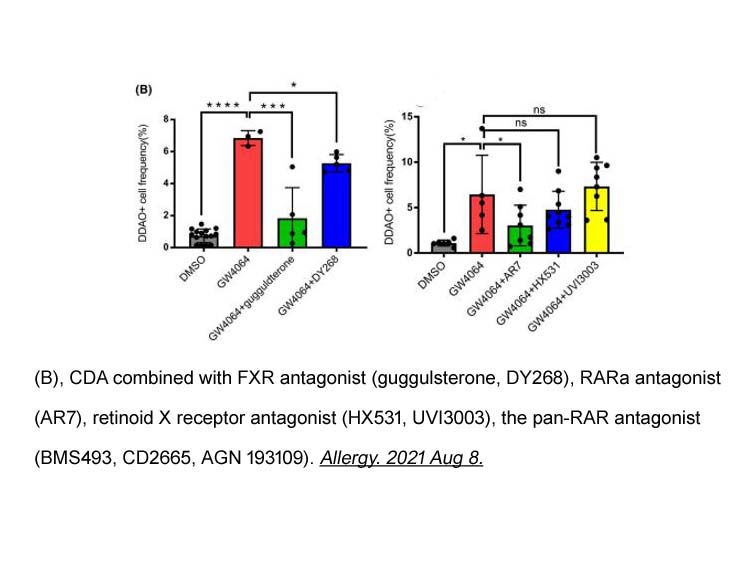
CD 2665
CD 2665 is a retinoic acid receptor β (RARβ) / RARγ antagonist [1] [2] [3] with binding Kd values of 306 nM and 110 nM to RARβ and RARγ, respectively [3].
Retinoic acid receptors include RARα, RARβ and RARγ. They are able to bind 9-cis and all-trans stereoisomers of retinoic acid (RA) [1], and mediate RA signal as transcription factors [2].
CD 2665 (1 µM) did not antagonize the luciferase activity induced by 9-cis- or all-trans-RA in HiB5 cells, but partially blocked the luciferase activity in 3XbRARE-Luc-transfected cells induced by CD 666 (a RARγ-selective agonist, 100 nM). CD 2665 at 1 µM reduced the viable cell number to about 60% level of vehicle-treated cells. CD 2665 (1 µM) clearly antagonized the increase in cell number resulted from the treatment with CD 666 (100 nM) [4].
The biosynthesis of retinoic acid can also be disordered by chronic ethanol consumption. CD 2665 administration did not modify blood alcohol levels in alcohol-treated mice, but totally reversed the impairment of spontaneous alternation rates resulted from alcohol consumption. Administration with CD2665 for 22 days in alcohol-treated mice significantly decreased both mRNA expression and enzymatic activity of tTG (a retinoic acid-target gene) and normalized the expression levels to the level in control mice [2].
References:
[1]. Yasmin Marikar, ZengQuan Wang, Elizabeth A. Duell, et al. Retinoic Acid Receptors Regulate Expression of Retinoic Acid 4-Hydroxylase that Specifically Inactivates All-Trans Retinoic Acid in Human Keratinocyte HaCaT Cells. The Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 1998, 111(3):434-439.
[2]. Serge Alfos, Catherine Boucheron, Véronique Pallet, et al. A Retinoic Acid Receptor Antagonist Suppresses Brain Retinoic Acid Receptor Overexpression and Reverses a Working Memory Deficit Induced by Chronic Ethanol Consumption in Mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res., 2001, 25(10): 1506-1514.
[3]. Zsuzsa Szondy, Uwe Reichert, Jean-Michel Bernardon, et al. Inhibition of activation-induced apoptosis of thymocytes by all-trans- and 9-cis-retinoic acid is mediated via retinoic acid receptor α. Biochem. J., 1998, 331:767-774.
[4]. Jean-Ju Chung, Sehyung Cho, Yunhee Kim Kwon, et al. Activation of retinoic acid receptor γ induces proliferation of immortalized hippocampal progenitor cells. Molecular Brain Research, 2000, 83:52-62.
- 1. Xingjie Li, Jinzhuo Tan, et al. "Ferroptosis activates retinoic acid inflammation and ignites the development of Silicosis." Research Square. 17 Nov, 2023.
- 2. Renlan Wu, Xiefang Yuan, et al. "The bile acid‐activated retinoic acid response in dendritic cells is involved in food allergen sensitization." Allergy. 2022 Feb;77(2):483-498. PMID:34365653
| Physical Appearance | A crystalline solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 486.6 |
| Cas No. | 170355-78-9 |
| Formula | C31H34O5 |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
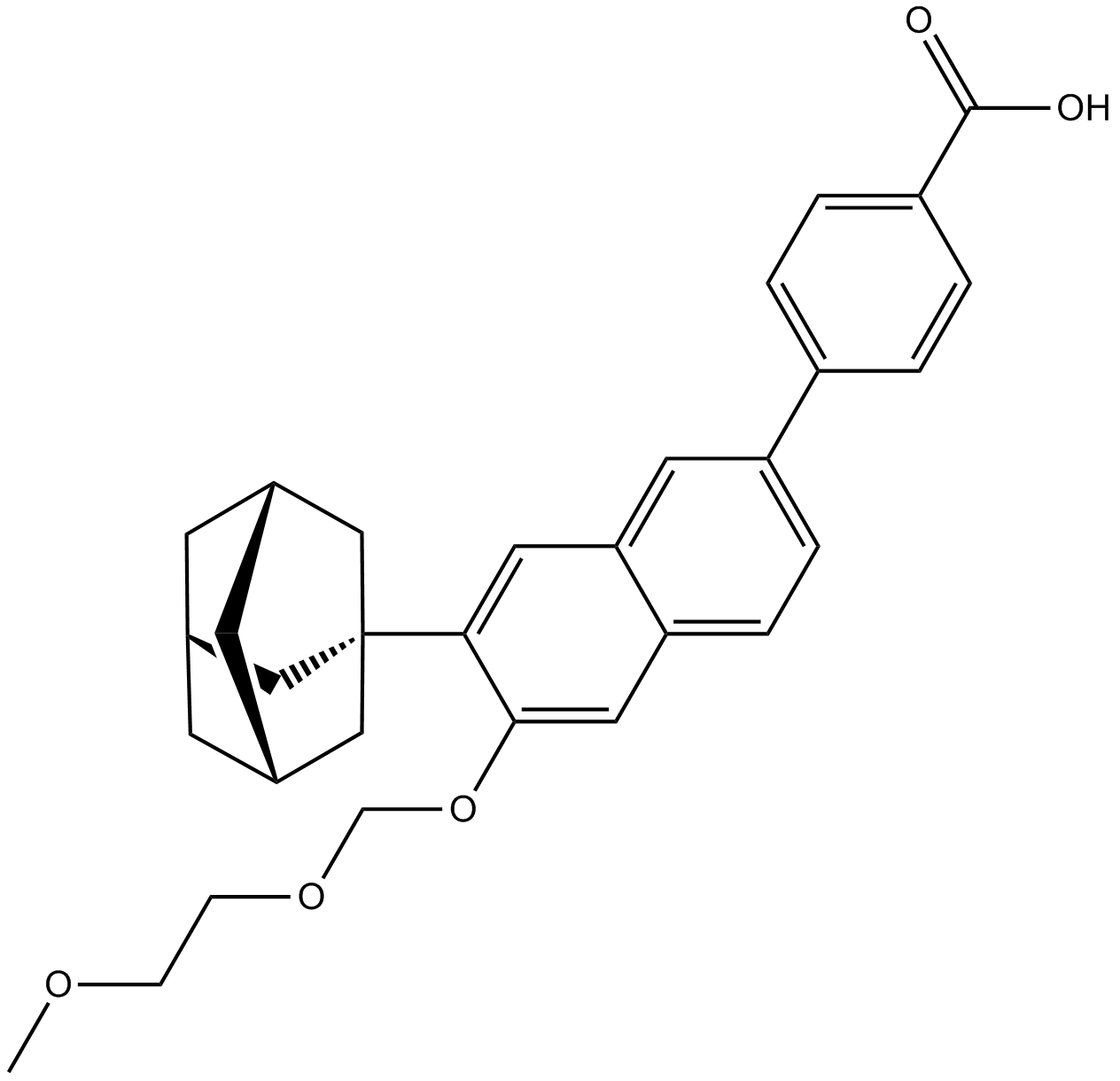
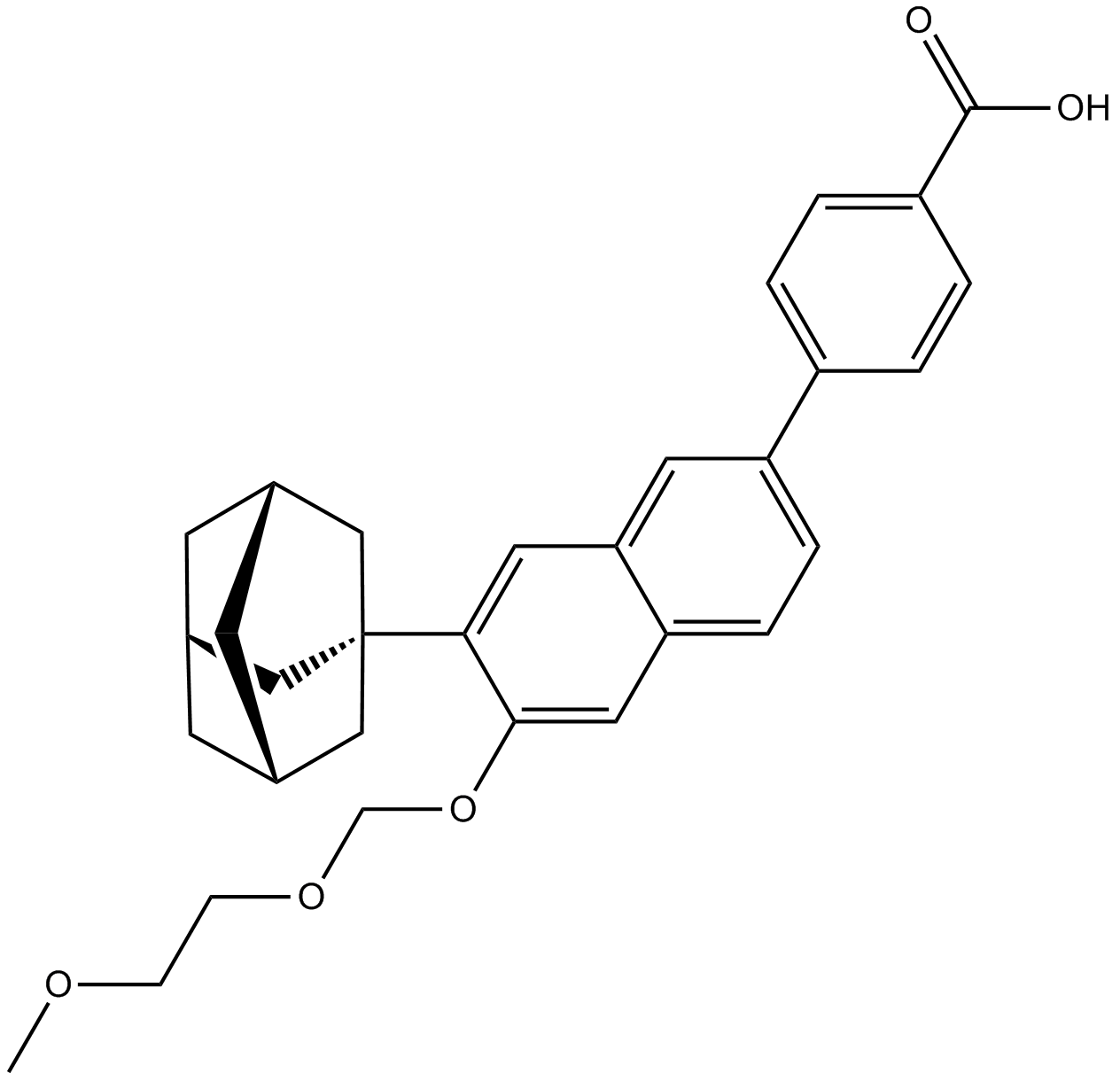
| Chemical Name | 4-(7-((1s,3R,5S,7s)-adamantan-1-yl)-6-((2-methoxyethoxy)methoxy)naphthalen-2-yl)benzoic acid |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | COCCOCOc(c(C1(C[C@H](C2)C3)C[C@H]3C[C@@H]2C1)c1)cc(cc2)c1cc2-c(cc1)ccc1C(O)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity = 98.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
- Datasheet
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data