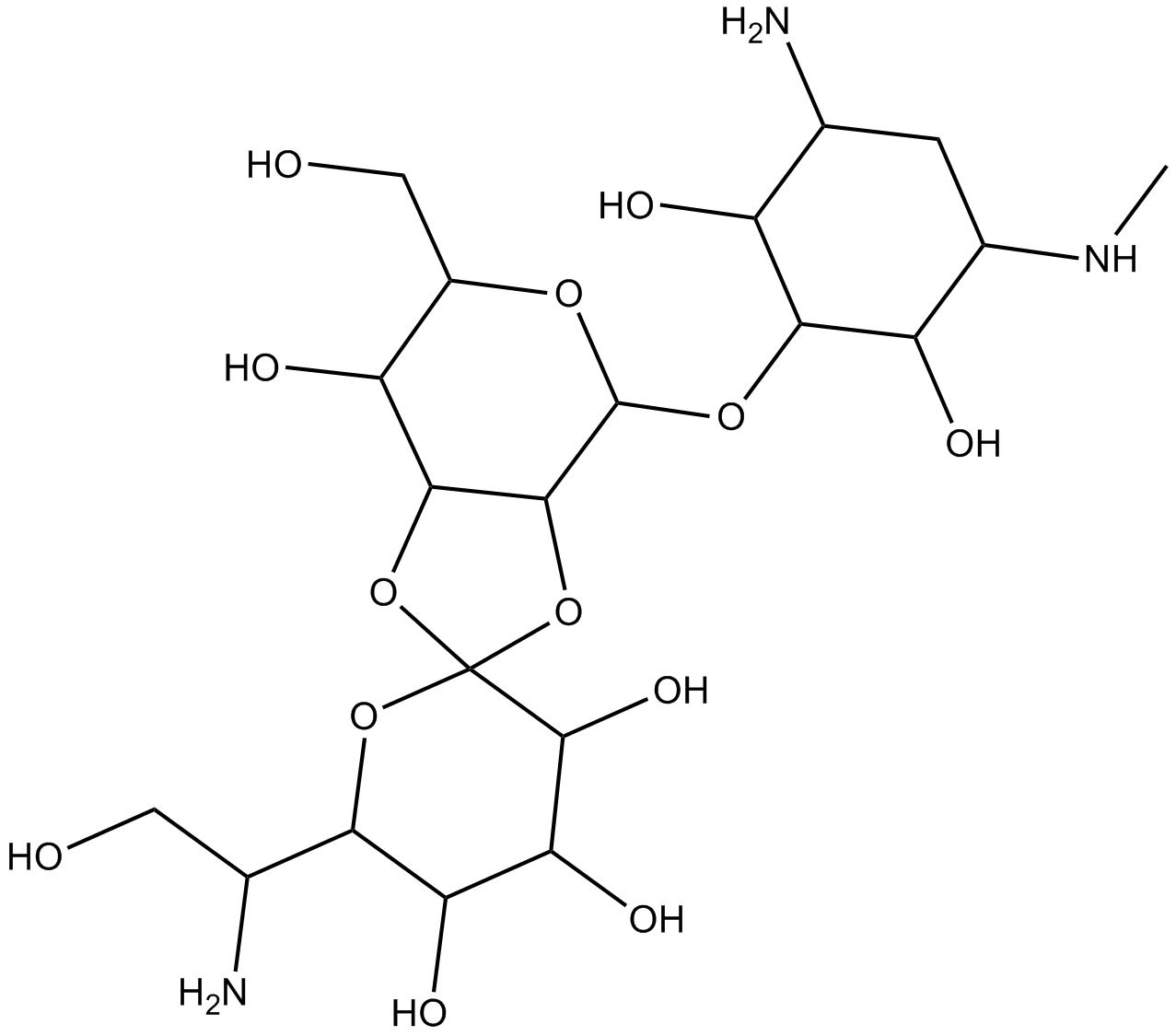
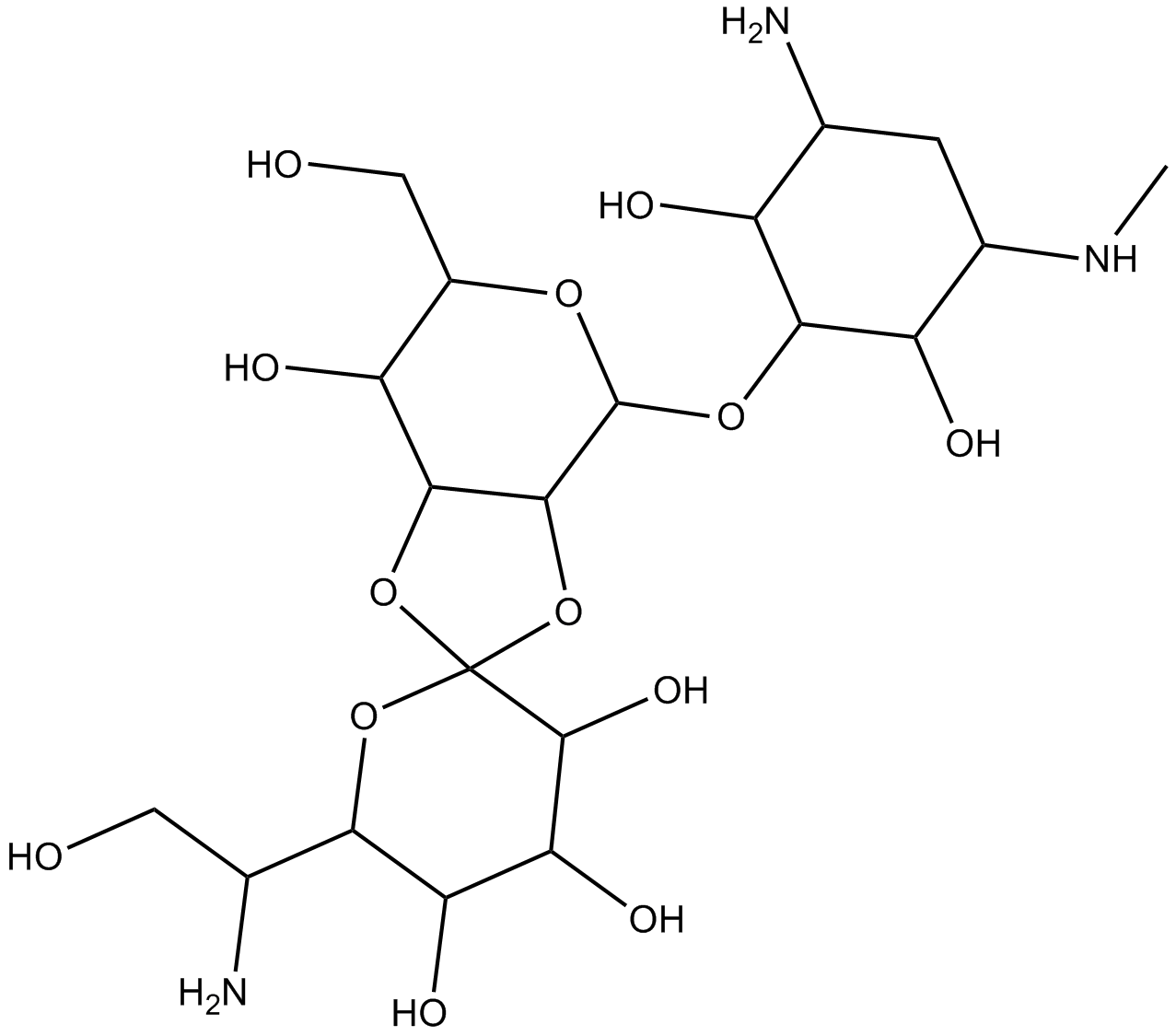
Hygromycin B
Hygromycin B is an aminoglycoside antibiotic commonly applied in molecular biology research as a selectable marker for transgenic cell lines. It inhibits protein synthesis by targeting the ribosomal 30S or 40S subunit, impairing ribosomal translocation during translation and inducing misreading of mRNA. In laboratory investigations, Hygromycin B is routinely employed to select genetically modified bacteria, fungi, and mammalian cells carrying Hygromycin-resistance genes. The IC50 values generally vary by organism and cell type, typically ranging from 50 µg/mL to 500 µg/mL.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 527.5 |
| Cas No. | 31282-04-9 |
| Formula | C20H37N3O13 |
| Solubility | ≥26.38 mg/mL in H2O; ≥5.35 mg/mL in EtOH; ≥9.14 mg/mL in DMSO |
| Chemical Name | (3'R,3aS,4S,4'R,5'R,6R,6'R,7S,7aS)-4-[(1R,2S,3R,5S,6R)-3-amino-2,6-dihydroxy-5-(methylamino)cyclohexyl]oxy-6'-[(1S)-1-amino-2-hydroxyethyl]-6-(hydroxymethyl)spiro[4,6,7,7a-tetrahydro-3aH-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-c]pyran-2,2'-oxane]-3',4',5',7-tetrol |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CNC1CC(C(C(C1O)OC2C3C(C(C(O2)CO)O)OC4(O3)C(C(C(C(O4)C(CO)N)O)O)O)O)N |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment:[1] | |
|
Cell lines |
Mouse L cells |
|
Reaction Conditions |
200 μg/ml hygromycin B for 2 ~ 6 weeks |
|
Applications |
Hygromycin B was used for resistance selection in mouse L cells transfected withEscherichia coli genes coding for resistance to the aminocyclitol antibiotics hygromycin B. |
| Animal experiment:[2] | |
|
Animal models |
Four-week-old BALB/c mice susceptible to MHV-A59 infection |
|
Dosage form |
0 ~ 10 μmol/kg Intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection |
|
Applications |
A single injection of hygromycin B reduced the number of lesions in the livers of MHV-A59-inoculated mice. Higher doses of the drug appeared to be slightly more effective at reducing virus-induced lesions. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Santerre RF, Allen NE, Hobbs JN Jr, et al. Expression of prokaryotic genes for hygromycin B and G418 resistance as dominant-selection markers in mouse L cells. Gene, 1984, 30(1-3): 147-156. 2. Macintyre G, Curry B, Wong F, et al. Hygromycin B therapy of a murine coronaviral hepatitis. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 1991, 35(10): 2125-2127. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure