G-15
G-15 (CAS 1161002-05-6) is a selective antagonist of G protein-coupled receptor 30 (GPR30), with a Ki of approximately 20 nM. GPR30 is an integral membrane receptor residing in the endoplasmic reticulum, mediating intracellular signaling responses triggered by ligands such as estradiol. G-15 specifically inhibits GPR30-mediated pathways without significantly interacting with estrogen receptors ERα or ERβ, even at higher concentrations. In cellular studies, G-15 blocks estrogen- or G-1-induced elevations of intracellular calcium and PI3K activation. In vivo research demonstrates that G-15 disrupts estradiol-associated improvements in spatial learning tasks, emphasizing its utility in investigating GPR30 function and estrogen signaling mechanisms.
- 1. Junita Desouza, Rushda Khan, Siddhanath Metkari. "G - protein coupled estrogen receptor 1 (GPER1): A potential target for chemoprevention of prostate cancer." Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2025 Apr;1871(4):167740. PMID: 39988180
- 2. Baofang Liang, Jinyao Chen, et al. "Mode of action exploration for prostate epithelial cell injury caused by bisphenol A." Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024 Nov 1:286:117228 PMID: 39442252
- 3. Qing Chen, Hui Wu, et al. "GPR30 in spinal cholecystokinin-positive neurons modulates neuropathic pain via mediating descending facilitation." bioRxiv. September 26, 2024
- 4. Meng Zhang, Chenhan Mao, et al. "Qixian granule inhibits ferroptosis in vascular endothelial cells by modulating TRPML1 in the lysosome to prevent postmenopausal atherosclerosis." J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jun 28:328:118076 PMID: 38521431
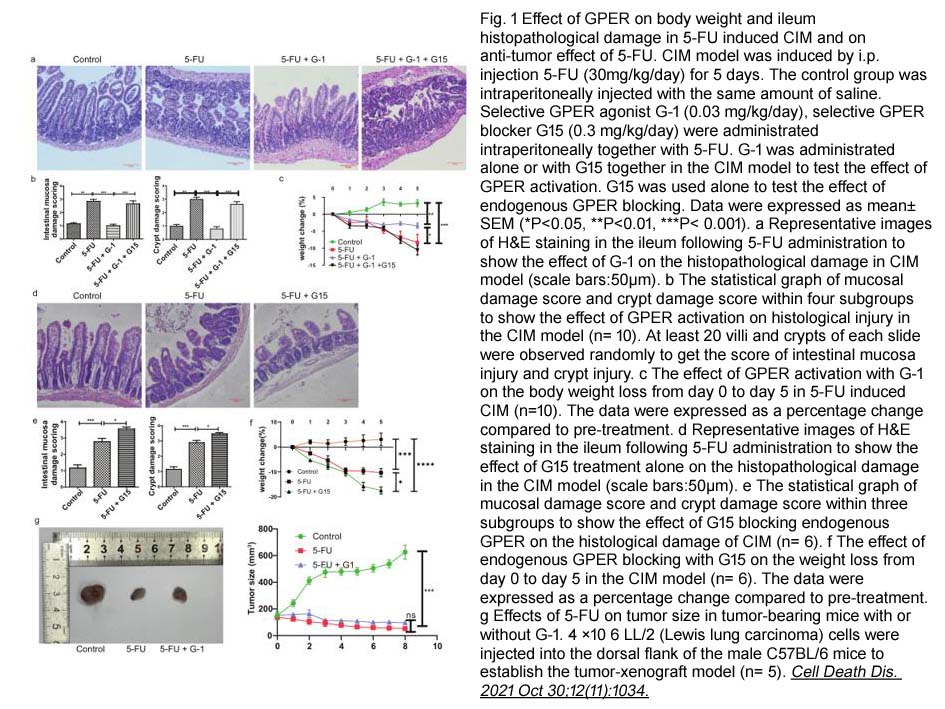
- 5. Guanyu Chen, Honghui Zeng, et al. "Activation of G protein coupled estrogen receptor prevents chemotherapy-induced intestinal mucositis by inhibiting the DNA damage in crypt cell in an extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1- and 2- dependent manner." Cell Death Dis. 2021 Oct 30;12(11):1034 PMID: 34718327
- 6. Linhao Xu, Yizhou Xu, et al. "Tanshinone IIA attenuates renal injury during hypothermic preservation via the MEK/ERK1/2/GSK-3β pathway." BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021 Oct 8;21(1):257 PMID: 34625061
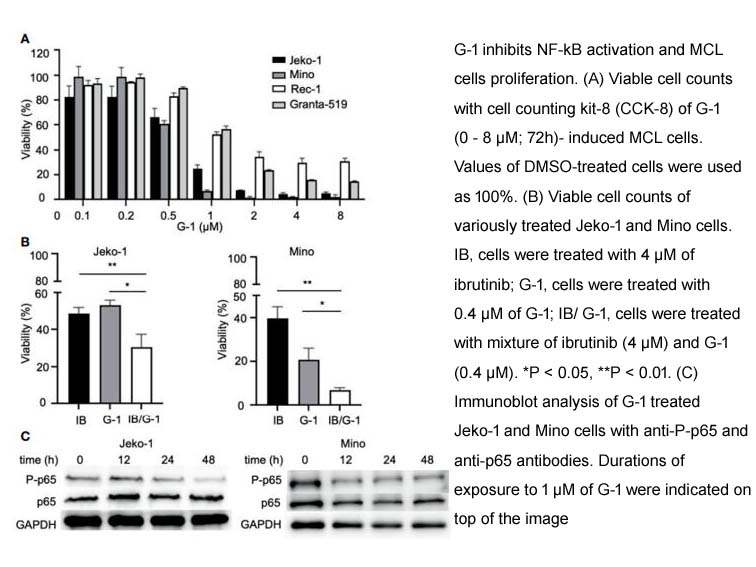
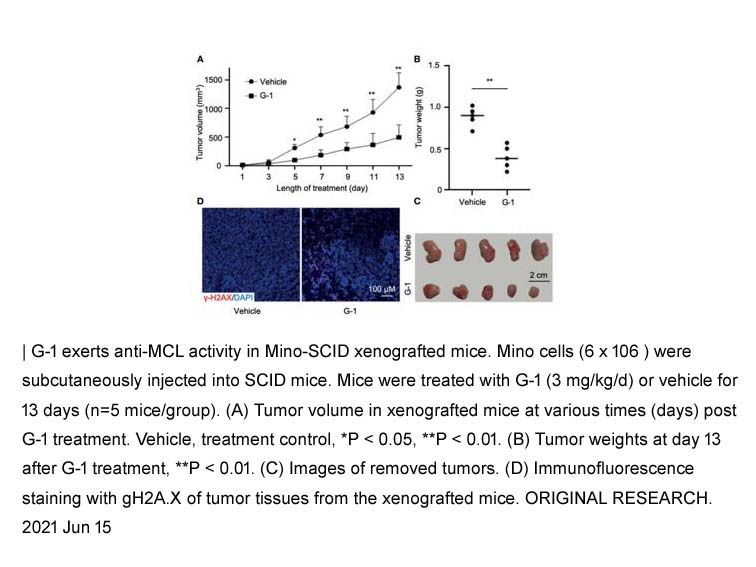
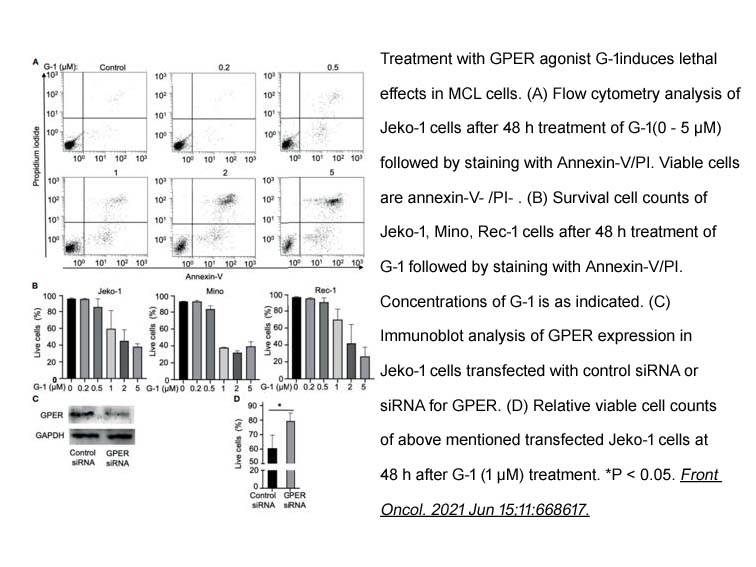
- 7. Lixia Zhou, Tenghua Yu, et al. "G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor Agonist G-1 Inhibits Mantle Cell Lymphoma Growth in Preclinical Models." Front Oncol. 2021 Jun 15;11:668617 PMID: 34211844
- 8. Peng Wang, Li-Na Jiang, et al. "Estradiol-induced inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress normalizes splenic CD4 + T lymphocytes following hemorrhagic shock." Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 5;11(1):7508 PMID: 33820957
- 9. Xiaoyu Hang, Zhenyu Zhang, et al. "Estrogen Protects Articular Cartilage by Downregulating ASIC1a in Rheumatoid Arthritis." J Inflamm Res. 2021 Mar 12;14:843-858 PMID: 33737825
- 10. Feiyan Meng, Lihong Zhang, et al. "Two forms of G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 in the ricefield eel: Expression and functional characterization in relation to ovarian follicle development." Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2021 Apr 1;304:113720 PMID: 33508329
- 11. Liping Gu, Yunyan Ke, et al. "Berberine suppresses bone loss and inflammation in ligature-induced periodontitis through promotion of the G protein-coupled estrogen receptor-mediated inactivation of the p38MAPK/NF-κB pathway." Archives of Oral Biology.Volume 122, February 2021, 104992 PMID: 33338754
- 12. Zhao B, Xiong Y, et al. "Rutin promotes osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells through the GPR30-mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway." Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020;1535370220903463 PMID: 32036685
