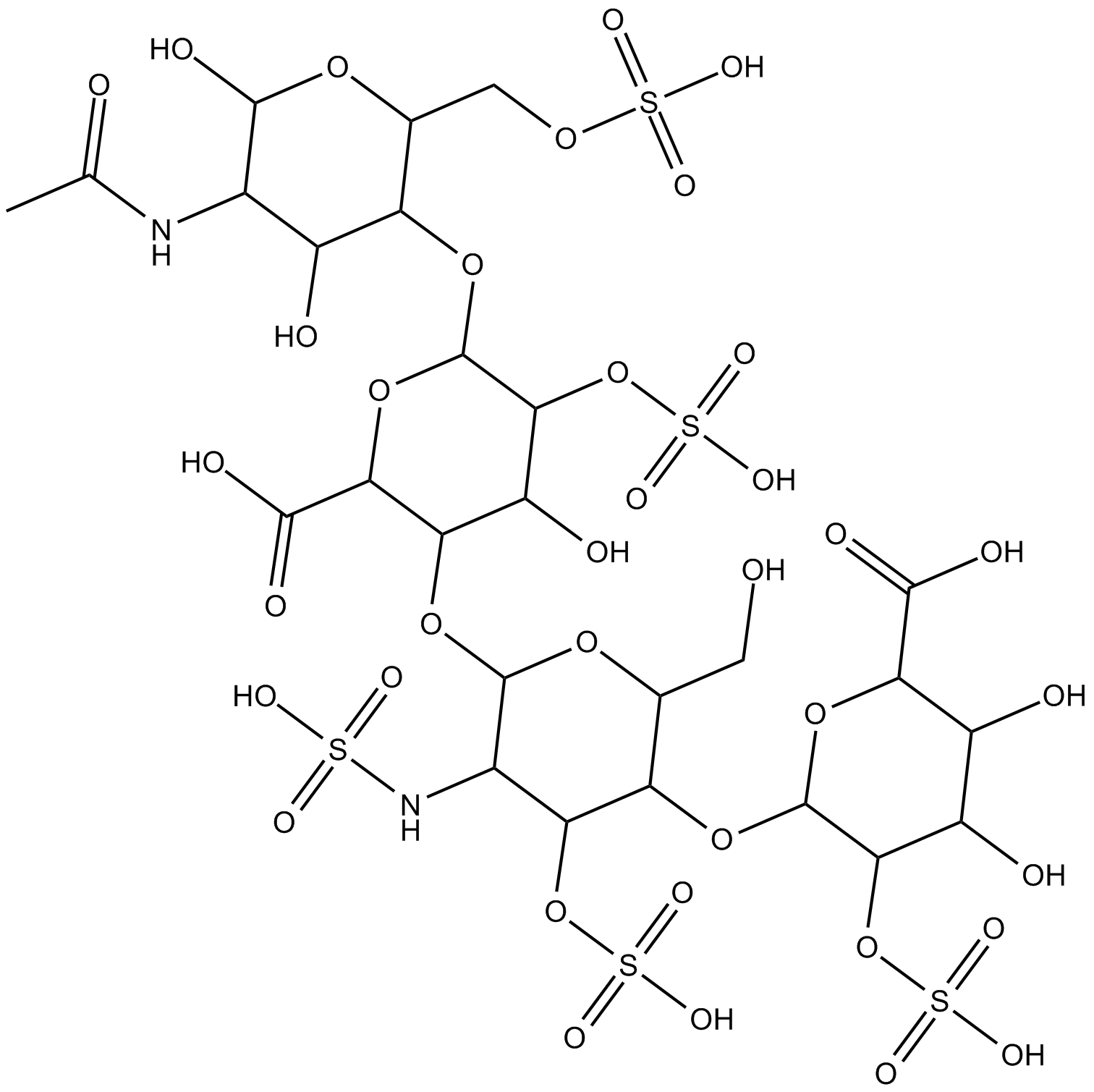
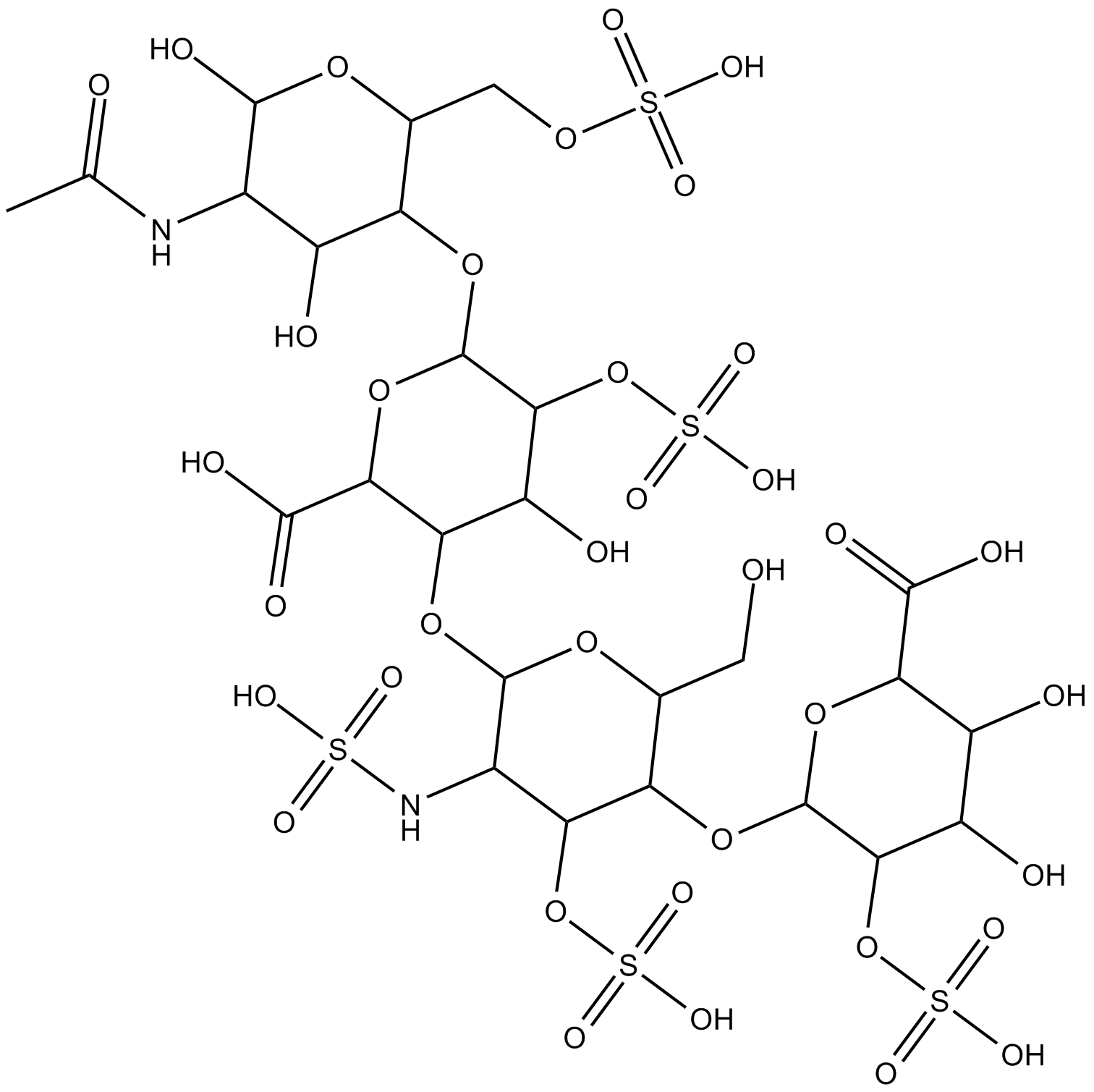
Heparin
Heparin (CAS 9005-49-6) is a highly sulfated glycosaminoglycan known primarily for its anticoagulant properties. In biological systems, it is stored in granules within specific animal tissues and cells, potentially serving defensive roles against pathogens. In vitro studies demonstrate that Heparin dose-dependently suppresses granulocyte aggregation and degranulation triggered by FMLP or serum-activated zymosan, and specifically blocks FMLP-induced superoxide anion production. Additionally, in rat models, Heparin treatment reduces both the binding affinity and density of angiotensin II receptors on adrenal cells, resulting in decreased angiotensin II-stimulated aldosterone secretion. Heparin is extensively applied in biomedical research to investigate granulocyte-mediated inflammation and renin-angiotensin system signaling.
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 1134.93 |
| Cas No. | 9005-49-6 |
| Formula | C26H42N2O37S5 |
| Solubility | ≥12.75mg/ml in H2O |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CC(NC1C(O)C(OC2C(OS(=O)(O)=O)C(O)C(OC3C(NS(=O)(O)=O)C(OS(=O)(O)=O)C(OC4C(OS(=O)(O)=O)C(O)C(O)C(C(O)=O)O4)C(CO)O3)C(C(O)=O)O2)C(COS(=O)(O)=O)OC1O)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity = 98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
Chemical structure