Abscisic Acid (Dormin)
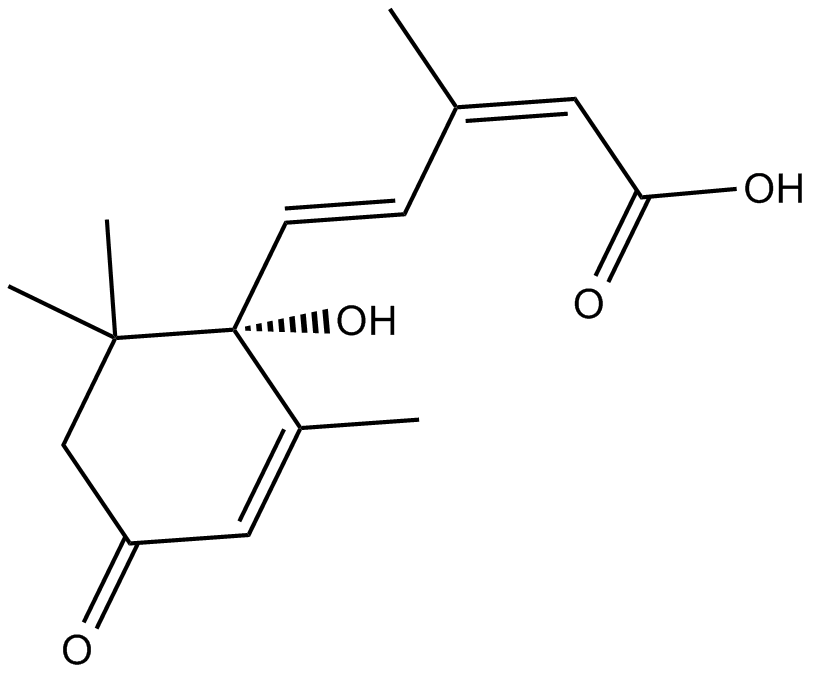
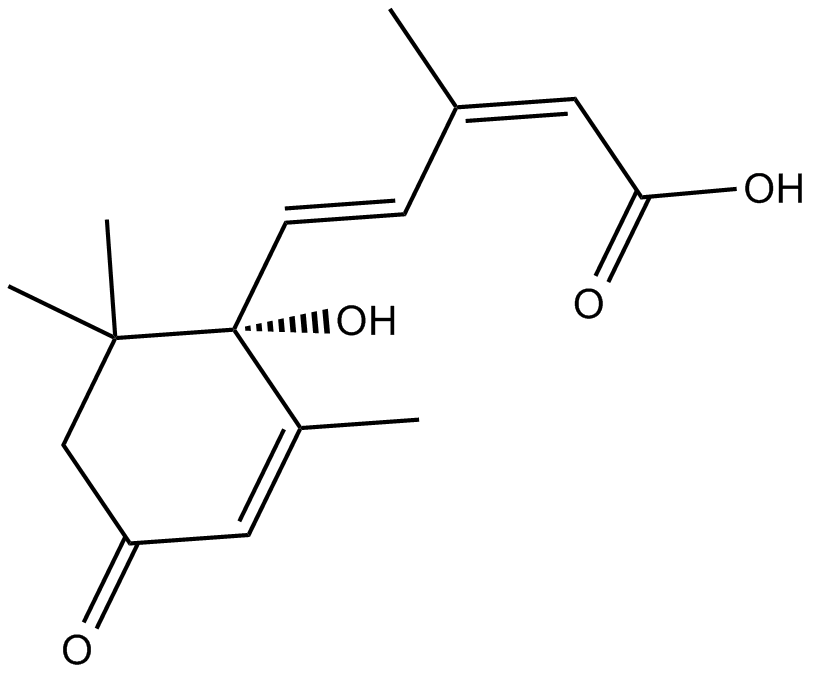
Abscisic acid (Dormin; CAS 21293-29-8) is a plant hormone involved in regulating plant growth, development, and stress responses. Its activity includes mediating seed dormancy, germination control, lateral root formation, and adaptive responses to abiotic stress. Mechanistically, ABA influences histone H2B ubiquitination and chromatin remodeling processes, thereby modulating gene expression during seed maturation and under environmental stress. ABA signaling also alters cellular redox status by enhancing synthesis of antioxidants such as α-tocopherol and L-ascorbate. It is widely utilized in plant biology research to study stress physiology, developmental biology, and epigenetic gene regulation.
| Physical Appearance | A solid |
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 264.32 |
| Cas No. | 21293-29-8 |
| Formula | C15H20O4 |
| Solubility | insoluble in H2O; ≥8.9 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥9.6 mg/mL in EtOH |
| Chemical Name | (2Z,4E)-5-[(1S)-1-hydroxy-2,6,6-trimethyl-4-oxocyclohex-2-en-1-yl]-3-methylpenta-2,4-dienoic acid |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CC(C)(CC(C=C1C)=O)[C@]1(/C=C/C(\C)=C\C(O)=O)O |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure