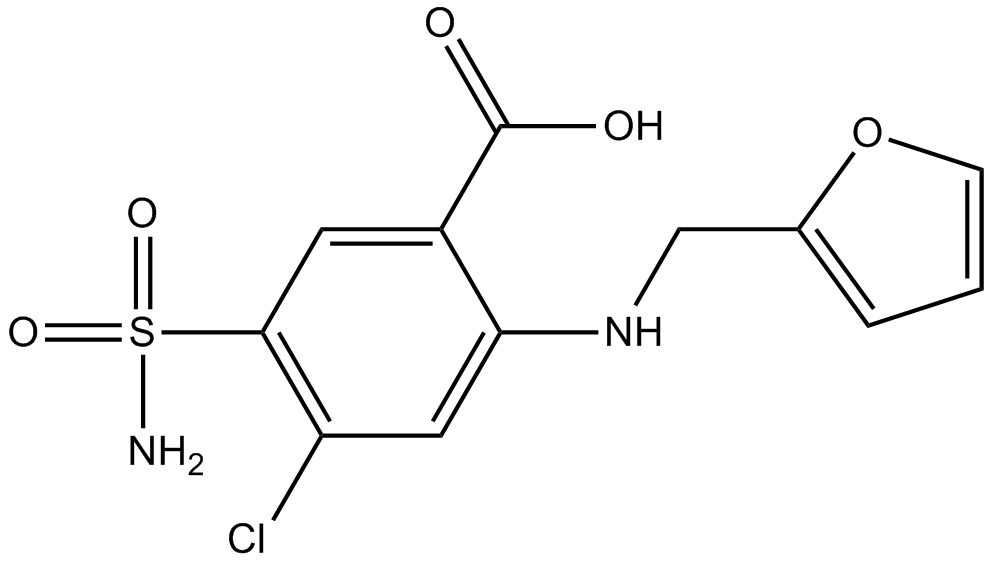
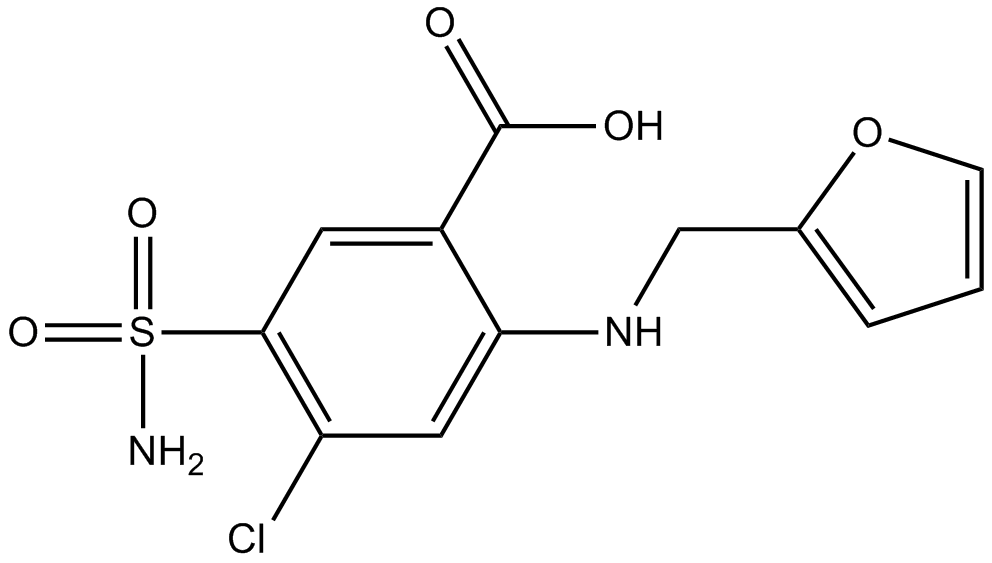
Furosemide
Furosemide is an inhibitor of Na+/2Cl-/K+ cotransporter [1].
The Na-K-Cl cotransporter (NKCC) is a protein that acts as an active transporter helping sodium, potassium, and chloride into and out of cells. NKCC1 has important functions in organs that secrete fluids. NKCC2 exists in the kidney and serves to extract sodium, potassium, and chloride from the urine [2].
Furosemide is an antagonist of Na+/2Cl-/K+ cotransporter. In adult brain tissue, furosemide blocked the epileptiform activity through inhibiting cell swelling, which was concomitant with its inhibition of activity-driven changes of the extracellular space (ECS) [1]. Furosemide inhibited the production and release of cytokines IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-ɑ from peripheral mononuclear cells and exhibited an anti-inflammatory effect [3].
In patients with liver cirrhosis, furosemide inhibited the natriuretic effect and increased the levels of atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) and circulating endothelin. In neonates, furosemide significantly increased the urinary excretion of aldosterone and endothelin-1 [3].
References:
[1]. Hochman DW. The extracellular space and epileptic activity in the adult brain: explaining the antiepileptic effects of furosemide and bumetanide. Epilepsia, 2012, 53 Suppl 1: 18-25.
[2]. Chen H, Sun D. The role of Na-K-Cl co-transporter in cerebral ischemia. Neurol Res, 2005, 27(3): 280-286.
[3]. Prandota J. Furosemide: progress in understanding its diuretic, anti-inflammatory, and bronchodilating mechanism of action, and use in the treatment of respiratory tract diseases. Am J Ther, 2002, 9(4): 317-328.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 330.74 |
| Cas No. | 54-31-9 |
| Formula | C12H11ClN2O5S |
| Solubility | insoluble in H2O; ≥13.35 mg/mL in EtOH; ≥14.9 mg/mL in DMSO |
| Chemical Name | 4-chloro-2-(furan-2-ylmethylamino)-5-sulfamoylbenzoic acid |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | NS(c(cc(C(O)=O)c(NCc1ccc[o]1)c1)c1Cl)(=O)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure