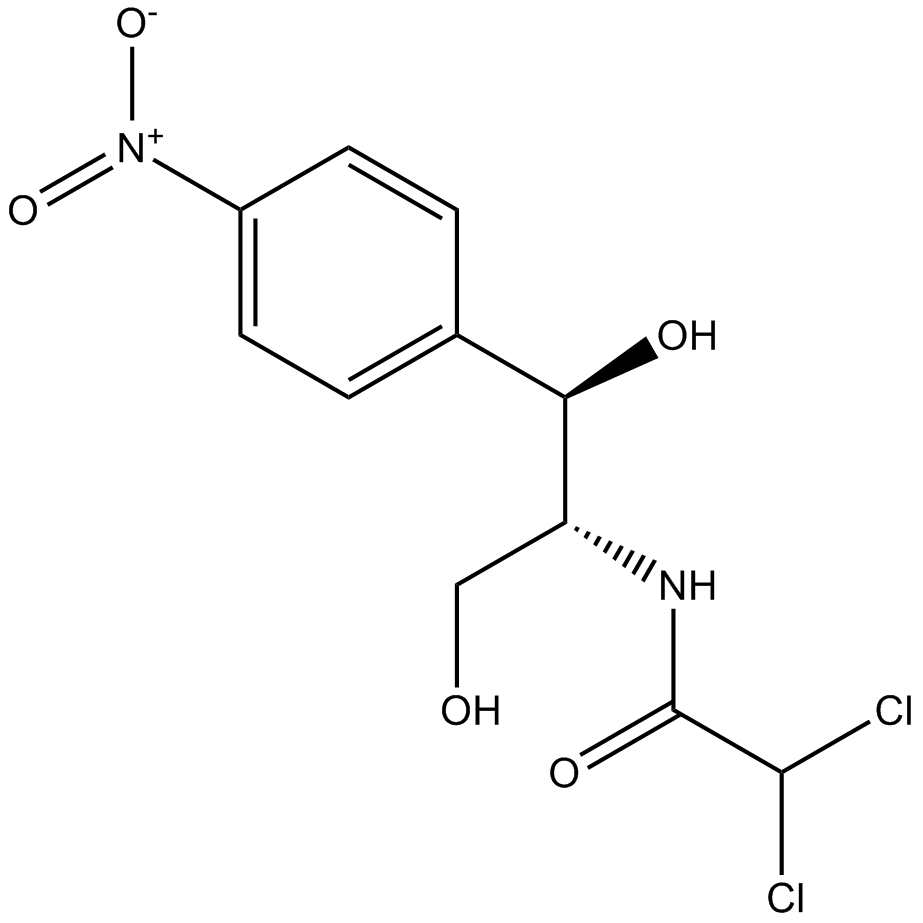
Chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol (CAS 56-75-7) is a small molecule antibiotic commonly utilized in molecular biology research. It exerts anti-microbial activity by specifically binding to the bacterial 50S ribosomal subunit, thereby inhibiting the peptidyl transferase reaction and subsequently blocking protein synthesis. At elevated concentrations, chloramphenicol may also impede DNA synthesis in eukaryotic cells. In plasmid selection assays, typical effective concentrations are approximately 25 μg/ml for stringent plasmids and 170 μg/ml for relaxed plasmids. For laboratory storage, chloramphenicol solutions are maintained at 4°C.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 323.13 |
| Cas No. | 56-75-7 |
| Formula | C11H12Cl2N2O5 |
| Solubility | ≥16.16 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥16.25 mg/mL in H2O with gentle warming and ultrasonic; ≥33 mg/mL in EtOH |
| Chemical Name | 2,2-dichloro-N-[(1R,2R)-1,3-dihydroxy-1-(4-nitrophenyl)propan-2-yl]acetamide |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | [O-][N+](c1ccc([C@H]([C@@H](CO)NC(C(Cl)Cl)=O)O)cc1)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure