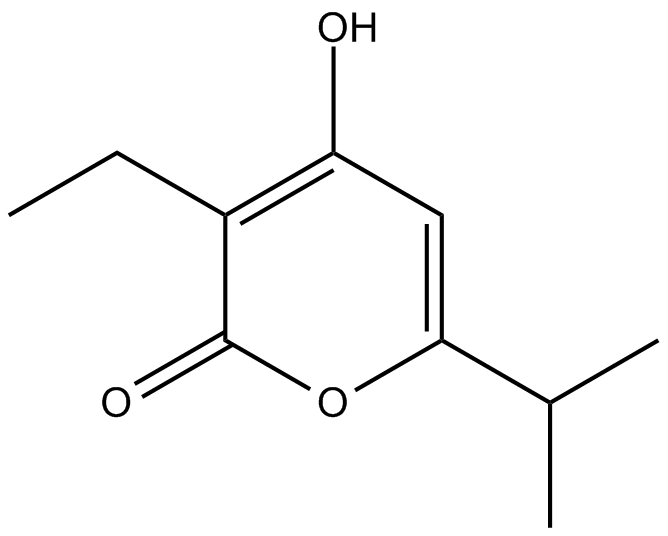
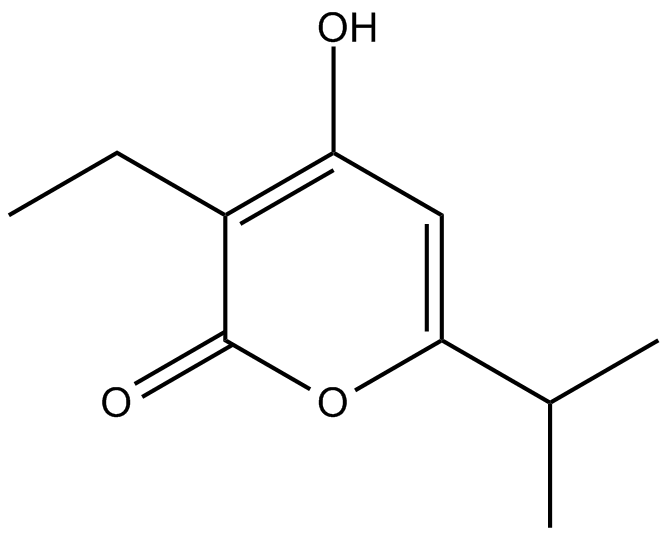
Germicidin B
Germicidin is a pyranone antibiotic originally excreted by Streptomyces viridochromogenes NRRL B-1551. Germicidin has an inhibitory effect on the germination of its own arthrospores at a concentration as low as 200 pM (40 pg/ml). Higher concentrations of germicidin inhibited porcine Na+/K+-activated ATPase and retarded the germination of the cress Lepidium sativum with an ID50 of 100 μM. Germicidin was the first known autoregulative inhibitor of spore germination in the genus Streptomyces and was isolated from the supernatant of germinated spores, but also from the supernatant of the submerged culture [1].
Germicidins B inhibited germination of S. coelicolor A3(2) spores above 1 μg/ml. The S. coelicolor A3(2) spores collected from a single petri dish (9 cm i.d.) contained 5.4 μg of germicidin A (~2.7 × 10-14 g per spore) and contents of germicidins B, C and D were 0.2–0.8 μg. The activity of the spore extract corresponded well with the sum of the activity of each germicidin. Germicidins functioned as self-germination inhibitors in S. coelicolor A3(2) [2].
References:
[1] PETERSEN F, ZHNER H, METZGER J W, et al. Germicidin, an autoregulative germination inhibitor of Streptomyces viridochromogenes NRRL B-1551[J]. The Journal of antibiotics, 1993, 46(7): 1126-1138.
[2] Aoki Y, Matsumoto D, Kawaide H, et al. Physiological role of germicidins in spore germination and hyphal elongation in Streptomyces coelicolor A3 (2)[J]. The Journal of antibiotics, 2011, 64(9): 607-611.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 182.2 |
| Cas No. | 150973-78-7 |
| Formula | C10H14O3 |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| Chemical Name | 3-ethyl-4-hydroxy-6-(1-methylethyl)-2H-pyran-2-one |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CCC(C(OC(C(C)C)=C1)=O)=C1O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure