atorvastatin
Atorvastatin (CAS 134523-00-5) is an orally bioavailable inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase, the enzyme catalyzing the rate-limiting step of cholesterol biosynthesis via the mevalonate pathway. Beyond its cholesterol-lowering activity, atorvastatin can modulate cardiovascular processes independently of lipid reduction, primarily through inhibiting small GTPases such as Ras and Rho, known contributors to cardiovascular pathology and vascular dysfunction. Additionally, atorvastatin has demonstrated inhibition of abdominal aortic aneurysm development by interfering with endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling pathways. This molecule is frequently used in biomedical studies involving cholesterol metabolism, vascular cell biology, and cardiovascular disease research.
- 1. Ling Wang, Xiaoqin He, et al. "A Novel Ferroptosis-Related Gene Prognosis Signature and Identifying Atorvastatin as a Potential Therapeutic Agent for Hepatocellular Carcinoma." Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Mar 18;47(3):201 PMID: 40136455
- 2. Hairong Li, lijun Niu, et al. "Mechanism investigation of anti-NAFLD of Shugan Yipi Granule based on network pharmacology analysis and experimental verification." August 01, 2024.
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 558.64 |
| Cas No. | 134523-00-5 |
| Formula | C33H35FN2O5 |
| Solubility | ≥104.9 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in EtOH; insoluble in H2O |
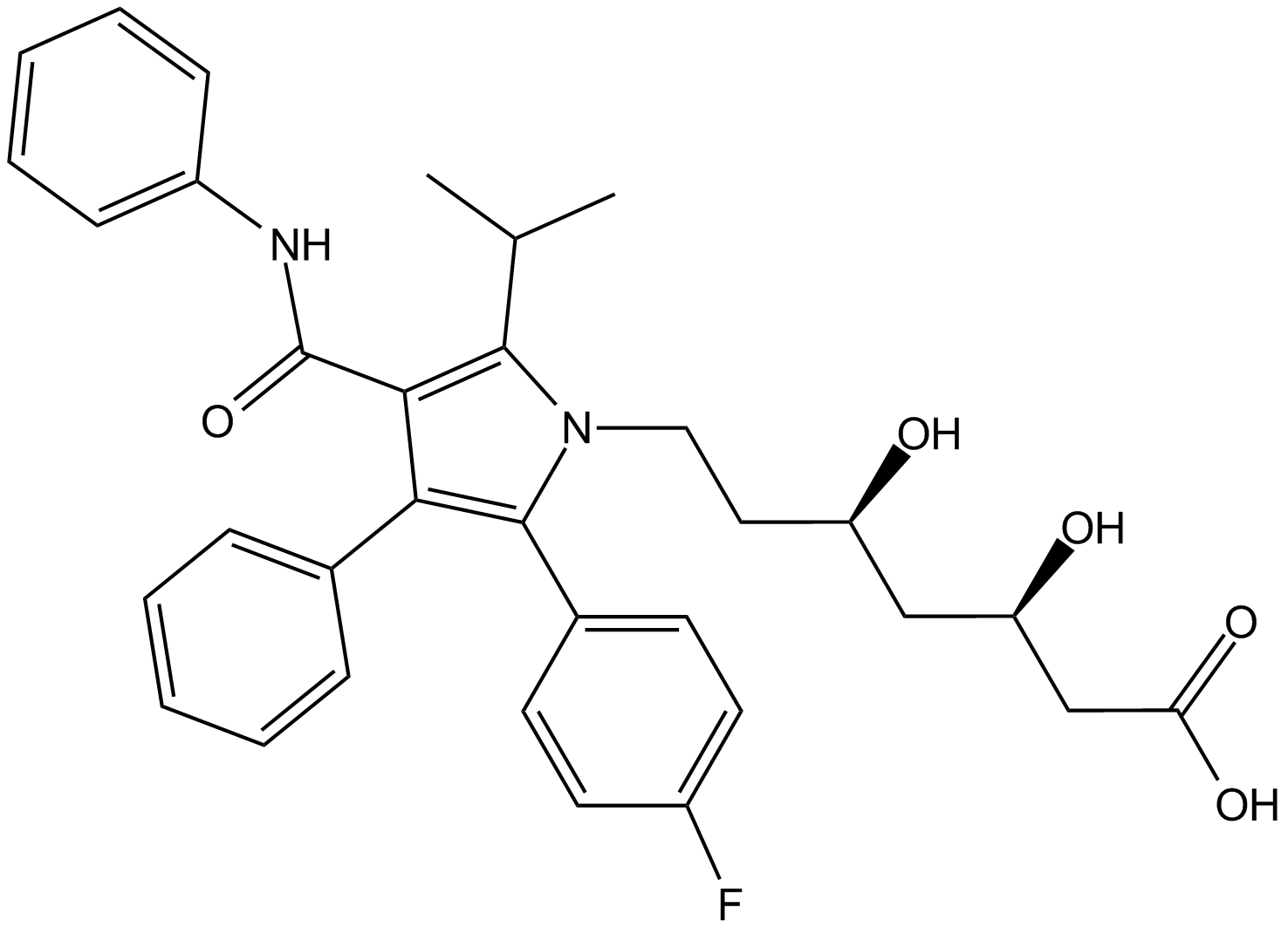
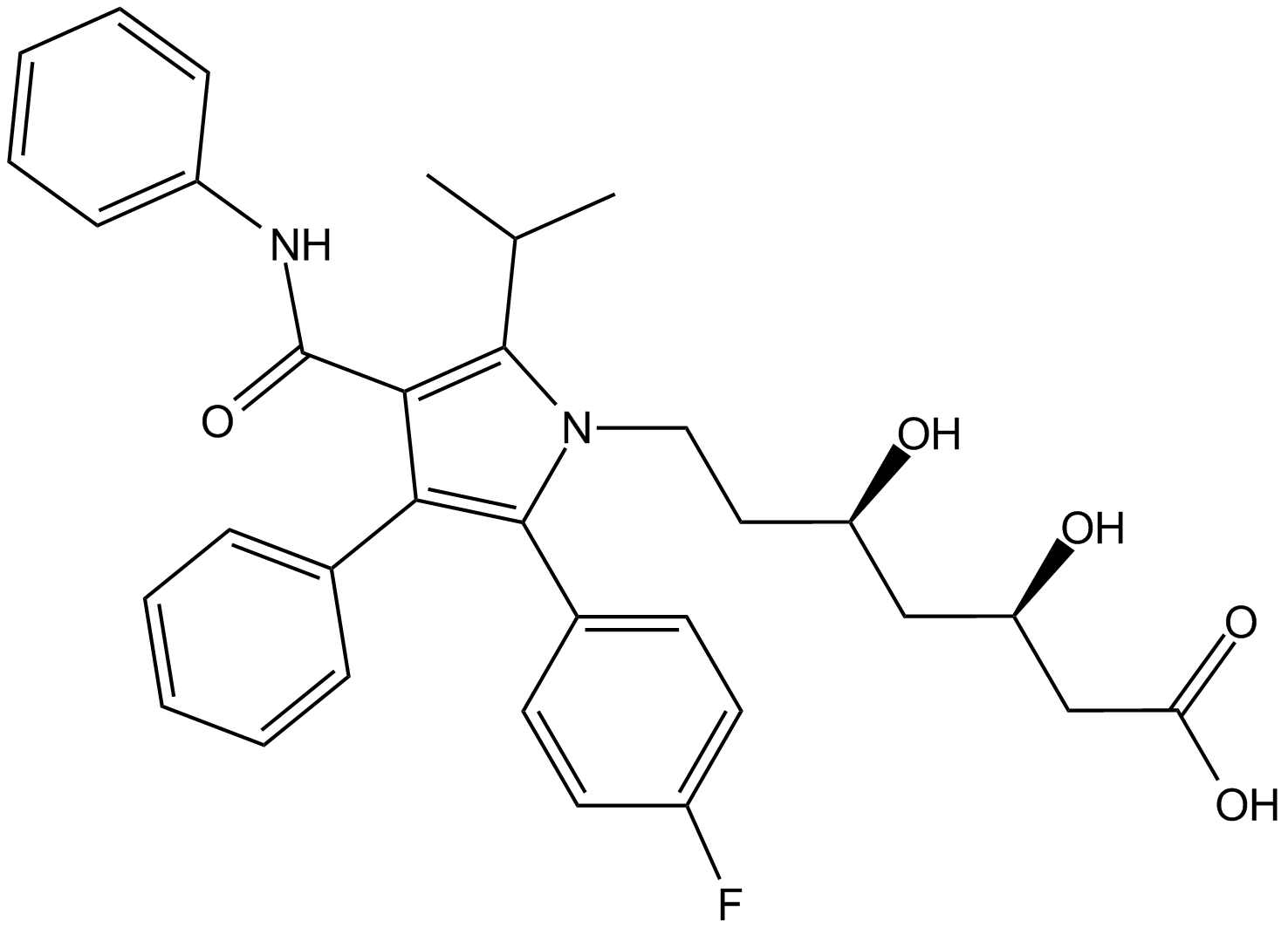
| Chemical Name | (3R,5R)-7-(2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-isopropyl-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl)-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CC(C)C1=C(C(NC2=CC=CC=C2)=O)C(C3=CC=CC=C3)=C(C4=CC=C(F)C=C4)N1CC[C@@H](O)C[C@@H](O)CC(O)=O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Cell experiment:[2] | |
|
Cell lines |
Human saphenous vein smooth muscle cells |
|
Reaction Conditions |
Incubated for 4 days |
|
Applications |
Atorvastatin inhibited the proliferation and invasion activities of human saphenous vein smooth muscle cells, with IC50 values of 0.39 μM and 2.39 μM, respectively |
| Animal experiment:[3] | |
|
Animal models |
Angiotensin Ⅱ (Ang Ⅱ)-induced Apolipoprotein E-deficient (ApoE−/−) mice |
|
Dosage form |
20 ~ 30 mg/kg Once daily by oral route for 28 days |
|
Applications |
In the Ang Ⅱ-induced ApoE−/− mice, Atorvastatin treatment significantly reduced endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling proteins, the number of apoptotic cells, as well as the activation of Caspase12 and Bax. Furthermore, Atorvastatin also remarkably inhibited a variety of proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, IL-8 and IL-1β. |
|
Note |
The technical data provided above is for reference only. |
|
References: 1. Nawrocki JW, Weiss SR, Davidson MH, et al. Reduction of LDL cholesterol by 25% to 60% in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia by atorvastatin, a new HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 1995, 15(5): 678-682. 2. Turner NA, Midgley L, O'Regan DJ, et al. Comparison of the efficacies of five different statins on inhibition of human saphenous vein smooth muscle cell proliferation and invasion. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology, 2007, 50(4): 458-461. 3. Li Y, Lu G, Sun D, et al. Inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling pathway: A new mechanism of statins to suppress the development of abdominal aortic aneurysm. PLoS One, 2017, 12(4): e0174821. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure