Indomethacin
Indomethacin (CAS 53-86-1) is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory compound that inhibits cyclooxygenase enzymes Cox-1 and Cox-2, displaying preferential inhibition toward Cox-1 (IC50: 230 nM) compared to Cox-2 (IC50: 630 nM). Additionally, it acts as an agonist of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ), a transcriptional regulator implicated in adipogenesis. Indomethacin can also activate PPARα. Furthermore, studies indicate that indomethacin stabilizes cholesterol-rich nanoscale clusters, enhancing membrane phase separation and potentially altering membrane-dependent signaling pathways. This profile makes indomethacin useful for investigating inflammation-associated processes, lipid metabolism, and membrane signaling mechanisms.
- 1. Zhongyu Xie, et al. "TNF‐α‐Induced KAT2A Impedes BMMSC Quiescence by Mediating Succinylation of the Mitophagy‐Related Protein VCP." Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Mar;11(10):e2303388. PMID: 38145956
- 2. Wentao Li, YI HUANG, et al. "Activation of Invariant Natural Killer T Cells Further Ameliorates Post-Infarct Cardiac Remodeling in Mice With MSC Transplantation." Research Square. May 20th, 2021.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 357.79 |
| Cas No. | 53-86-1 |
| Formula | C19H16ClNO4 |
| Solubility | insoluble in H2O; ≥16.97 mg/mL in EtOH with ultrasonic; ≥35.73 mg/mL in DMSO |
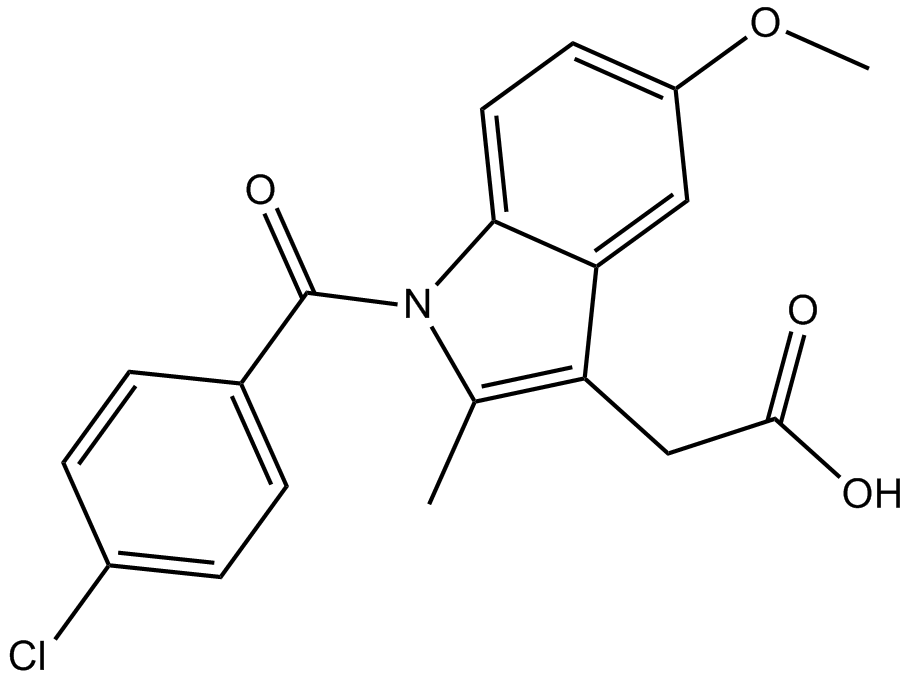
| Chemical Name | 2-[1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-yl]acetic acid |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | Cc1c(CC(O)=O)c(cc(cc2)OC)c2[n]1C(c(cc1)ccc1Cl)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure