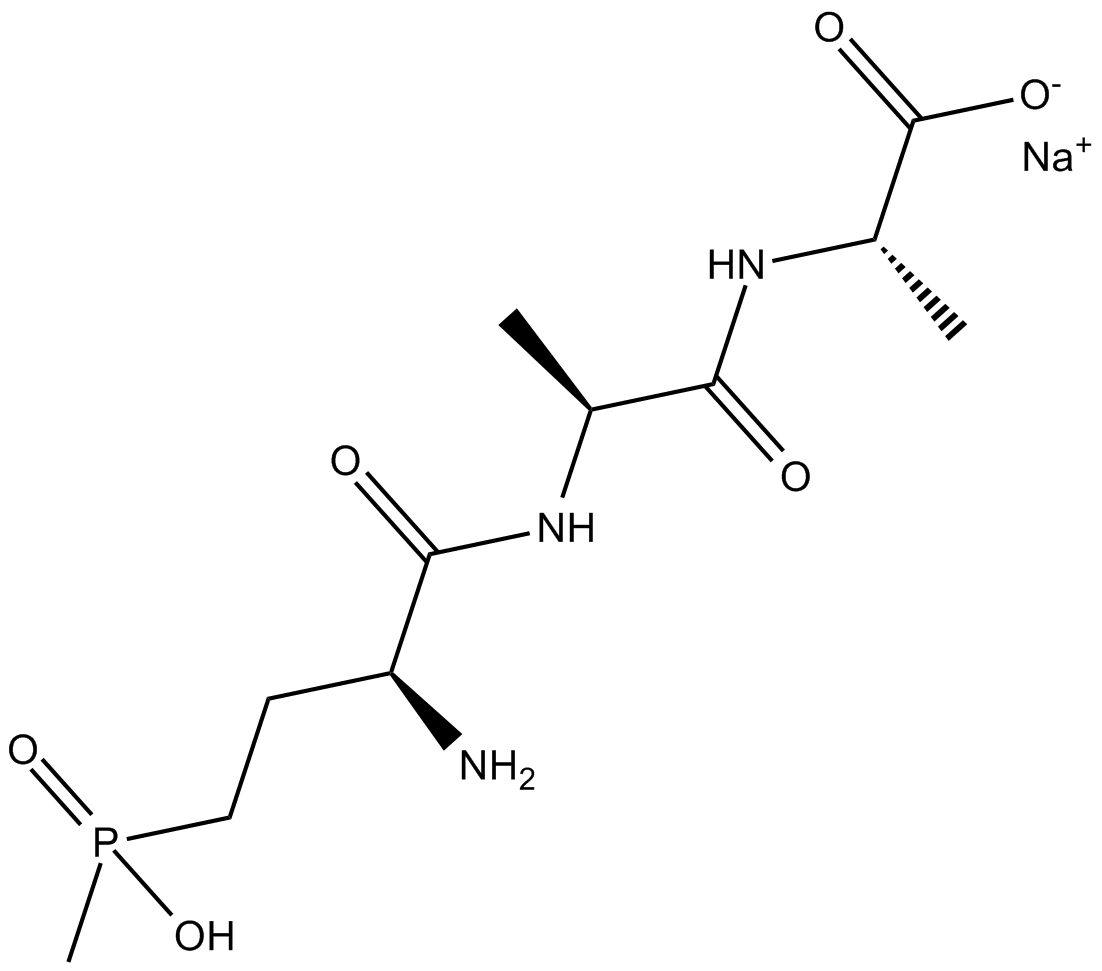
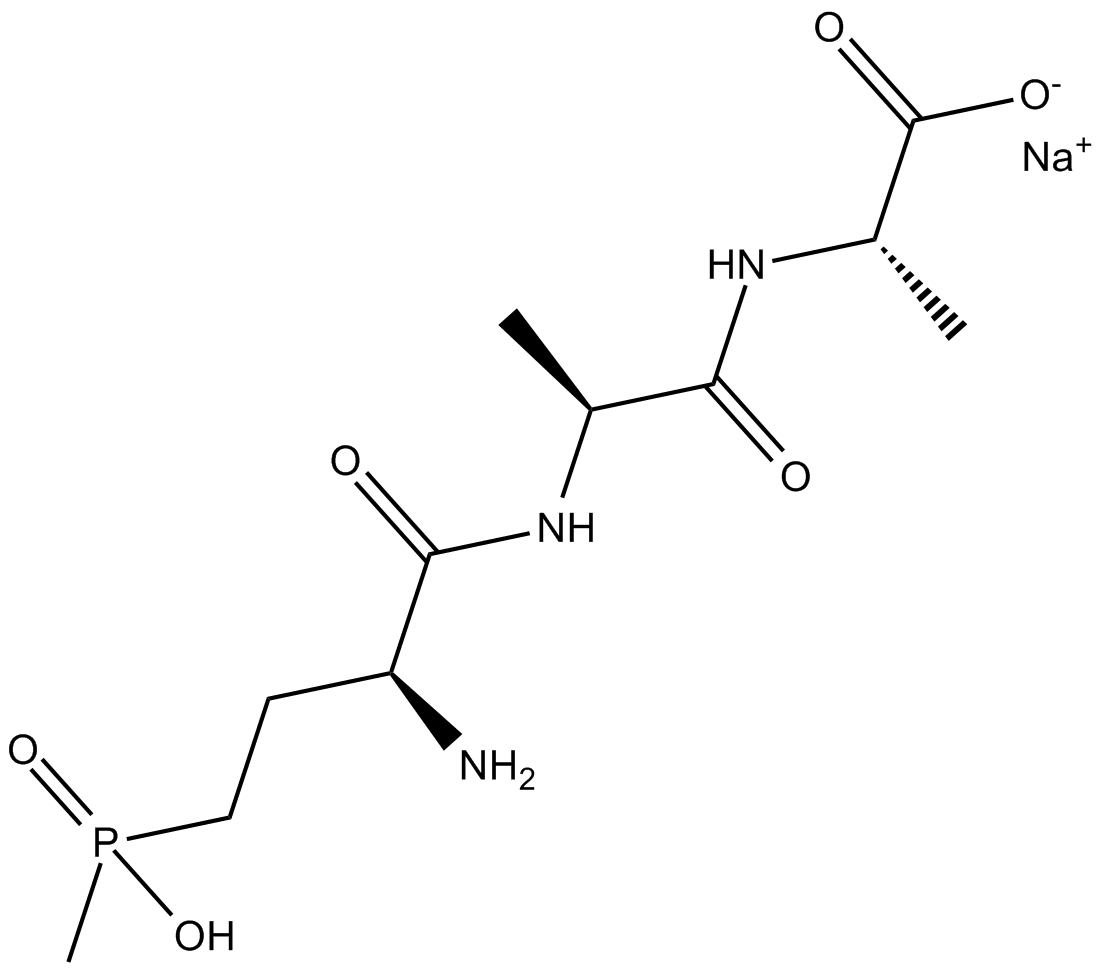
Bialaphos (sodium salt)
The antibiotic bialaphos (or SF1293) is a natural non-selective phytotoxin produced by Streptomyces hygroscopicus. Bialaphos is a tripeptide consisting of two L-alanine molecules and an L-glutamic acid analogue called phosphinothricin. Bialaphos is converted to the active agent phosphinothricin by peptidases. The phosphinothricin moiety is a potent inhibitor of glutamine synthetase [1].
Glutamine synthetase is an enzyme that plays an essential role in the metabolism of nitrogen. Glutamine synthetase in the brain participates in the metabolic regulation of glutamate, the detoxification of brain ammonia, the assimilation of ammonia, recyclization of neurotransmitters, and termination of neurotransmitter signals. Upregulation of glutamine synthetase in glutamatergic areas or other adaptations alleviates high levels of glutamate and ammonia [2].
Bialaphos has been used to select the transgenic plants that express the bar gene, usually under the control of a constitutively active viral promoter. In bialaphos resistant rice plants expressing a bar gene, treatment with the herbicide completely protected from symptomatic infection. In transgenic plants infected with R. solani two days before herbicide treatment, bialaphos induced substantial suppression of sheath blight symptoms [3]. In transgenic rice harboring the Bar-gene, treatment with bialaphos decreased the lesions caused by the fungal pathogen. Pretreatment with bialaphos 1 day before the inoculation suppressed disease symptoms to 20% of control [4].
