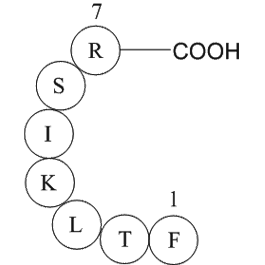
immunoglobulin light chain variable region fragment [Homo sapiens]
Immunoglobulin light chain variable region fragment [Homo sapiens] is a fragment (Phe-Thr-Leu-Lys-Ile-Ser-Arg) on the variable region of the human immunoglobulin light chain.
Immunoglobulins (Ig) are the antigen recognition molecules of B cells. An Ig molecule is made up of 2 identical heavy chains and 2 identical light chains joined by disulfide bonds so that each heavy chain is linked to a light chain and the 2 heavy chains are linked together. On each of the light chain, there is one variable region and a constant region. The variable region is the most important for binding to antigens.
The antigen combining site of an antibody is made up of the variable regions of one light chain and one heavy chain. Within the variable regions, typically comprising 105-110 amino acids, some positions show more sequence variation than others. The variable fragments are the smallest fragment made from enzymatic cleavage of IgG and IgM class antibodies.
Figure1 Diagram of the immunoglobulin structure
Figure 2: Immunoglobulin light chain variable region fragment [Homo sapiens]
Ref:
1. Janeway CA, Jr et al. (2001). Immunobiology. (5th ed.). Garland Publishing. ISBN 0-8153-3642-X
2. Woof J, Burton D (2004). “Human antibody-Fc receptor interactions illuminated by crystal structures”. Nat Rev Immunol 4 (2): 89–99. doi :10.1038/nri1266. PMID 15040582.
3. Mattu T, Pleass R, Willis A, Kilian M, Wormald M, Lellouch A, Rudd P, Woof J, Dwek R (1998). “The glycosylation and structure of human serum IgA1, Fab, and Fc regions and the role of N-glycosylation on Fc alpha receptor interactions”. J Biol Chem 273 (4): 2260–72. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.4.2260. PMID 9442070.
4. Roux K (1999). “Immunoglobulin structure and function as revealed by electron microscopy”. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 120 (2): 85–99. doi :10.1159/000024226. PMID 10545762.
5. Barclay A (2003). “Membrane proteins with immunoglobulin-like domains–a master superfamily of interaction molecules”. Semin Immunol 15 (4): 215–23. doi :10.1016/S1044-5323(03)00047-2. PMID 14690046 .
6. Putnam FW, Liu YS, Low TL (1979). “Primary structure of a human IgA1 immunoglobulin. IV. Streptococcal IgA1 protease, digestion, Fab and Fc fragments, and the complete amino acid sequence of the alpha 1 heavy chain”. J Biol Chem 254 (8): 2865–74. PMID 107164.
7. Huber R (1980). “Spatial structure of immunoglobulin molecules”. Klin Wochenschr 58 (22): 1217–31. doi :10.1007/ BF01478928 6780722.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 864.04 |
| Formula | C40H69N11O10 |
| Synonyms | H2N-Phe-Thr-Leu-Lys-Ile-Ser-Arg-OH |
| Solubility | ≥86.4 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in EtOH; ≥14.43 mg/mL in H2O |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | NC(C(NC(C(C)O)C(NC(CC(C)C)C(NC(CCCCN)C(NC(C(C)CC)C(NC(CO)C(NC(CCCNC(N)=N)C(O)=O)=O)=O)=O)=O)=O)=O)CC1=CC=CC=C1 |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
![immunoglobulin light chain variable region fragment [Homo sapiens]](/media/diy/images/struct/A1071.png)