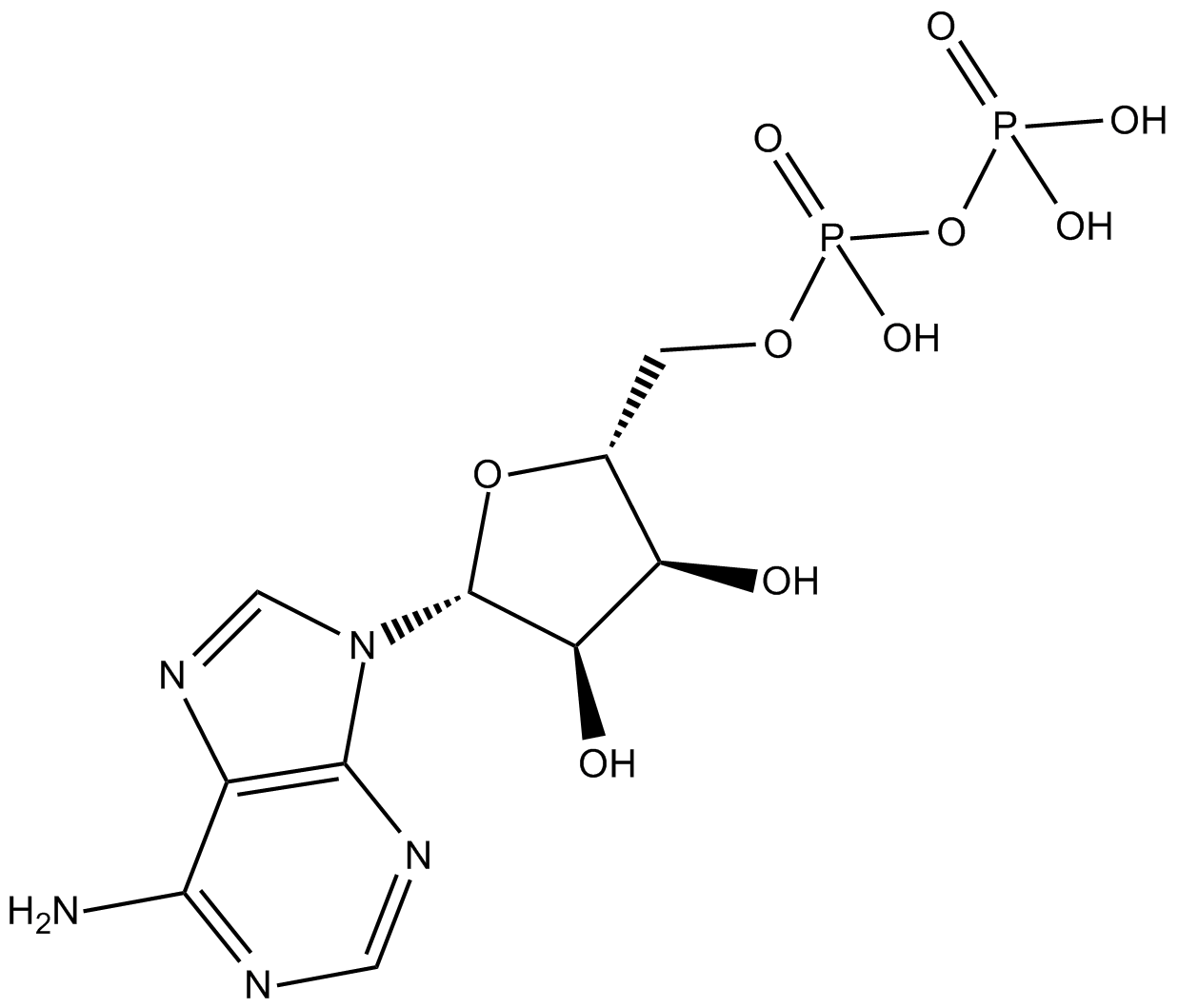
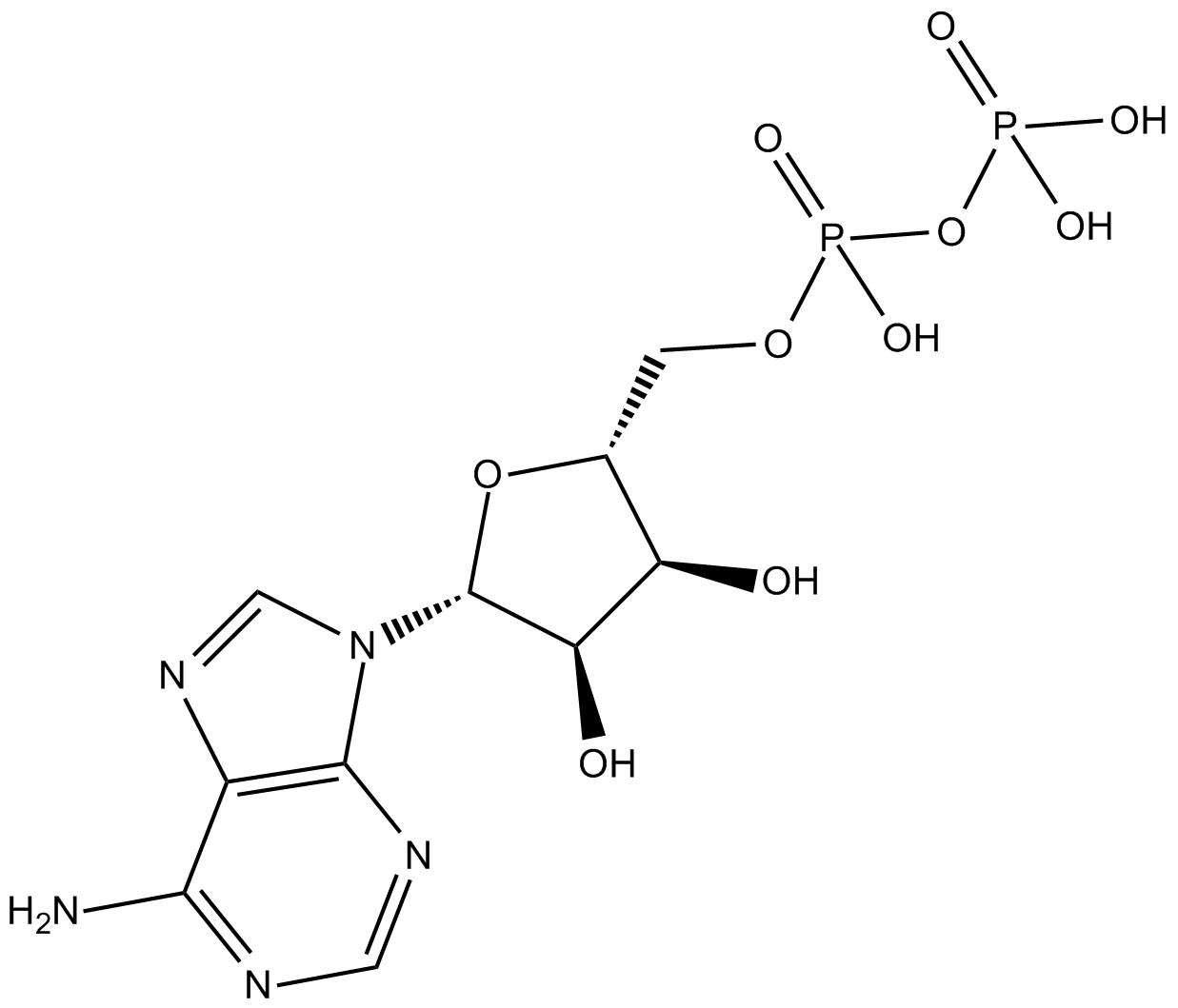
Adenosine-5'-diphosphate
Adenosine-5'-diphosphate (CAS 58-64-0), commonly known as ADP, is an endogenous nucleotide serving as an agonist of purinergic receptors. It activates various P2 receptor subtypes, exhibiting an IC50 of 67 nM at P2X2/3 receptors. ADP results from ATP hydrolysis mediated by ATPases and can be reconverted to ATP via ATP synthases or further processed to AMP and other metabolites. Through receptor modulation, ADP influences cellular functions including neural stem cell proliferation, vascular response, apoptosis, cytokine secretion, and kinase-driven phosphorylation pathways, thus playing a critical role in purinergic signaling research.
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 427.2 |
| Cas No. | 58-64-0 |
| Formula | C10H15N5O10P2 |
| Synonyms | Adenosine Pyrophosphate,ADP,5′-ADP |
| Solubility | ≥21.35 mg/mL in DMSO with gentle warming; insoluble in EtOH; ≥24.85 mg/mL in H2O |
| Chemical Name | adenosine 5'-(trihydrogen diphosphate) |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | Nc1c2nc[n]([C@@H]([C@@H]3O)O[C@H](COP(O)(OP(O)(O)=O)=O)[C@H]3O)c2ncn1 |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure