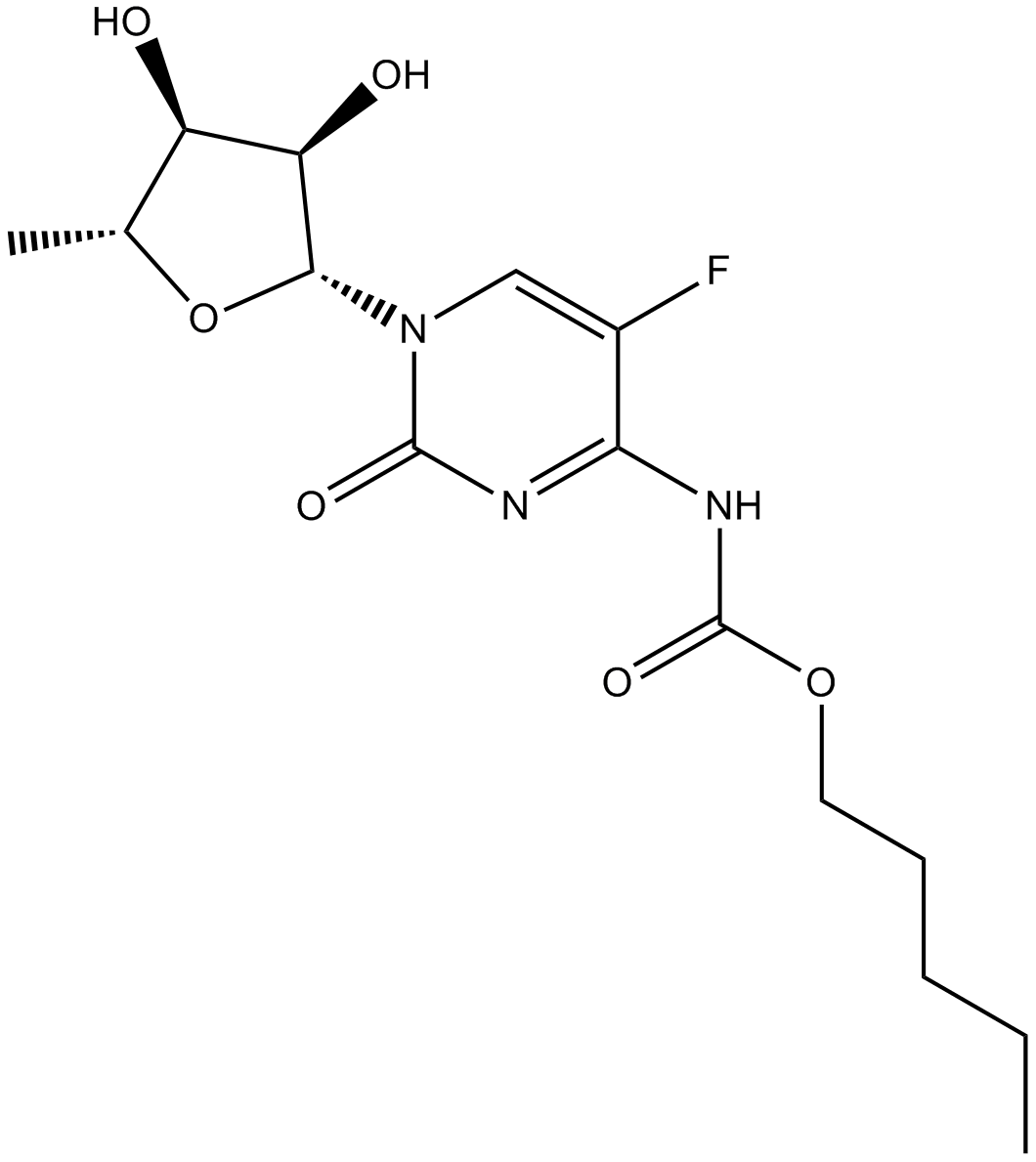
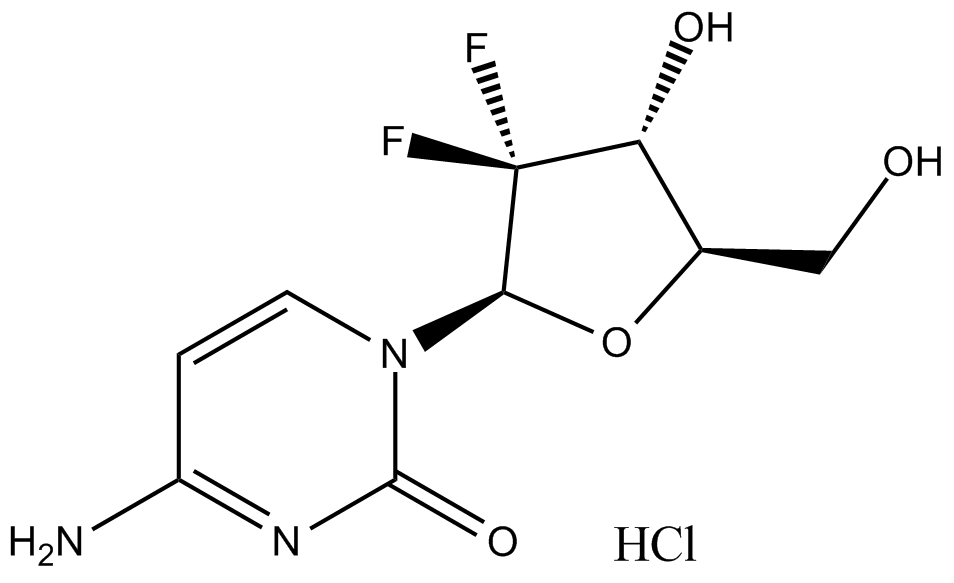
Capecitabine
Capecitabine (CAS 154361-50-9), chemically defined as N4-pentyloxycarbonyl-5'-deoxy-5-fluorocytidine, is an anticancer fluoropyrimidine prodrug that enzymatically converts into the cytotoxic agent 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) through sequential activation by enzymes predominantly expressed in tumors and liver tissues. Mechanistically, Capecitabine induces apoptosis via Fas-dependent pathways, particularly in cells with elevated thymidine phosphorylase (TP) activity, as observed in engineered LS174T colon cancer cell lines. In mouse xenograft models of colon carcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma, Capecitabine administration reduced tumor growth, metastasis, and recurrence, correlating to PD-ECGF expression. These characteristics make Capecitabine relevant in preclinical oncology studies investigating chemotherapy selectivity and tumor-targeted drug delivery.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 359.35 |
| Cas No. | 154361-50-9 |
| Formula | C15H22FN3O6 |
| Solubility | ≥10.97 mg/mL in H2O with ultrasonic; ≥17.95 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥66.9 mg/mL in EtOH |
| Chemical Name | pentyl N-[1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-methyloxolan-2-yl]-5-fluoro-2-oxopyrimidin-4-yl]carbamate |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CCCCCOC(NC(C(F)=CN1[C@@H]([C@@H]2O)O[C@H](C)[C@H]2O)=NC1=O)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure