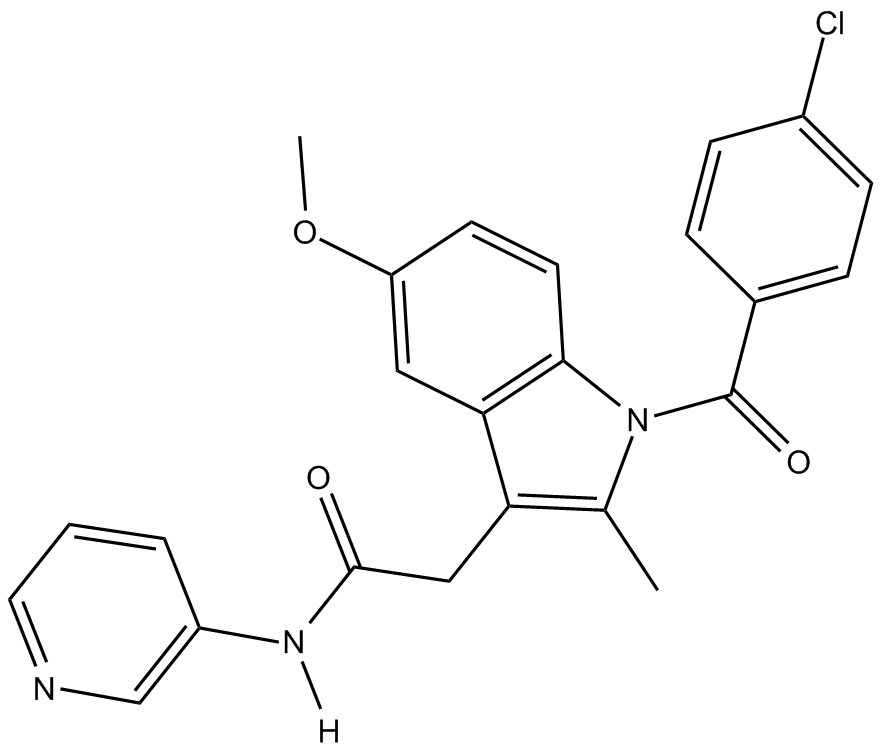
N-(3-pyridyl)-Indomethacin amide
N-(3-pyridyl)-Indomethacin amide is a reversible, potent and selective COX-2 inhibitor [1].
Cyclooxygenase (COX) is an enzyme responsible for formation of prostanoids, including thromboxane and prostaglandins such as prostacyclin. COX-1 is the constitutive isoform and is mainly responsible for the synthesis of cytoprotective prostaglandins in the gastrointestinal tract (GI) and of the proaggregatory thromboxane in blood platelets. COX-2 is inducible and short-lived that is stimulated by endotoxin, cytokines, and mitogens. COX-2 plays important roles in prostaglandin biosynthesis in inflammatory cells the central nervous system [1].
N-(3-pyridyl)-indomethacin amide (N-3PyIA) is a reversible, potent and selective COX-2 inhibitor that inhibits human recombinant COX-2 and ovine COX-1 with IC50 values of 0.052 and >66 μM, respectively. It is over 1300 times less potent as an inhibitor of ovine COX-1. N-(3-pyridyl)-indomethacin amide is the 3-pyridyl amide derivative of indomethacin that shows selective against COX-2 [1].
Reference:
[1]. Kalgutkar AS, Marnett AB, Crews BC, et al. Ester and amide derivatives of the nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug, indomethacin, as selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2000 Jul 27;43(15):2860-70.
| Physical Appearance | A crystalline solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 433.9 |
| Cas No. | 261766-29-4 |
| Formula | C24H20ClN3O3 |
| Synonyms | N-3PyIA |
| Solubility | ≤3mg/ml in ethanol;3mg/ml in DMSO;3mg/ml in dimethyl formamide |
| Chemical Name | N-(3-pyridyl)-1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl-1H-indole-3-acetamide |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | Cc1c(CC(Nc2cnccc2)=O)c(cc(cc2)OC)c2[n]1C(c(cc1)ccc1Cl)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity = 98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
Chemical structure