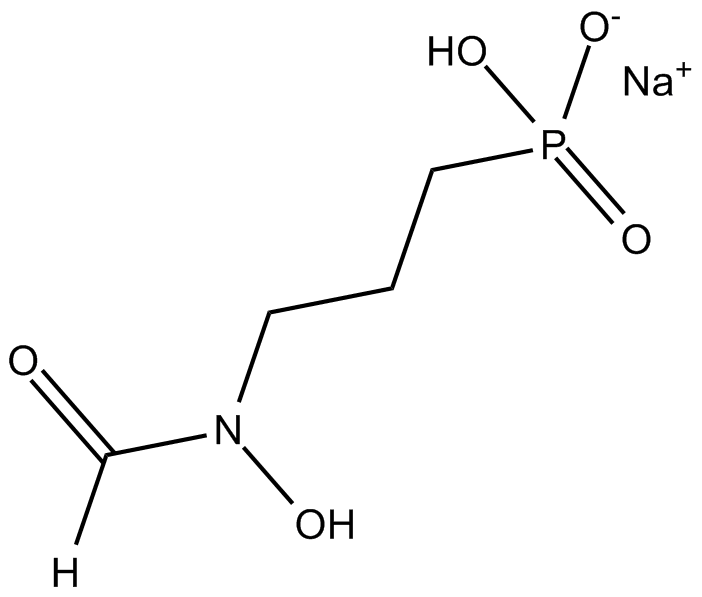
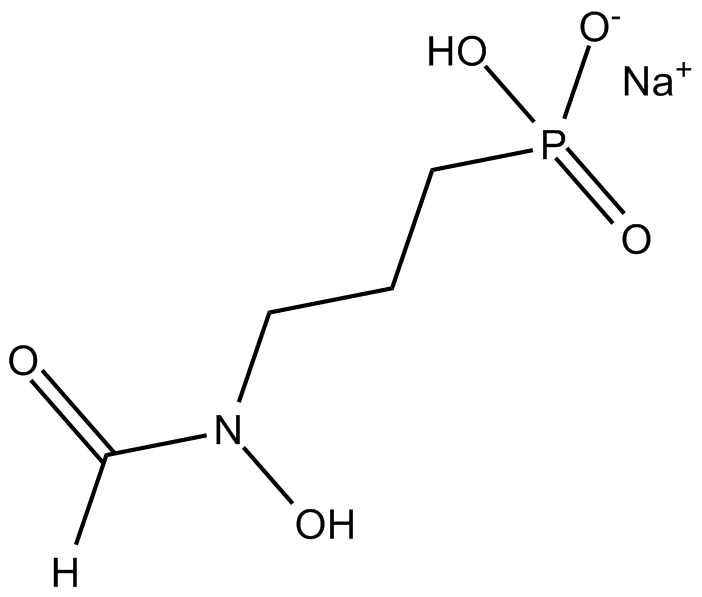
Fosmidomycin (sodium salt)
Fosmidomycin is a specific inhibitor of 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase (DXP) [1]. Fosmidomycin is an antibiotic originally isolated from bacteria of the genus Streptomyces.
1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase is an enzyme that interconverts DXP and 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate (MEP) [2].
Fosmidomycin was active against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria and the human malarial parasite P. falciparum with the IC50 of 290-370 nM[3]. Fosmidomycin inhibited 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase in an alternative nonmevalonate pathway for terpenoid biosynthesis with IC50 of 8.2 nM [1]. Fosmidomycin has been shown to possess activity against Plasmodium falciparum in vitro and in the mouse model. In patients with acute uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria, oral administration of 1,200 mg fosmidomycin every 8 h for 7 days was effective in curing uncomplicated Plasmodiumfalciparum malaria in humans [4]. Fosmidomycin was an effective and safe antimalarial drug [4]. The treatment was well tolerated and showed a fast parasite and fever clearance [4].
References:
[1] Kuzuyama T, Shimizu T, Takahashi S, et al. Fosmidomycin, a specific inhibitor of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase in the nonmevalonate pathway for terpenoid biosynthesis[J]. Tetrahedron letters, 1998, 39(43): 7913-7916.
[2] Takahashi S, Kuzuyama T, Watanabe H, et al. A 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase catalyzing the formation of 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate in an alternative nonmevalonate pathway for terpenoid biosynthesis[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 1998, 95(17): 9879-9884.
[3] Jomaa H, Wiesner J, Sanderbrand S, et al. Inhibitors of the nonmevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis as antimalarial drugs[J]. Science, 1999, 285(5433): 1573-1576.
[4] Lell B, Ruangweerayut R, Wiesner J, et al. Fosmidomycin, a novel chemotherapeutic agent for malaria[J]. Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy, 2003, 47(2): 735-738.
| Physical Appearance | A crystalline solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 205.1 |
| Cas No. | 66508-37-0 |
| Formula | C4H9NO5P·Na |
| Synonyms | Antibiotic FR31564,FR31564 |
| Solubility | ≤5mg/ml in PBS, pH 7.2 |
| Chemical Name | P-[3-(formylhydroxyamino)propyl]-phosphonic acid, monosodium salt |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | [O-]P(CCCN(C=O)O)(O)=O.[Na+] |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
|
Cell lines |
P. falciparum strains |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in PBS is ≤ 5mg/ml, pH 7.2. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 ℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
|
Reacting condition |
45nM~370nM |
|
Applications |
Fosmidomycin is active against three different Plasmodium falciparum strains (HB3, A2, and Dd2) with IC50 values of 45nM to 370nM. |
| Animal experiment [1]: | |
|
Animal models |
Mice infected with the rodent malaria parasite P. vinckei |
|
Dosage form |
10 mg/kg (i.p.) |
|
Application |
With intraperitoneal injection of fosmidomycin greater than 10 mg / kg, the animals were apparently free of parasites. Treated with 5 mg / kg fosmidomycin, parasitemia was <1%. Animals treated with 50 or 100 mg / kg fosmidomycin for oral administration apparently is free of parasites, and parasiteemia was <1% after treatment with the 20 mg / kg drug. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1]. Jomaa H, Wiesner J, Sanderbrand S, Altincicek B, Weidemeyer C, Hintz M, Türbachova I, Eberl M, Zeidler J, Lichtenthaler HK, Soldati D, Beck E. Inhibitors of the nonmevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis as antimalarial drugs. Science. 1999 Sep 3;285(5433):1573-6. PubMed PMID: 10477522. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity ≥ 95.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
Chemical structure