References:
[1] Meister A. 23. Glutamine synthetase of mammals[J]. The enzymes, 1974, 10: 699-754.
[2] Murakami T, Anzai H, Imai S, et al. The bialaphos biosynthetic genes ofStreptomyces hygroscopicus: Molecular cloning and characterization of the gene cluster[J]. Molecular and General Genetics MGG, 1986, 205(1): 42-53.
[3] Uchimiya H, Iwata M, Nojiri C, et al. Bialaphos treatment of transgenic rice plants expressing a bar gene prevents infection by the sheath blight pathogen (Rhizoctonia solani)[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 1993, 11(7): 835-836.
[4] Tada T, Kanzaki H, Norita E, et al. Decreased symptoms of rice blast disease on leaves of bar-expressing transgenic rice plants following treatment with bialaphos[J]. MPMI-Molecular Plant Microbe Interactions, 1996, 9(8): 762.
| Physical Appearance | A crystalline solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 345.26 |
| Cas No. | 71048-99-2 |
| Formula | C11H21N3NaO6P |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| Chemical Name | sodium (2S)-2-((2S)-2-((2S)-2-amino-4-(hydroxy(methyl)phosphoryl)butanamido)propanamido)propanoate |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | C[C@@H](C(N[C@@H](C)C([O-])=O)=O)NC([C@H](CCP(C)(O)=O)N)=O.[Na+] |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
-
Purity ≥95.00%
- COA (Certificate Of Analysis)
- MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet)
Chemical structure