Moxifloxacin
Moxifloxacin (CAS 151096-09-2) is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic targeting bacterial DNA gyrase, an enzyme essential for DNA replication and transcription. It demonstrates broad-spectrum antibacterial activity through inhibition of this enzyme. Research indicates that Moxifloxacin exerts dose-dependent antiproliferative and cytotoxic effects in mammalian cell models, with concentrations between 50 and 1500 μg/mL significantly impacting cell viability and inducing morphological damage, such as binucleation. Animal studies show intravenous administration (100 mg/kg, rats) elevates blood glucose and serum adrenaline levels, accompanied by enhanced histamine release, but no effect was noted at 75 mg/kg. Therefore, Moxifloxacin is valuable in biomedical studies exploring antibiotic toxicity, cellular proliferation, and metabolic responses.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 401.43 |
| Cas No. | 151096-09-2 |
| Formula | C21H24FN3O4 |
| Solubility | ≥11.62 mg/mL in EtOH with gentle warming and ultrasonic; ≥25.6 mg/mL in H2O with gentle warming and ultrasonic; ≥50.8 mg/mL in DMSO with gentle warming |
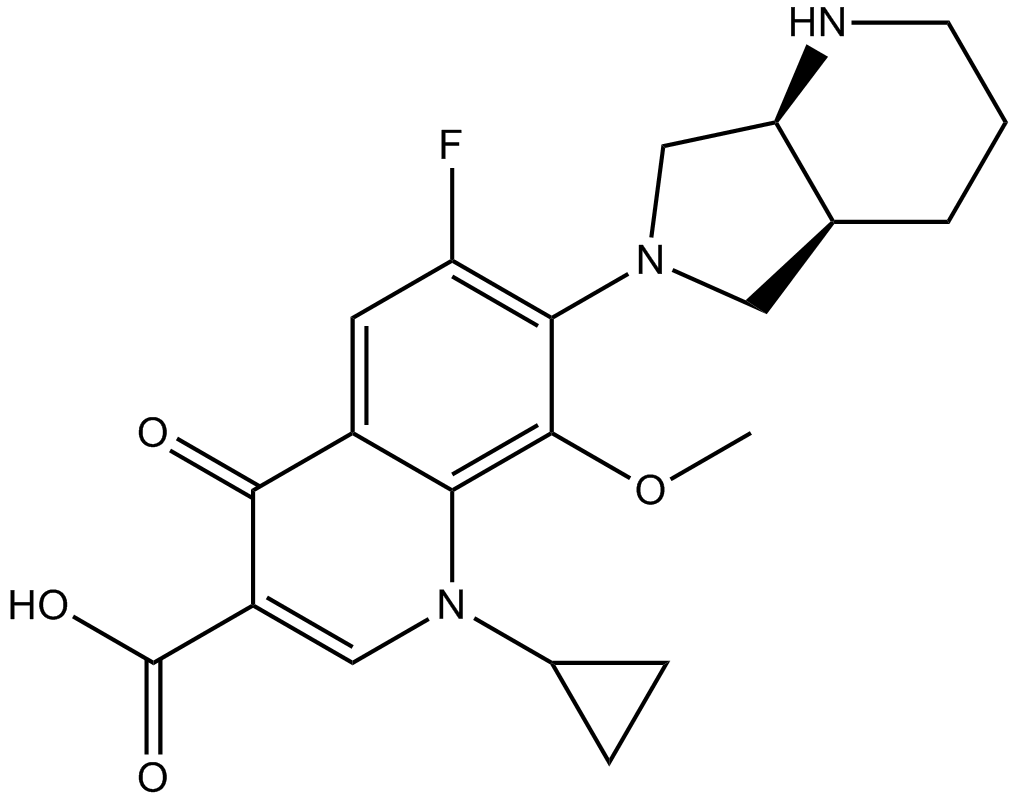
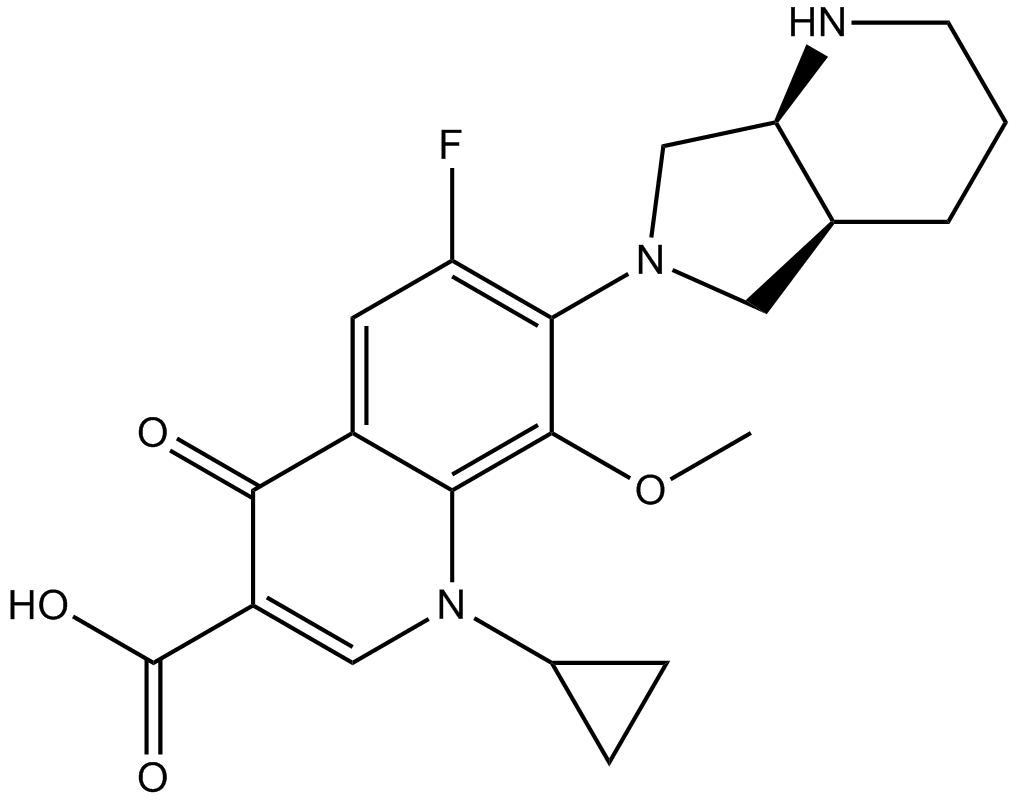
| Chemical Name | 7-[(4aS,7aS)-1,2,3,4,4a,5,7,7a-octahydropyrrolo[3,4-b]pyridin-6-yl]-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | COc(c(N1C[C@H]2NCCC[C@H]2C1)c(cc12)F)c1N(C1CC1)C=C(C(O)=O)C2=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
|
Cell lines |
Rat retinal ganglion cells |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is ≥50.8 mg/mL. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 ℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
|
Reacting condition |
5~1500 μg/mL |
|
Applications |
After 24 and 72 hours of incubation, no cytotoxicity or antiproliferative effect was observed in RGC5 cells when the concentration of moxifloxacin was less than 50 μg / mL. At higher concentrations (150 μg / mL, 500 μg / mL and 1500 μg / mL), the number and proliferation rate of RGC5 cells were significantly reduced. |
| Animal experiment [1]: | |
|
Animal models |
Male Wistar rats |
|
Dosage form |
75, 100mg/kg (i.v.) |
|
Application |
Serum glucose concentration increased, and serum adrenaline and histamine concentrations increased over time with moxifloxacin at 100 mg/kg. Intravenous injection of 75 mg / kg of moxifloxacin did not affect the concentration of glucose, epinephrine or histamine in the serum. The serum immunoreactive insulin concentration did not change with the concentration of moxifloxacin at 75 and 100 mg / kg. In conclusion, moxifloxacin can induce histamine release, leading to increased serum adrenaline concentrations and hyperglycemia. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1]. Sobolewska B, Hofmann J, Spitzer MS, Bartz-Schmidt KU, Szurman P, Yoeruek E.Antiproliferative and cytotoxic properties of moxifloxacin on rat retinal ganglion cells. Curr Eye Res. 2013 Jun;38(6):662-9. doi:10.3109/02713683.2012.746991. PubMed PMID: 23654355. [2]. Ishiwata Y, Takahashi Y, Nagata M, Yasuhara M. Effects of moxifloxacin on serum glucose concentrations in rats. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(4):686-90. Epub 2013 Jan 25. PubMed PMID: 23358329. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure