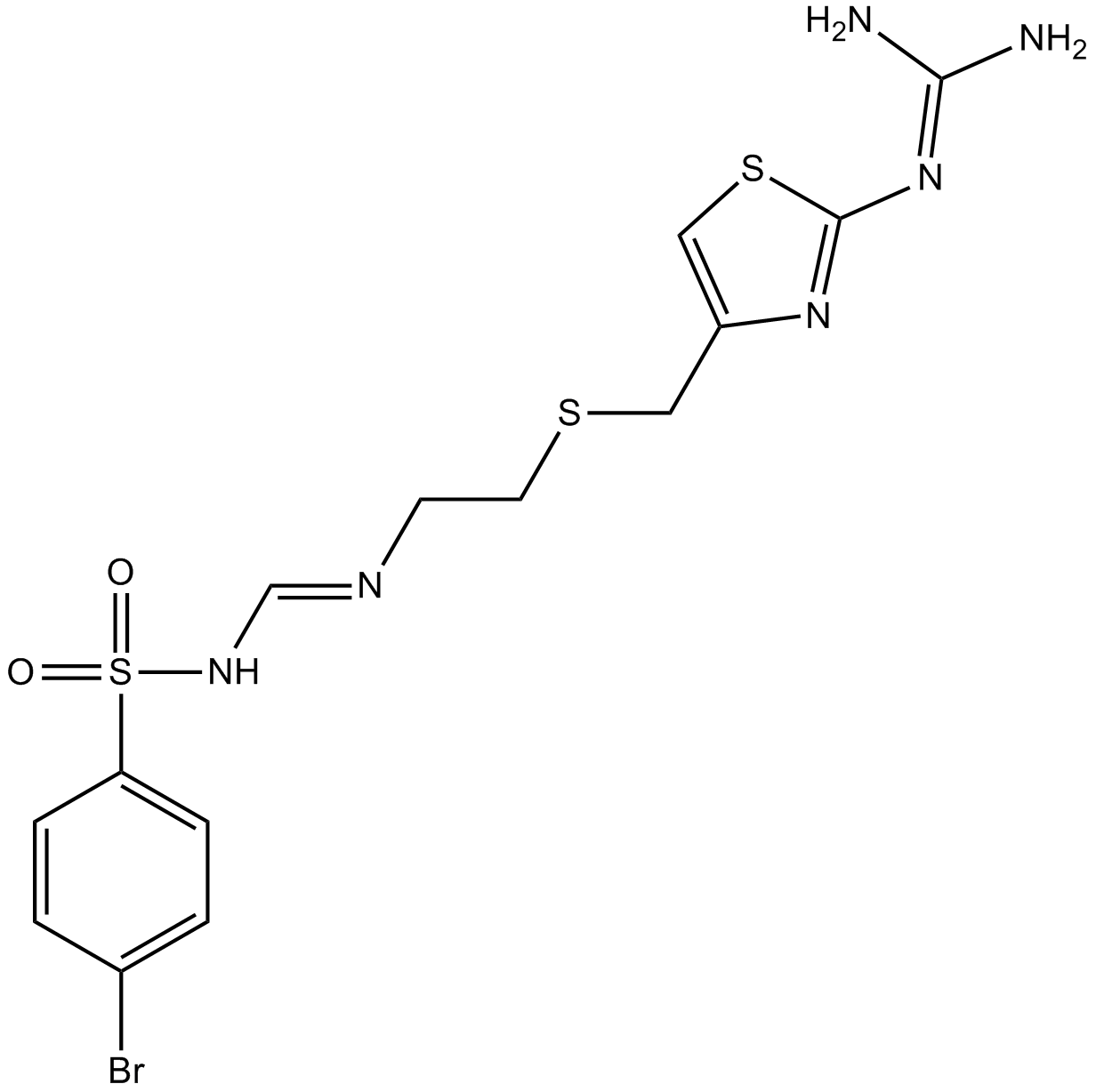
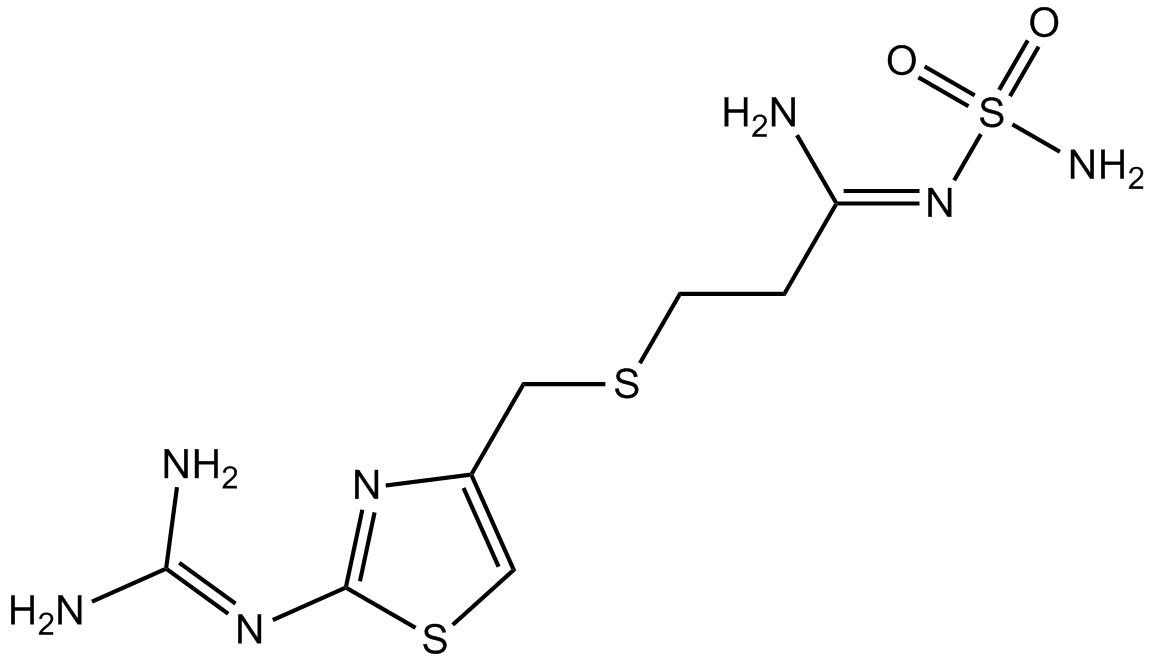
Ebrotidine
Ebrotidine is a selective antagonist of histamine H2-receptor with Ki value of 127.5 nM [1].
Ebrotidine inhibited the secretion of gastric acid through competing with histamine for the combination with H2-receptor. It was found to have gastroprotective effect via abating the hyperplastic effects in gastric enteroendocrine cells and interfering the proteolytic and lipolytic activities and the urease of Helicobacter pylori. Besides that, ebrotidine promoted the proliferation of the epithelial cells and alleviated the effects brought by stress, ethanol and aspirin. Unlike other H2 inhibitors, ebrotidine showed no carcinogenic risk enterochromaffin-like cells of mice [1 and 2].
Ebrotidine showed about 10-fold higher anti-secretory effects than cimetidine. Its affinity for H2-receptor was 1.5- and 2-fold higher than that of ranitidine and cimetidine, respectively. In the in vitro assays, ebrotidine promoted the phospholipid secretion of gastric mucosa and maintained the calcium balance of mucosal cells through suppressing EGF-induced phosphorylation of calcium channel proteins. Ebrotidine exerted anti- Helicobacter pylori potency with MIC90 value of 256 mg/L. It inhibited 57% of the proteolytic activity and 93% of the lipolytic activity of the bacteria at concentrations of 35 and 60 mg/L, respectively. In addition, ebrotidine displayed inhibition effects on the urease at a low concentration of 2.1 μM by 77% [1].
The administration of 1 to 100 mg/kg ebrotidine dose-dependently inhibited gastric acid secretion in rats. The effects could last for about 8 hours when the dose was 100 mg/kg. Ebrotidine was also found to have the ability of helping healing ulcer [1].
References:
[1]. Patel S S, Wilde M I. Ebrotidine. Drugs, 1996, 51(6): 974-80; discussion 981.
[2]. Romero A, Gómez F, Villamayor F, et al. Study of the population of enterochromaffin-like cells in mouse gastric mucosa after long-term treatment with ebrotidine. Toxicologic pathology, 1996, 24(2): 160-165.
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 477.42 |
| Cas No. | 100981-43-9 |
| Formula | C14H17BrN6O2S3 |
| Synonyms | FI 3542;Ulsanic;FI-3542;FI3542 |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| Chemical Name | N-(4-bromophenyl)sulfonyl-N'-[2-[[2-(diaminomethylideneamino)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]methylsulfanyl]ethyl]methanimidamide |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | NC(N)=Nc1nc(CSCCN=CNS(c(cc2)ccc2Br)(=O)=O)c[s]1 |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment: [1] | |
|
Cell lines |
Helicobacter. pylori |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 °C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20°C for several months. |
|
Reaction Conditions |
MIC: 75 micrograms/ml, 5 days |
|
Applications |
Ebrotidine gave a mean MIC value of 75 micrograms/ml. Ebrotidine at 100 micrograms/ml enhanced the activity of the antimicrobials studied as follows: erythromycin 3 times, tetracycline 1.1 times, amoxicillin 3 times, metronidazole-sensitive strains 9 times and clarithromycin 5 times. |
| Animal experiment: [2] | |
|
Animal models |
Sprague-Dawley rats with chronic gastric ulcers |
|
Dosage form |
Intragastric route100 mg/kg, twice daily for 14 days |
|
Applications |
Treatment with ebrotidine resulted in an accelerated ulcer healing. A 40% decrease in ulcer area was observed by the third day and a 71% decrease by the fifth day; the ulcers were essentially healed by the seventh day. |
|
Other notes |
Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
|
References: [1] Palacin C, Tarrago C, Sacristan A, et al. In vitro anti-Helicobacter pylori activity of ebrotidine. Arzneimittel-Forschung, 1997, 47(4A): 471-474. [2] Slomiany B L, Piotrowski J, Slomiany A. Cell cycle progression during gastric ulcer healing by ebrotidine and sucralfate. General Pharmacology: The Vascular System, 1997, 29(3): 367-370. | |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity = 98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
- Datasheet
Chemical structure