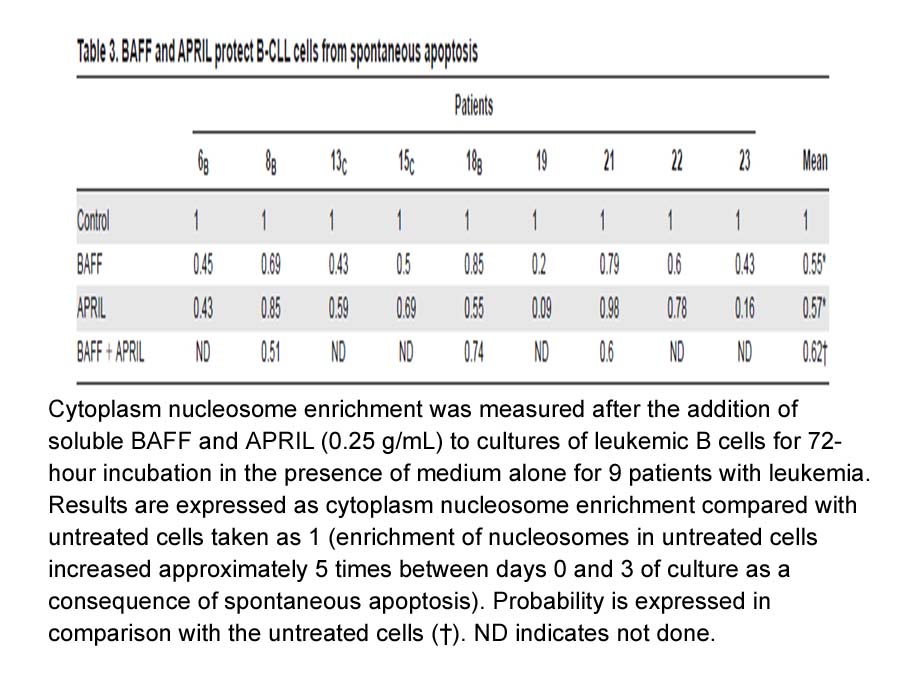
BAFF, human recombinant protein
B-cell activating factor (BAFF), also known as Blys, TALL-1, TNAK, and zTNF4, is a TNF ligand superfamily member and has been designated TNFSF13B. Produced by macrophages, dendritic cells, and T lymphocytes, BAFF promotes the survival of B cells and is essential for B cell maturation. BAFF binds to three TNF receptor superfamily members: B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA/TNFRSF17), transmembrane activator and calcium-modulator and cyclophilin ligand interactor (TACI/TNFRSF13B) and BAFF receptor (BAFF R/BR3/TNFRSF 13C). These receptors are type III transmembrane proteins that lack a signal peptide. Whereas TACI and BCMA bind BAFF and another TNF superfamily ligand, APRIL (a proliferation-inducing ligand), BAFF R selectively binds BAFF. The BAFF R extracellular domain lacks the TNF receptor canonical cysteine-rich domain (CRD) and contains only a partial CRD with four cysteine residues. Human and mouse BAFF R share 56 % a.a. sequence identity. BAFF R is highly expressed in spleen, lymph node and resting B cells. It is also expressed at lower levels in activated B cell, in resting CD4+ T cells, in thymus and peripheral blood leukocytes.
Reference:
1. Craxton A, Draves KE, Gruppi A, et al. 2005. J Exp Med, 202: 1363-74
2. Kalled SL. 2005. Immunol Rev, 204: 43-54
3. Kuo SH, Yeh PY, Chen LT, et al. 2008. Blood, 112: 2927-34
4. Rowland SL, Leahy KF, Halverson R, et al. 2010. J Immunol, 185: 4570-81
5. Liu ZandDavidson A. 2011. Exp Cell Res, 317: 1270-7.
|
Gene ID |
10673 |
|
Accession # |
Q9Y275 |
|
Alternate Names |
TNFSF13B, TNFSF20, TALL-1, BLys, THANK, B cell Activating Factor belonging to the TNF family |
|
Source |
Escherichia coli. |
|
M.Wt |
Approximately 17.2 kDa, a single non-glycosylated polypeptide chain containing 153 amino acids. |
|
AA Sequence |
MAVQGPEETV TQDCLQLIAD SETPTIQKGS YTFVPWLLSF KRGSALEEKE NKILVKETGY FFIYGQVLYT DKTYAMGHLI QRKKVHVFGD ELSLVTLFRC IQNMPETLPN NSCYSAGIAK LEEGDELQLA IPRENAQISL DGDVTFFGAL KLL |
|
Appearance |
Sterile Filtered White lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder. |
|
Stability & Storage |
Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. - 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied. - 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution. - 3 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution. |
|
Formulation |
Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered concentrated solution in PBS, pH 7.0. |
|
Reconstitution |
We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Reconstitute in sterile distilled water or aqueous buffer containing 0.1 % BSA to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Stock solutions should be apportioned into working aliquots and stored at ≤ -20 °C. Further dilutions should be made in appropriate buffered solutions. |
|
Biological Activity |
Fully biologically active when compared to standard. The ED50 as determined by a mouse splenocyte survival assay is 0.5-2 µg/ml. |
|
Shipping Condition |
Gel pack. |
|
Handling |
Centrifuge the vial prior to opening. |
|
Usage |
For Research Use Only! Not to be used in humans. |
Quality Control & DataSheet
- View current batch:
-
Purity > 95 % by SDS-PAGE and HPLC analyses.
- Datasheet
Endotoxin: Less than 1 EU/μg of rHuBAFF as determined by LAL method.
Related Biological Data