MLCK inhibitor peptide 18
MLCK inhibitor peptide 18 is a cell-permeable inhibitor of MLCK (IC50 = 50 nM), with 4000-fold selectivity for MLCK over another closely related calmodulin (CaM)-regulated protein kinase, CaM-dependent kinase II (CaMPKII). MLCK inhibitor peptide 18 can cross cell membrane, and regulate paracellular permeability by reducing intracellular MLC phosphorylation, with the potential to restore barrier function in intestinal disease states. In addition, MLCK inhibitor peptide 18 can also inhibit chromosome-mediated cortical reorganization in mouse oocytes, as well as complement receptor-3 (CR3) mediated phagocytosis of C3bi-opsonized zymosan by mouse microglia.
References:
1. Lukas TJ, Mirzoeva S, Slomczynska U, et al. Identification of novel classes of protein kinase inhibitors using combinatorial peptide chemistry based on functional genomics knowledge. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 1999, 42(5): 910-919.
2. Zolotarevsky Y, Hecht G, Koutsouris A, et al. A membrane-permeant peptide that inhibits MLC kinase restores barrier function in in vitro models of intestinal disease. Gastroenterology, 2002, 123(1): 163-172.
3. Deng M, Williams CJ, Schultz RM. Role of MAP kinase and myosin light chain kinase in chromosome-induced development of mouse egg polarity. Developmental Biology, 2005, 278(2): 358-366.
4. Gitik M, Reichert F, Rotshenker S. Cytoskeleton plays a dual role of activation and inhibition in myelin and zymosan phagocytosis by microglia. The FASEB Journal, 2010, 24(7): 2211-2221.
| Physical Appearance | A crystalline solid |
| Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 1324.64 |
| Cas No. | 224579-74-2 |
| Formula | C60H105N23O11 |
| Solubility | ≥58.5 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥45.3 mg/mL in EtOH; ≥49.4 mg/mL in H2O |
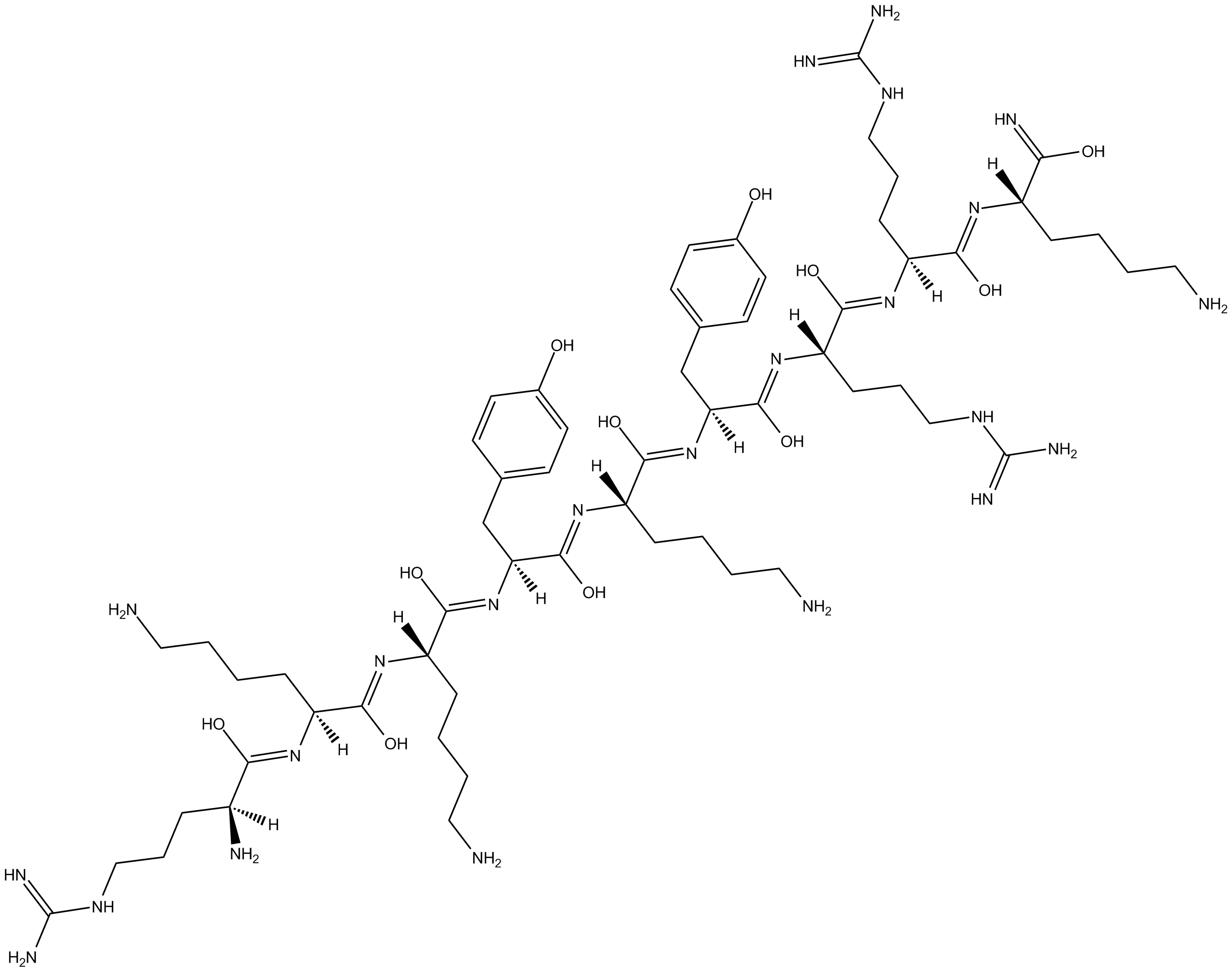
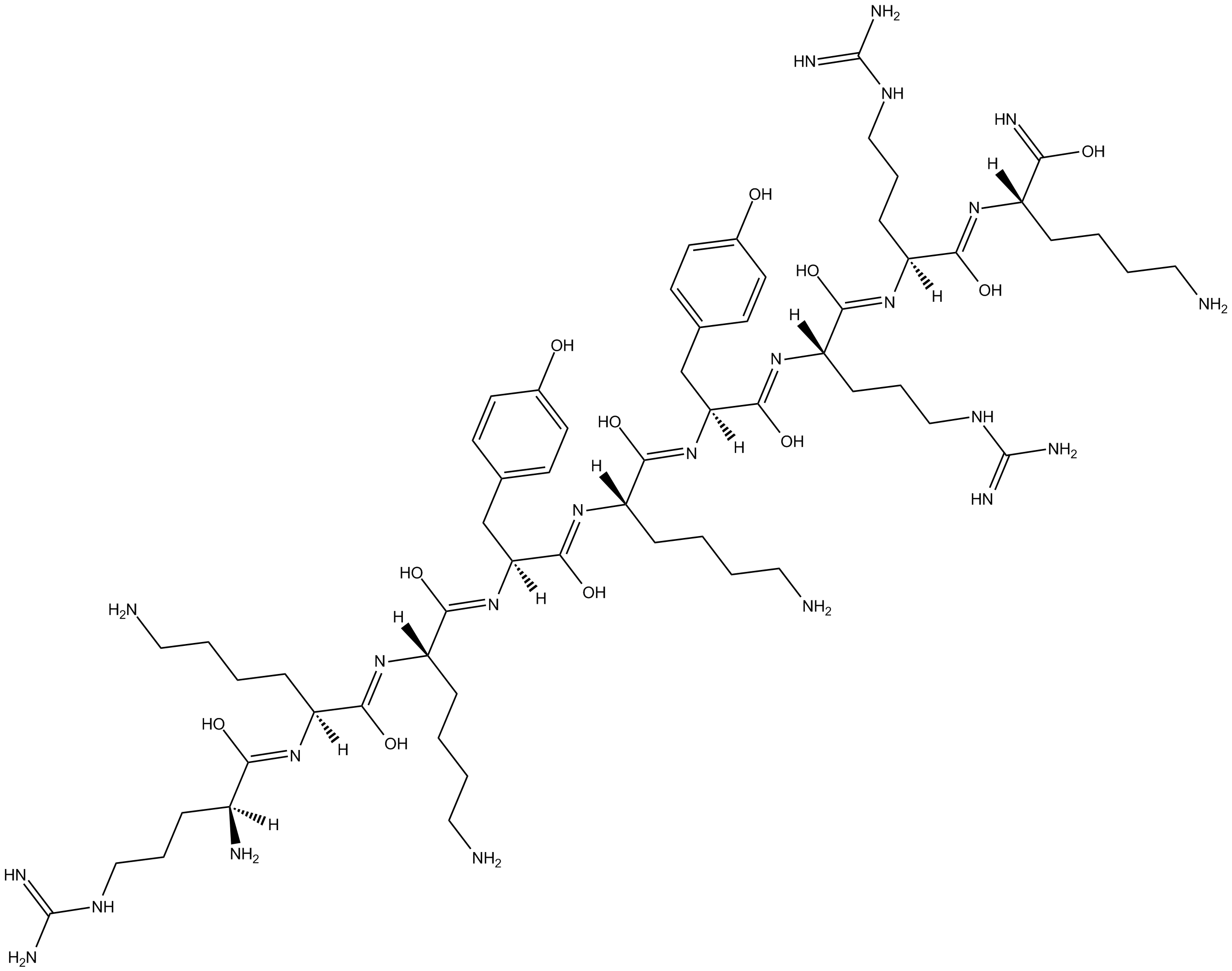
| Chemical Name | (S,Z)-6-amino-N-((S,Z)-1-(((S,Z)-1-(((S,Z)-1-(((S)-6-amino-1-hydroxy-1-iminohexan-2-yl)imino)-5-guanidino-1-hydroxypentan-2-yl)imino)-5-guanidino-1-hydroxypentan-2-yl)imino)-1-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propan-2-yl)-2-((Z)-((6S,7Z,9S,10Z,12S,13Z,15S)-1,6- |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | NCCCC[C@@](/N=C(O)/[C@](/N=C(O)/[C@](/N=C(O)/[C@](/N=C(O)/[C@](/N=C(O)/[C@](/N=C(O)/[C@](/N=C(O)/[C@](/N=C(O)/[C@](N)([H])CCCNC(N)=N)([H])CCCCN)([H])CCCCN)([H])CC1=CC=C(O)C=C1)([H])CCCCN)([H])CC2=CC=C(O)C=C2)([H])CCCNC(N)=N)([H])CCCNC(N)=N)([H])C(O)=N |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment:[2] | |
|
Cell lines |
Escherichia coli-infected T84 monolayers, as well as TNF-α and IFN-γ stimulated Caco-2 monolayers |
|
Reaction Conditions |
330 μM MLCK inhibitor peptide 18 |
|
Applications |
MLCK inhibitor peptide 18 prevented defects in transepithelial barrier resistance induced by bacteria or TNF-α plus IFN-γ. Moreover, MLCK inhibitor peptide 18 effectively reduced MLC phosphorylation triggered by TNF-α and IFN-γ. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Combinatorial peptide chemistry based on functional genomics knowledge. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 1999, 42(5): 910-919. 2. Zolotarevsky Y, Hecht G, Koutsouris A, et al. A membrane-permeant peptide that inhibits MLC kinase restores barrier function in in vitro models of intestinal disease. Gastroenterology, 2002, 123(1): 163-172. 3. Deng M, Williams CJ, Schultz RM. Role of MAP kinase and myosin light chain kinase in chromosome-induced development of mouse egg polarity. Developmental Biology, 2005, 278(2): 358-366. 4. Gitik M, Reichert F, Rotshenker S. Cytoskeleton plays a dual role of activation and inhibition in myelin and zymosan phagocytosis by microglia. The FASEB Journal, 2010, 24(7): 2211-2221. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure