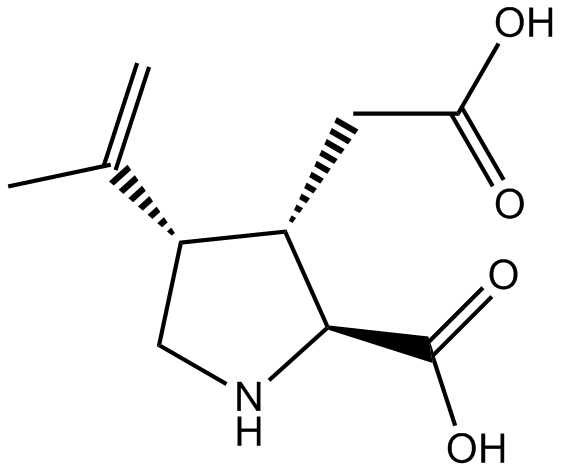
Kainic acid
Kainic Acid (CAS 487-79-6) is a water-soluble heterocyclic dicarboxylic acid compound, functioning as a potent agonist of ionotropic glutamate receptors, specifically targeting kainate receptors in the central nervous system. It exhibits excitatory agonist activity toward these receptors, and also displays partial agonist effects on AMPA receptors. Additionally, it induces excitotoxicity by promoting persistent neuronal depolarization and calcium influx.
In experimental neuroscience research, Kainic Acid induces status epilepticus and seizure-like neuronal activity at nanomolar to micromolar concentrations, tested in various in vivo rodent animal models and in vitro neuronal cultures. It can also trigger hippocampal neurodegeneration, synaptic reorganization, and activation of glial cells, making it a widely used pharmacological tool for investigating mechanisms of neurotoxicity and epileptogenesis.
In the context of central nervous system disorder studies, Kainic Acid is widely used for modeling epilepsy, screening anticonvulsant drugs, and exploring excitotoxic pathways underlying neurodegenerative diseases. Its administration replicates seizure phenotypes and neuropathological changes observed in human temporal lobe epilepsy, facilitating the development and evaluation of neuroprotective strategies and antiepileptic therapeutics.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at RT |
| M.Wt | 213.23 |
| Cas No. | 487-79-6 |
| Formula | C10H15NO4 |
| Synonyms | 2S-carboxy-4S-(1-methylethenyl)-3S-pyrrolidineacetic acid |
| Solubility | ≥11.05 mg/mL in H2O with gentle warming |
| Chemical Name | (2S,3S,4S)-3-(carboxymethyl)-4-(prop-1-en-2-yl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CC([C@@H]1[C@H](CC(O)=O)[C@@H](C(O)=O)NC1)=C |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity = 98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
- Datasheet
Chemical structure