- 13. Yang S, Cheng W, et al. "Use of embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes to study cardiotoxicity of bisphenol AF via the GPER/CAM/eNOS pathway." Toxicology. 2020;432:152380 PMID: 31981723
- 14. Qing-changWua, Xi-yangTanga, et al. "Sweroside promotes osteoblastic differentiation and mineralization via interaction of membrane estrogen receptor-α and GPR30 mediated p38 signalling pathway on MC3T3-E1 cells." Phytomedicine. Available online 7 December 2019, 153146
- 15. Zhong J, Ge HF, et al. "G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor 1 Negatively Regulates the Proliferation of Mouse-Derived Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells via Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase Pathway." Brain Res. 2019 Feb 21. pii: S0006-8993(19)30108-8 PMID: 30797747
- 16. Chang Y, Han Z, et al. "G protein-coupled estrogen receptor activation improves contractile and diastolic functions in rat renal interlobular artery to protect against renal ischemia reperfusion injury." Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Apr;112:108666 PMID: 30784936
- 17. Wu Y, Feng D, et al. "Downregulation of G protein coupled receptor 30 in the hippocampus attenuates the neuroprotection of estrogen in the critical period hypothesis." Mol Med Rep. 2018 Apr;17(4):5716-5725 PMID: 29484405
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 370.24 |
| Cas No. | 1161002-05-6 |
| Formula | C19H16BrNO2 |
| Solubility | insoluble in H2O; insoluble in EtOH; ≥37 mg/mL in DMSO |
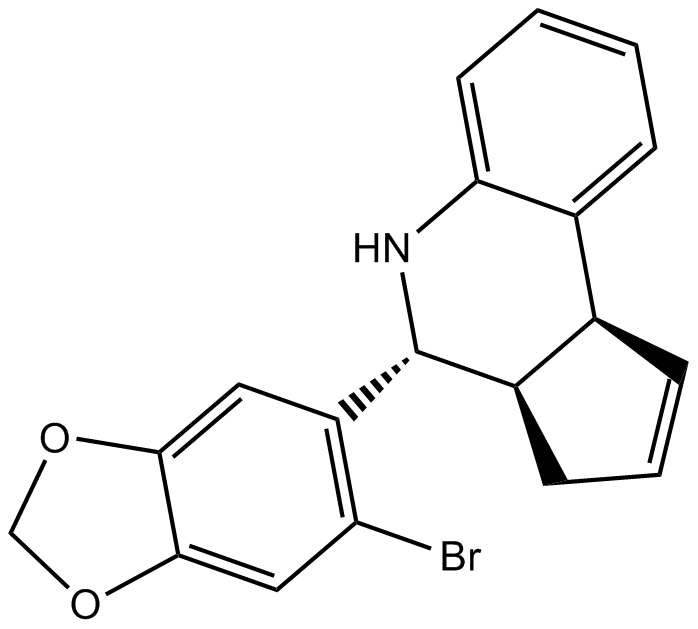
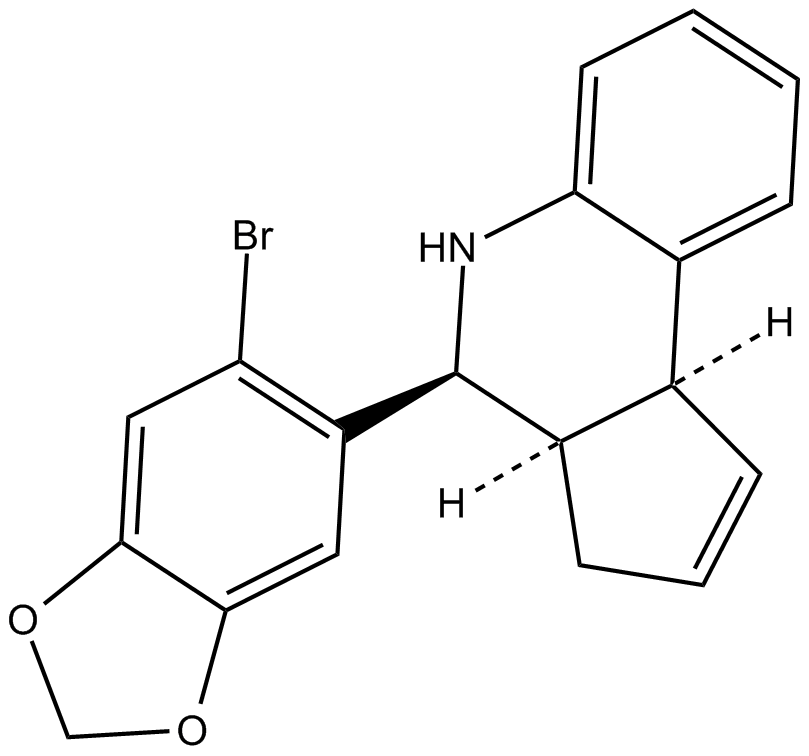
| Chemical Name | (3aR,4S,9bS)-4-(6-bromobenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-3a,4,5,9b-tetrahydro-3H-cyclopenta[c]quinoline |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | Brc1c([C@H]([C@H]2[C@@H]3C=CC2)Nc2c3cccc2)cc2OCOc2c1 |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment [1,2]: | |
|
Cell lines |
Immortalized epithelial endometriotic cell line (11z) |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37°C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20°C for several months. |
|
Reacting condition |
10, 30, or 60 μM for 24, 48, or 72 hours |
|
Applications |
G-1 (30 μM) led to Akt phosphorylation at serine 473 within 2 hours. Pretreatment with G-15 (60 μM) prevented this phosphorylation by G-1. Treatment with 10 μM G-1 for 72 hours significantly stimulated the cells with an increase of the relative proliferation. A subsequent 72-hour treatment with 30 μM G-15 significantly reversed this stimulation. Treatment with G-15 alone led to a decrease of the relative proliferation. G-15 dose-dependently inhibited G-1-mediated calcium mobilization in SKBr3 cells with IC50 of ~185 nM. G15 inhibited the G-1-mediated activation of PI (3) K in GPR30-transfected COS7 cells. |
| Animal experiment [3]: | |
|
Animal models |
Ovariectomized female rats |
|
Dosage form |
Subcutaneous injection, 5 μg/day, 10 μg/day |
|
Application |
G-15 dose-dependently impaired DMP acquisition. G-15 specifically reduced the rate of acquisition. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1] Imesch P, Samartzis E P, Dedes K J, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors down-regulate G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor and the GPER-antagonist G-15 inhibits proliferation in endometriotic cells [J]. Fertility and sterility, 2013, 100 (3): 770-776. [2] Dennis M K, Burai R, Ramesh C, et al. In vivo effects of a GPR30 antagonist [J]. Nature chemical biology, 2009, 5 (6): 421-427. [3] Hammond R, Nelson D, Kline E, et al. Chronic treatment with a GPR30 antagonist impairs acquisition of a spatial learning task in young female rats [J]. Hormones and behavior, 2012, 62 (4): 367-374. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data