Dinactin
Dinactin is a macrotetrolide antibiotic that acts as an ionophore for monovalent cations, such as NH4+, K+, and Rb+. Dinactin has been used to study the membrane properties [1]. Dinactin is considered as an active molecule that S. araujoniae produced to control B. cinerea[2].
In vitro: Dinactin inhibited T-cell proliferation induced by IL-2, by mAb to CD3, and by mAbs to CD3 plus α-CD28 with identical dose-response curves. The IC50 was 10–20 ng/ml. Dinactin inhibited cytokine production with IC50 values of 10 ng/ml for IL-4 and IL-5, 30 or 60 ng/ml for interferong or IL-2, respectively [3].Dinactin inhibited cytokine production through a post-transcriptional mechanism. Dinactin also reduced pulmonary eosinophilia when administered within 1 d of airway antigen challenge [3].
References:
[1] Laprade R, Grenier F, Pagé-Dansereau M, et al. Carrier-mediated ion transport in lipid bilayer membranes[J]. Canadian journal of biochemistry and cell biology, 1984, 62(8): 738-751.
[2] Silva L J, Crevelin E J, Souza W R, et al. Streptomyces araujoniae produces a multiantibiotic complex with ionophoric properties to control Botrytis cinerea[J]. Phytopathology, 2014, 104(12): 1298-1305.
[3] Umland S P, Shah H, Jakway J P, et al. Effects of cyclosporin A and dinactin on T-cell proliferation, interleukin-5 production, and murine pulmonary inflammation[J]. American journal of respiratory cell and molecular biology, 1999, 20(3): 481-492.
| Physical Appearance | A film |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 765 |
| Cas No. | 20261-85-2 |
| Formula | C42H68O12 |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
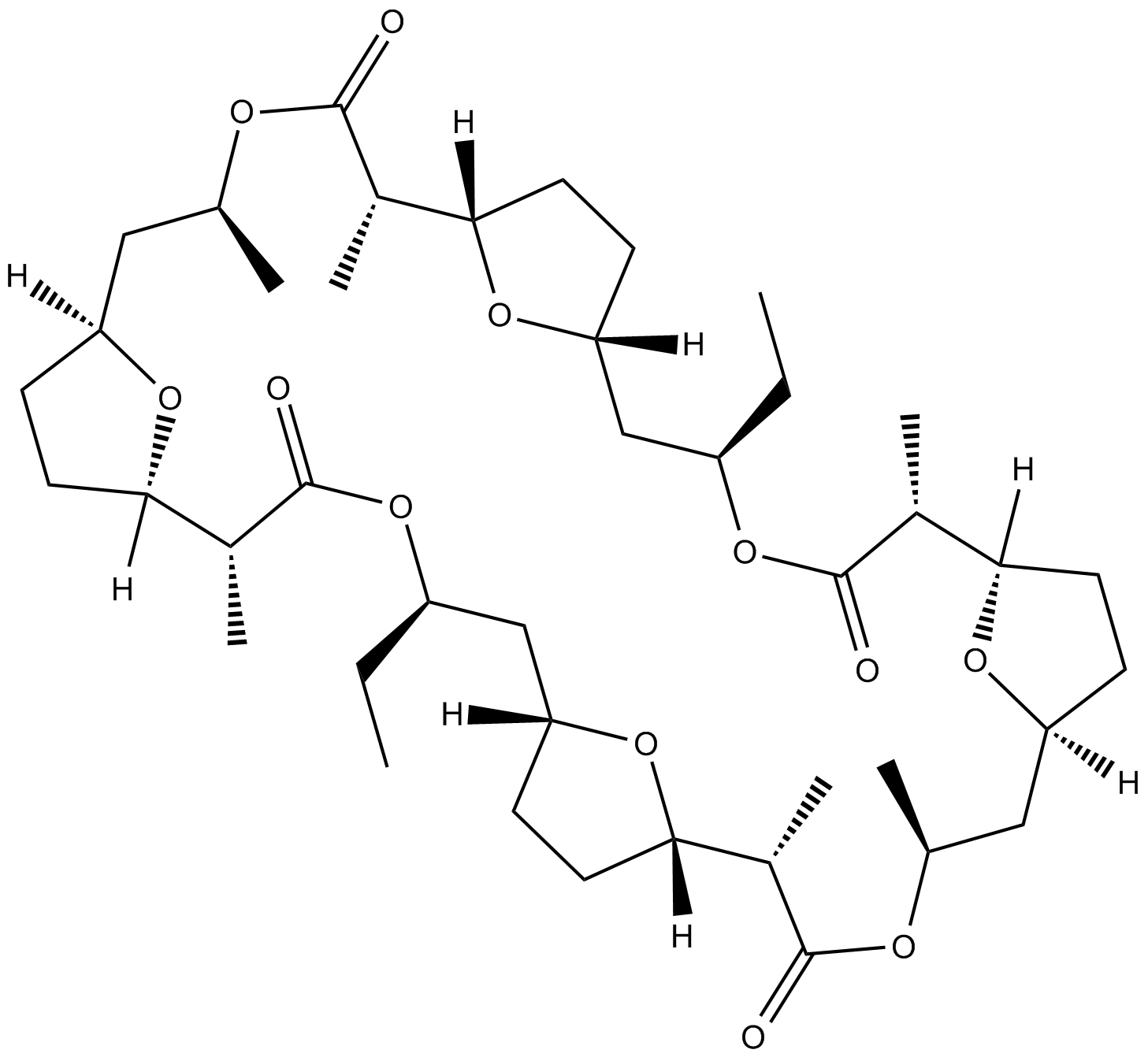
| Chemical Name | (1R,2R,5R,7R,10S,11S,14S,16S,19R,20R,23R,25R,28S,29S,32S,34S)-5,23-diethyl-2,11,14,20,29,32-hexamethyl-4,13,22,31,37,38,39,40-octaoxapentacyclo[32.2.1.17,10.116,19.125,28]tetracontane-3,12,21,30-tetrone |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | O=C(O[C@H](CC)C[C@]1([H])O[C@@]([C@@H]2C)([H])CC1)[C@H](C)[C@@]3([H])CC[C@](C[C@H](C)OC([C@H]([C@@]4([H])O[C@](C[C@H](OC([C@H](C)[C@]5([H])O[C@](CC5)([H])C[C@H](C)OC2=O)=O)CC)([H])CC4)C)=O)([H])O3 |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
|
Cell lines |
CD4+ cell |
|
Preparation method |
The solubility of this compound in DMSO is soluble. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
|
Reacting condition |
10~1000ng/ml |
|
Applications |
Dinactin and monactin have similar inhibitory effects on IL-5 production (IC50 = 20 ng / ml), and show a weak inhibitory effect on cell viability in MTS experiments (30% inhibition at 1,000 ng / ml). In contrast, nonactin is a weaker inhibitor that inhibits IL-5 production (IC50 = 200 ng / ml). CSA is a potent inhibitor of IL-5 production by SP-B21 cells stimulated by α-CD3 mAb (IC50 = 50 ng / ml); complete inhibition was observed at 100 ng / ml with no evidence of toxicity. |
|
References: [1]. Umland SP, Shah H, Jakway JP, Shortall J, Razac S, Garlisi CG, Falcone A, Kung TT, Stelts D, Hegde V, Patel M, Motasim Billah M, Egan RW. Effects of cyclosporin A and dinactin on T-cell proliferation, interleukin-5 production, and murine pulmonary inflammation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999 Mar;20(3):481-92. PubMed PMID: 10030847. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure