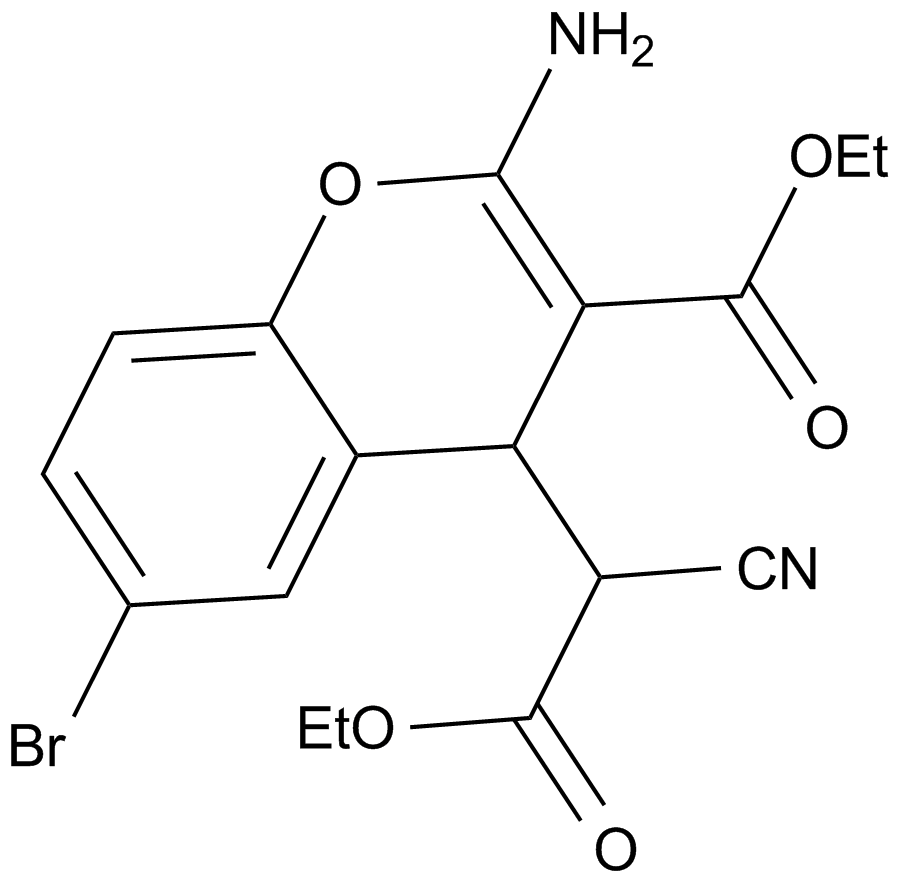
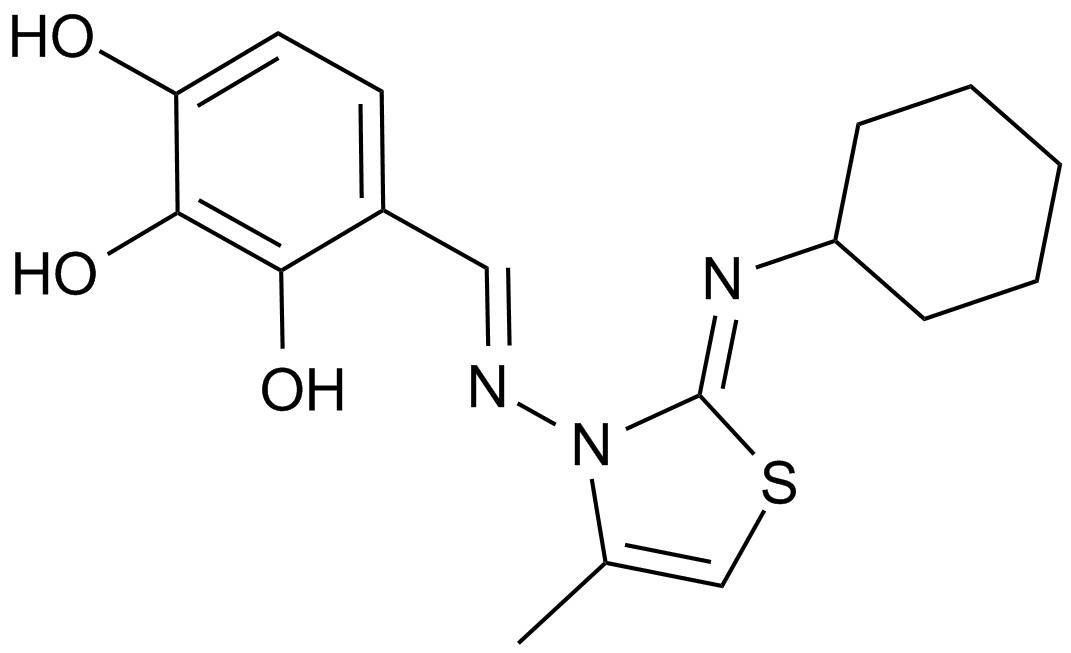
MIM1
MIM1 (CAS 509102-00-5) effectively competed with FITC-MCL-1 SAHBA and FITC-BID BH3 for MCL-1ΔNΔC binding with IC50 values of 4.7 and 4.8 mM, respectively. And MIN1 shows a combination of favorable biophysical and biological properties, including its solubility, stability, nonreactivity, MCL-1 binding potency and selectivity, compatibility with and activity in a BAX-mediated liposomal release assay, and relatively little to no toxicity in Bax-/-Bak-/- MEFs [1].
As an MCL-1 inhibitor, MIM1 selectively targets the BH3-binding groove of MCL-1, neutralizes its biochemical lockhold on apoptosis, and induces caspase activation and leukemia cell death in the specific context of MCL-1 dependence.
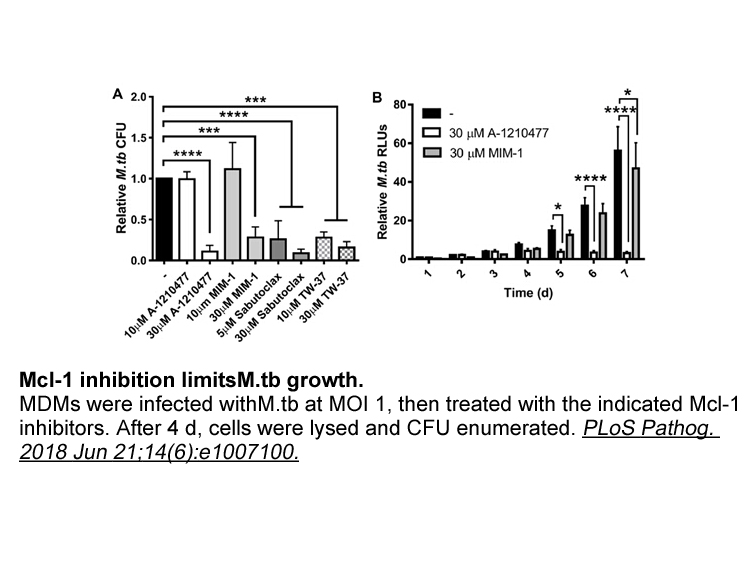
The activity and specificity of MIM1 in cancer cells were dependent on assessing MCL-1 and BCL-XL dependence by employing murine BCRABL (p185)-transformed, Arf null, B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Compared to the effect of ABT-737 on p185+Arf-/-/Mcl-1-deleted B-ALL cells, MIM1 had the exact opposite effect, impacting the viability of the MCL-1-dependent cells (IC50, 4.2 mM), including dose-dependent induction of caspase 3/7 activity, but having no effect on the BCL-XL-dependent cells. A combination of MIM1 (IC50, 10.6 mM) and ABT-737 (IC50, 5.1 mM) resulted in synergistic cytotoxicity. Strikingly, when the MIM1/ABT-737 combination was applied to MCL-1-reconstituted p185+Arf-/-/Mcl-1-deleted B-ALL cells, the addition of ABT-737 had little effect [1].
MIM1 emerged as a potent and selective small molecule inhibitor of MCL-1 DNDC, capable of targeting the canonical BH3-binding point of MCL-1 and blocking MCL-1-mediated suppression of tBID-induced BAX activation in vitro. MIM1 may serve as a prototype for the development of next-generation small molecules that effectively reduce the apoptotic threshold in cancers specifically driven by antiapoptotic MCL-1 [1].
References:
[1].? Cohen NA, Stewart ML, Gavathiotis E, et al. A Competitive Stapled Peptide Screen Identifies a Selective Small Molecule that Overcomes MCL-1-Dependent Leukemia Cell Survival. Chemistry & Biology, 2012, 19(9): 1175-1186.
| Storage | Store at 4°C |
| M.Wt | 347.43 |
| Cas No. | 509102-00-5 |
| Formula | C17H21N3O3S |
| Solubility | insoluble in EtOH; insoluble in H2O; ≥12.15 mg/mL in DMSO |
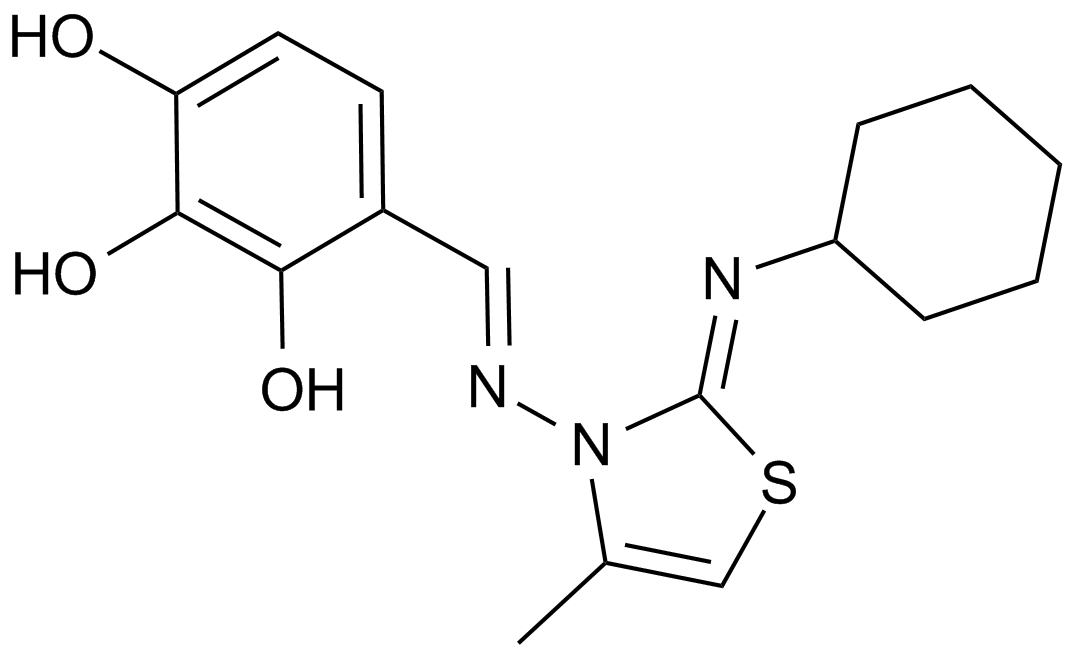
| Chemical Name | 4-((E)-(((Z)-2-(cyclohexylimino)-4-methylthiazol-3(2H)-yl)imino)methyl)benzene-1,2,3-triol |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CC(N1/N=C/c(ccc(O)c2O)c2O)=CS/C\1=N\C1CCCCC1 |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment: [1] | |
|
Cell lines |
p185+Arf−/−Mcl-1-deleted B-ALL cells |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 °C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20°C for several months. |
|
Reaction Conditions |
IC50: 4.2 μM, 24 hours for impairing the cell viability rescued by MCL-1 |
|
Applications |
MIM1 negatively impacted the viability of the MCL-1-dependent cells (p185+Arf−/−Mcl-1-deleted B-ALL cells) with IC50 value of 4.2 μM, including dose-dependent induction of caspase 3/7 activity, but having little to no effect on the BCL-XL-dependent cells. MIM1’s cytotoxic effect on the MCL-1-dependent cells likewise corresponded to dose-dependent dissociation of the inhibitory MCL-1/BAK complex, as assessed by co-immunoprecipitation analysis. |
| Animal experiment: | |
|
Animal models |
|
|
Dosage form |
|
|
Applications |
|
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1] Cohen N A, Stewart M L, Gavathiotis E, et al. A competitive stapled peptide screen identifies a selective small molecule that overcomes MCL-1-dependent leukemia cell survival. Chemistry & biology, 2012, 19(9): 1175-1186. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data