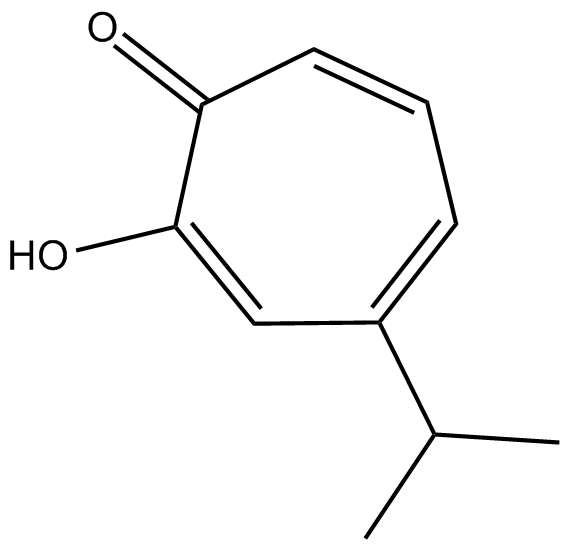
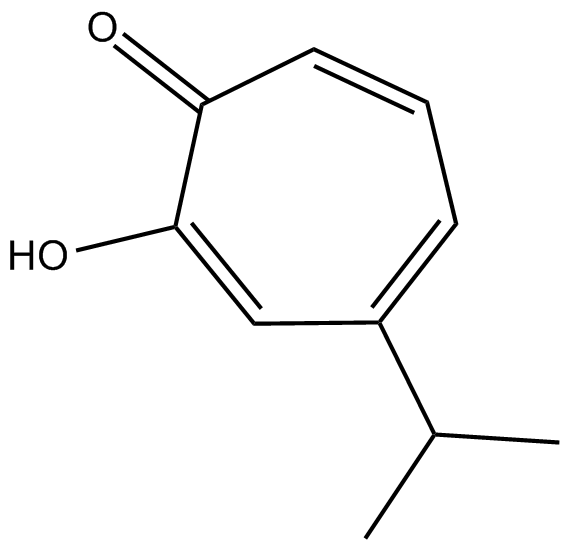
Hinokitiol
Hinokitiol (CAS: 499-44-5) is a small-molecule inhibitor targeting DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1), UHRF1, and the Nrf2 pathway. It is designed to modulate redox regulatory and epigenetic modification processes, thereby regulating cellular antioxidant defense and DNA methylation status.
Hinokitiol exerts its biological activity primarily through induction of apoptosis and iron chelation, as well as suppression of Nrf2 and downregulation of DNMT1 and UHRF1. In in vitro studies, hinokitiol demonstrates apoptosis induction with IC50 values in the micromolar range, varying according to cell line and assay conditions.
Hinokitiol holds research potential in oncology, particularly in studies of tumor cell apoptosis, epigenetic regulation, and cancer stem cell biology.
References:
1. Ouyang WC, Liao YW, Chen PN, et al. Hinokitiol suppresses cancer stemness and oncogenicity in glioma stem cells by Nrf2 regulation. Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology, 2017, 80(2): 411-419.
2. Seo JS, Choi YH, Moon JW, et al. Hinokitiol induces DNA demethylation via DNMT1 and UHRF1 inhibition in colon cancer cells. BMC Cell Biology, 2017, 18(1): 14.
3. Ido Y, Muto N, Inada A, et al. Induction of apoptosis by hinokitiol, a potent iron chelator, in teratocarcinoma F9 cells is mediated through the activation of caspase-3. Cell Proliferation, 1999, 32(1): 63-73.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 164.20 |
| Cas No. | 499-44-5 |
| Formula | C10H12O2 |
| Solubility | insoluble in H2O; ≥118.6 mg/mL in EtOH; ≥16.4 mg/mL in DMSO |
| Chemical Name | 2-hydroxy-4-isopropylcyclohepta-2,4,6-trienone |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CC(C)C(C=C1O)=CC=CC1=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment:[1] | |
|
Cell lines |
Glioma stem cells derived from U87MG and T98G glioma cell lines |
|
Reaction Conditions |
24 h incubation |
|
Applications |
Hinokitiol dose-dependently decreased cell viability, with IC50 values being 316.5 ± 35.5 and 152.5 ± 25.3 µM for U87MG and T98G glioma cell lines, respectively. Furthermore, hinokitiol effectively inhibited the CD133 positivity and aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 (ALDH1) activity, and repressed the self-renewal, migration, invasion, and colony formation abilities of glioma stem cells. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Ouyang WC, Liao YW, Chen PN, et al. Hinokitiol suppresses cancer stemness and oncogenicity in glioma stem cells by Nrf2 regulation. Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology, 2017, 80(2): 411-419. 2. Seo JS, Choi YH, Moon JW, et al. Hinokitiol induces DNA demethylation via DNMT1 and UHRF1 inhibition in colon cancer cells. BMC Cell Biology, 2017, 18(1): 14. 3. Ido Y, Muto N, Inada A, et al. Induction of apoptosis by hinokitiol, a potent iron chelator, in teratocarcinoma F9 cells is mediated through the activation of caspase-3. Cell Proliferation, 1999, 32(1): 63-73. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure