appearance | A crystalline solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 788.87 |
| Cas No. | 17466-45-4 |
| Formula | C35H48N8O11S |
| Solubility | Soluble to 1 mg/ml in sterile water |
| Chemical Name | A name could not be generated for this structure. |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | O[C@@H]1C[C@H](C(N[C@@H](C)C(N[C@@H](C(N[C@@H](C(N[C@@H]2C)=O)C[C@](CO)(C)O)=O)CC3=C(NC4=CC=CC=C34)SC[C@H]5NC([C@H]([C@H](C)O)NC2=O)=O)=O)=O)N(C5=O)C1 |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment:[2] | |
|
Cell lines |
Mouse 3T3 and rat kangaroo PtK2 cells |
|
Reaction Conditions |
0.2 or 1 mM phalloidin in 0.14 M KCI (Me2SO concentration 0.4 or 2%), for 3 h incubation |
|
Applications |
When phalloidin was injected into cells, it recruited the less highly polymerized forms of actin and/or G actin, to form "islands" of aggregated actin in a focal plane above the stress fibers. In addition, microinjection of phalloidin interfered cell locomotion and cell growth in a concentration-dependent manner. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Chazotte B. Labeling cytoskeletal F-actin with rhodamine phalloidin or fluorescein phalloidin for imaging. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2010 May;2010(5):pdb.prot4947. 2. Wehland J, Osborn M, Weber K. Phalloidin-induced actin polymerization in the cytoplasm of cultured cells interferes with cell locomotion and growth. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1977, 74(12): 5613-5617. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity = 98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
Chemical structure