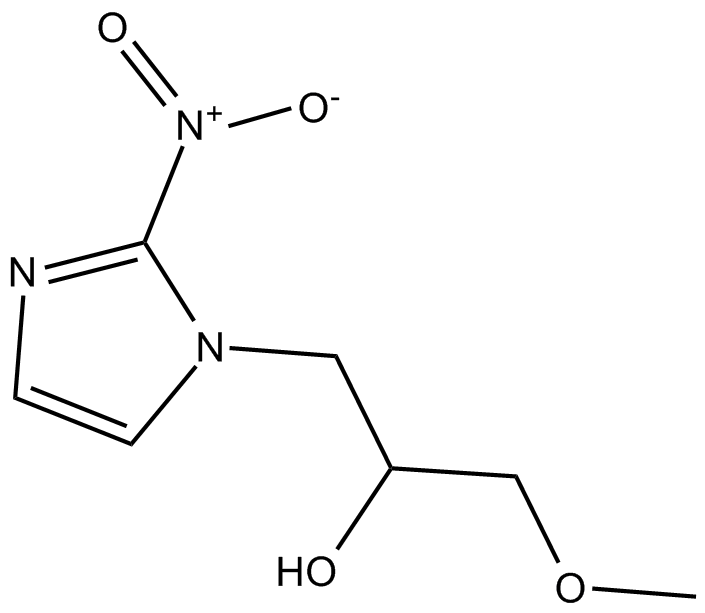
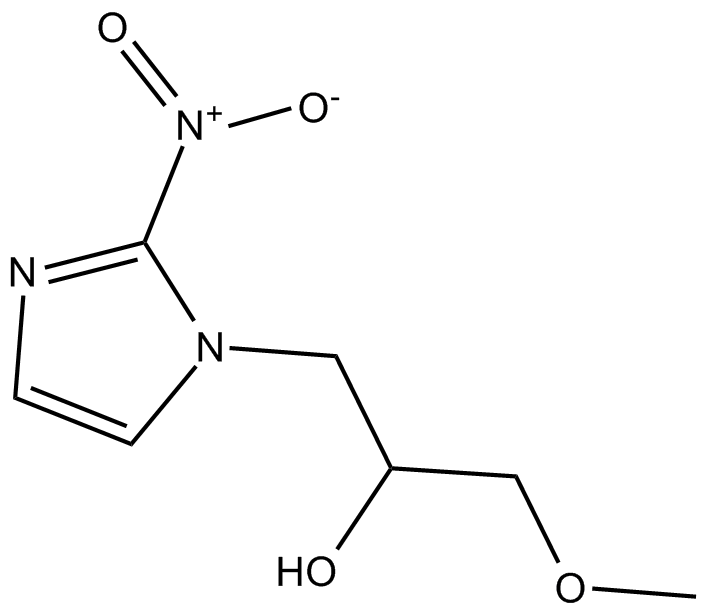
Misonidazole
Misonidazole (MISO), a hypoxic cell radiosensitizer, is selectively metabolized by hypoxic cells to reactive products that bind covalently to cellular constituents. The drug also possesses a substantial cytotoxic effect, independent of radiation, which is selectively expressed in hypoxic cells. Misonidazole may be cytotoxic to the normal hypoxic tissues in the human body, making this became a major concern in the clinical application of the drug. Misonidazole leads to strand breaks in cellular DNA and those cells which fail to survive also fail to repair these strand breaks. Misonidazole depletes intracellular glutathione and is more toxic in glutathione depleted cells. The depletion is time, temperature, drug concentration and cell line dependent.
In vitro: In cultured CHO cells, pretreatment with 5 mM MISO for 2 hr exihibited the marginal toxicity [2].
In vivo: Pretreatment with misonidazole (MISO) enhanced the number of cross-links formed in a fibrosarcoma and in the spleen and gut of mice for periods up to 48 h following a single injection of melphalan (MEL). MISO pretreatment could result in a greater amount of binding of MEL to DNA at early times after injection. MISO may exert its affect by inhibiting the repair of cross-links or monoadducts at early times post-injection [3].
Clinical trials: Various dose schedules of misonidazole have proven to be tolerable, with a moderate incidence of nausea and vomiting and mild peripheral neuropathy, and a low incidence of more severe peripheral neuropathy or central neuropathy [4].
References:
[1] Josephy P D, Palcic B, Skarsgard L D. Ascorbate-enhanced cytotoxicity of misonidazole[J]. Nature, 1978, 271(5643): 370-372.
[2]Taylor Y C, Bump E A, Brown J M. Studies on the mechanism of chemosensitization by misonidazole in vitro[J]. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics, 1982, 8(3-4): 705-708.
[3] Murray D, Meyn R E. Enhancement of the DNA cross-linking activity of melphalan by misonidazole in vivo[J]. British journal of cancer, 1983, 47(2): 195.
[4] Wasserman T H, Stetz J A, Phillips T L. Clinical trials of misonidazole in the United States[J]. Cancer clinical trials, 1980, 4(1): 7-16.
| Physical Appearance | A crystalline solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 201.2 |
| Cas No. | 13551-87-6 |
| Formula | C7H11N3O4 |
| Synonyms | NSC 261037,Ro 7-0582,SR 1354 |
| Solubility | ≤5mg/ml in ethanol;15mg/ml in DMSO;15mg/ml in dimethyl formamide |
| Chemical Name | α-(methoxymethyl)-2-nitro-1H-imidazole-1-ethanol |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | COCC(C[n]1c([N+]([O-])=O)ncc1)O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure