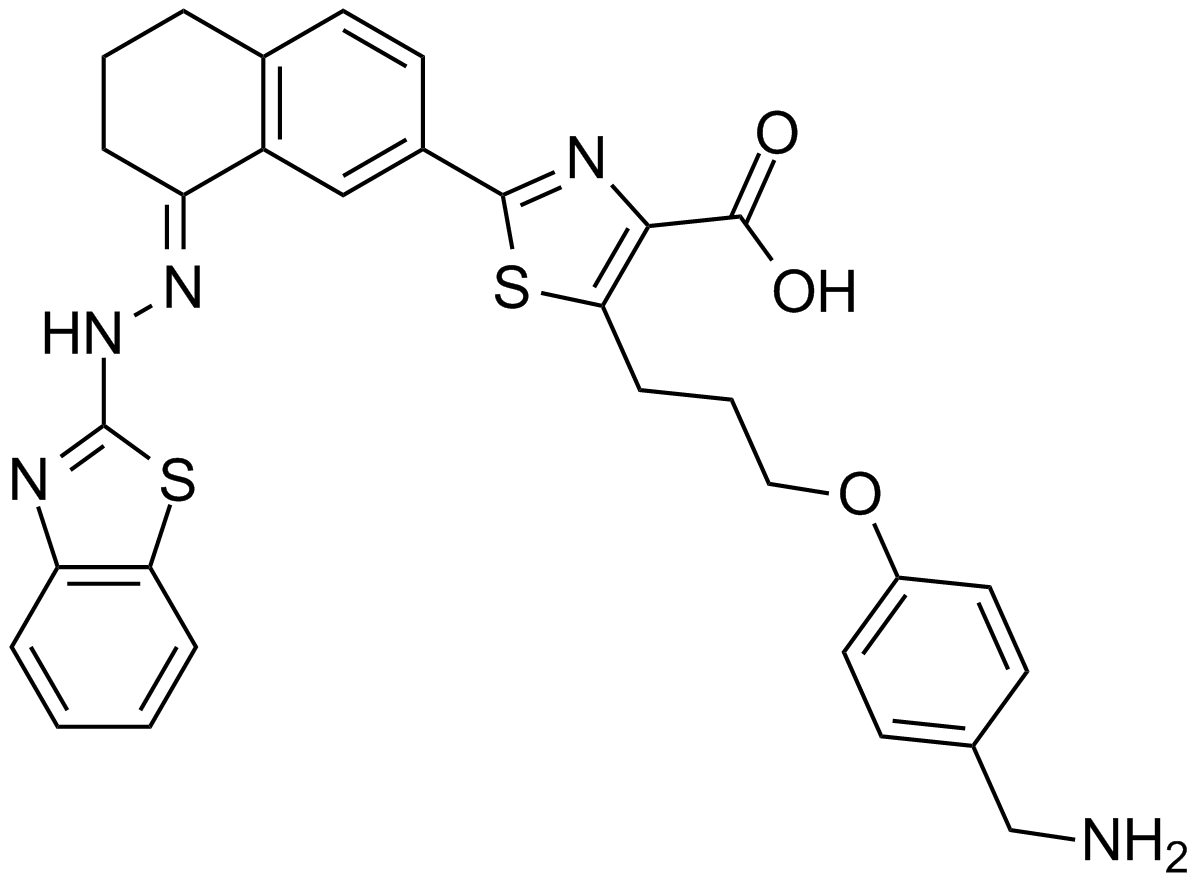
A-1210477
A-1210477 is an effective and specific MCL-1 inhibitor with an EC50 value below 5 µmol/L [1]. Selectively, it binds to MCL-1 with an affinity of 0.45 nM [2].
MCL-1, an anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family member, is an anti-apoptotic protein. It is a key regulator of cancer cell survival [3, 4].
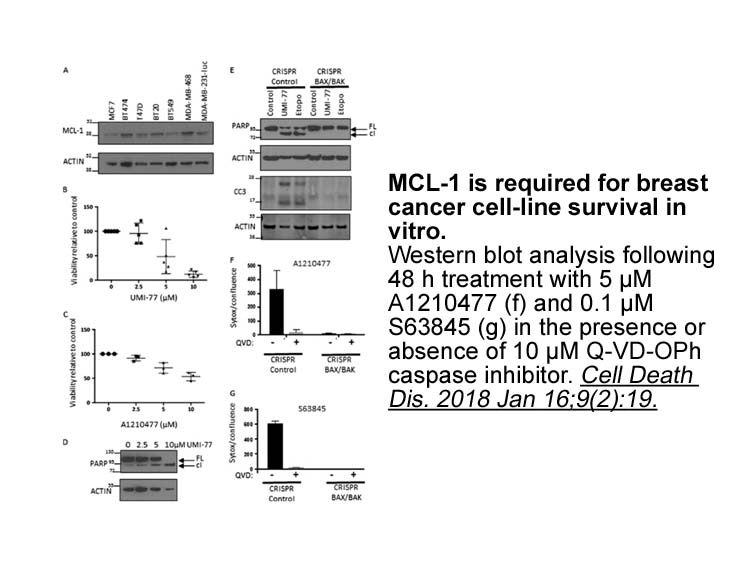
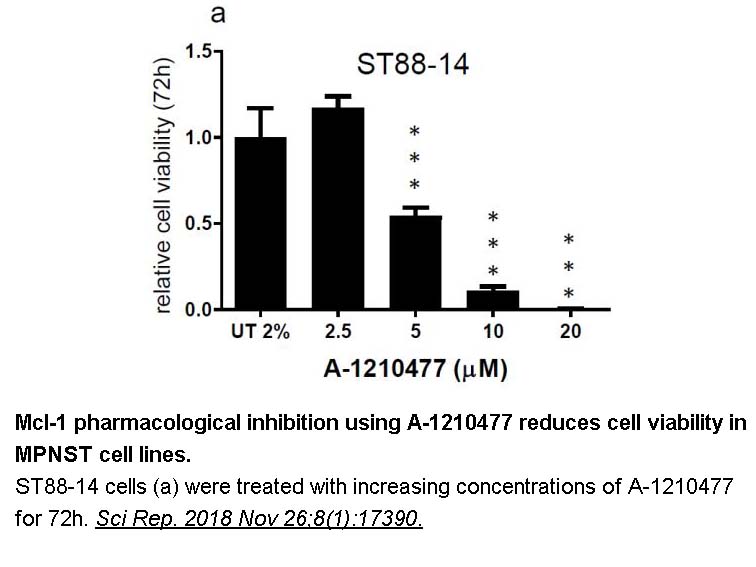
In MCL-1-dependent SVEC cells, treatment with A-1210477 at varying doses, induced cell death in a dose-dependent manner. SYTOX Green exclusion and live-cell imaging were used to determine cell viability. In line with increased potency, cell death was more rapidly induced by A-1210477. To examine the selectivity of A-1210477 for targeting Bcl-2 family members, BcL-xL-, BcL-2-, and MCL-1-dependent SVEC cells were treated with A-1210477. A-1210477 only killed MCL-1-dependent cells. Compared with UMI-77, A-1210477 showed greater potency and specificity as an MCL-1 inhibitor, the EC50 value of UMI-77 is 10 µmol/L [1]. In living cells, A-1210477 disrupted BIM/MCL-1 complexes. In MCL-1-dependent cancer cells, A-1210477 induced the hallmarks of mitochondrial apoptosis. In various malignant cell lines, A-1210477 induced apoptosis, synergizing with navitoclax. Data also demonstrate that A-1210477 acted through an on-target mechanism. It appeared as the first BH3 mimetic targeting MCL-1 [2].
The pharmacokinetics of A-1210477 are not favorable for in vivo use [5].
References:
[1]. Lopez J, Bessou M, Riley JS, et al. Mito-priming as a method to engineer Bcl-2 addiction. Nature communications, 2016, 7:10538.
[2]. Besbes S, Mirshahi M, Pocard M, et al. New dimension in therapeutic targeting of BCL-2 family proteins. Oncotarget, 2015, 6(15): 12862.
[3]. Leverson JD, Zhang H, Chen J, et al. Potent and selective small-molecule MCL-1 inhibitors demonstrate on-target cancer cell killing activity as single agents and in combination with ABT-263 (navitoclax). Cell death & disease, 2015, 6(1): e1590.
[4]. Mott JL, Kobayashi S, Bronk SF, et al. mir-29 regulates Mcl-1 protein expression and apoptosis. Oncogene, 2007, 26(42): 6133-6140.
[5]. Opferman JT. Attacking cancer's Achilles heel: antagonism of anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family members. FEBS Journal, 2015.
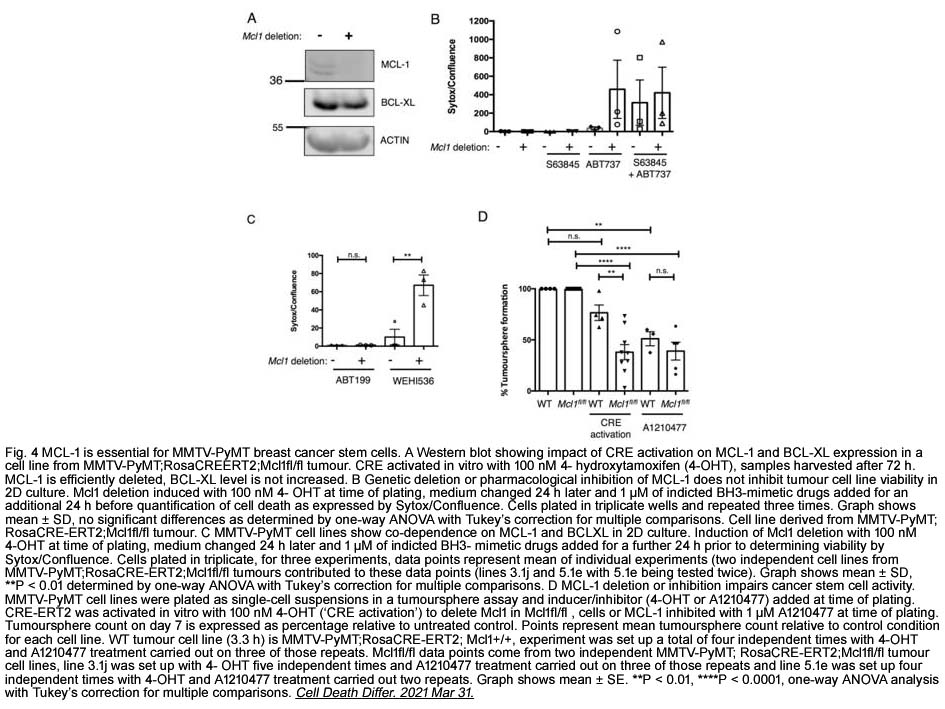
- 1. Kirsteen J. Campbell, Susan M. Mason, et al. "Breast cancer dependence on MCL-1 is due to its canonical anti-apoptotic function." Cell Death Differ. 2021 Sep;28(9):2589-2600. PMID:33785871
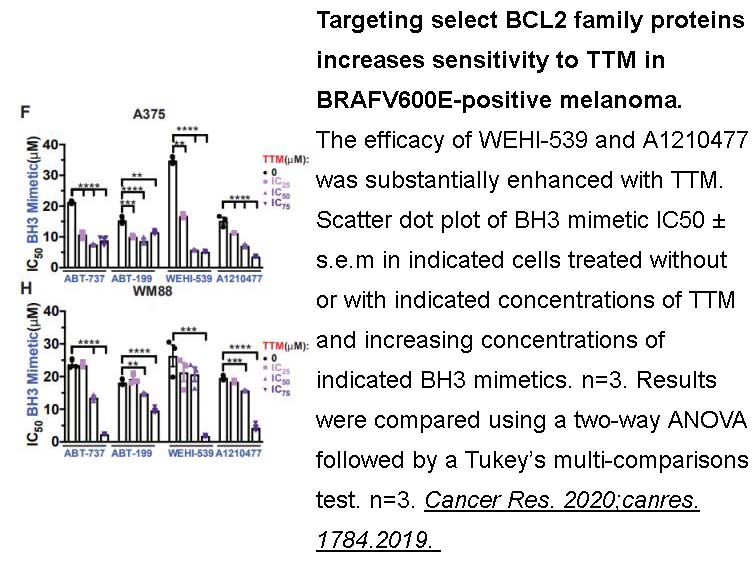
- 2. Kim YJ, Tsang T, et al. "Inhibition of BCL2 family members increases the efficacy of copper chelation in BRAFV600E-driven melanoma." Cancer Res. 2020;canres.1784.2019. PMID:32005716
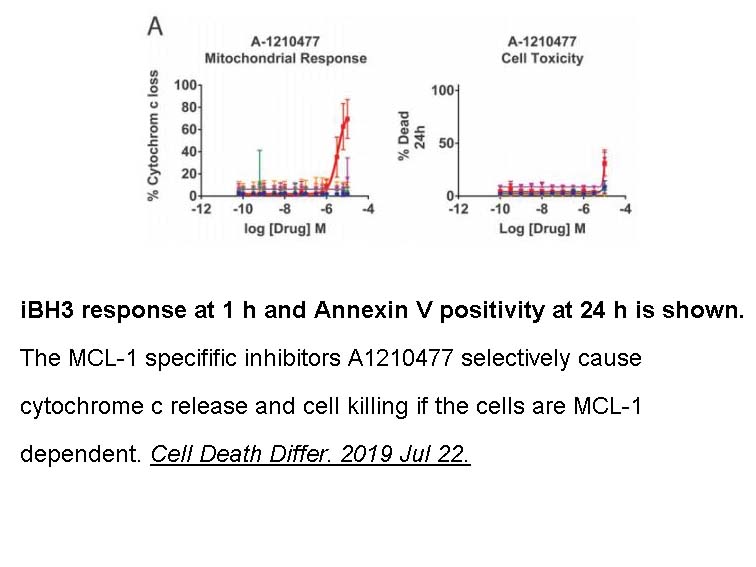
- 3. Villalobos-Ortiz M, Ryan J, et al. "BH3 profiling discriminates on-target small molecule BH3 mimetics from putative mimetics." Cell Death Differ. 2019 Jul 22. PMID:31332296
- 4. Bianchetti E, Bates SJ, et al. "Usp9X Regulates Cell Death in Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors." Sci Rep. 2018 Nov 26;8(1):17390. PMID:30478285
- 5. Campbell KJ, Dhayade S, et al. "MCL-1 is a prognostic indicator and drug target in breast cancer." Cell Death Dis. 2018 Jan 16;9(2):19. PMID:29339815
| Storage | Store at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 850.04 |
| Cas No. | 1668553-26-1 |
| Formula | C46H55N7O7S |
| Solubility | insoluble in DMSO; insoluble in H2O; insoluble in EtOH |
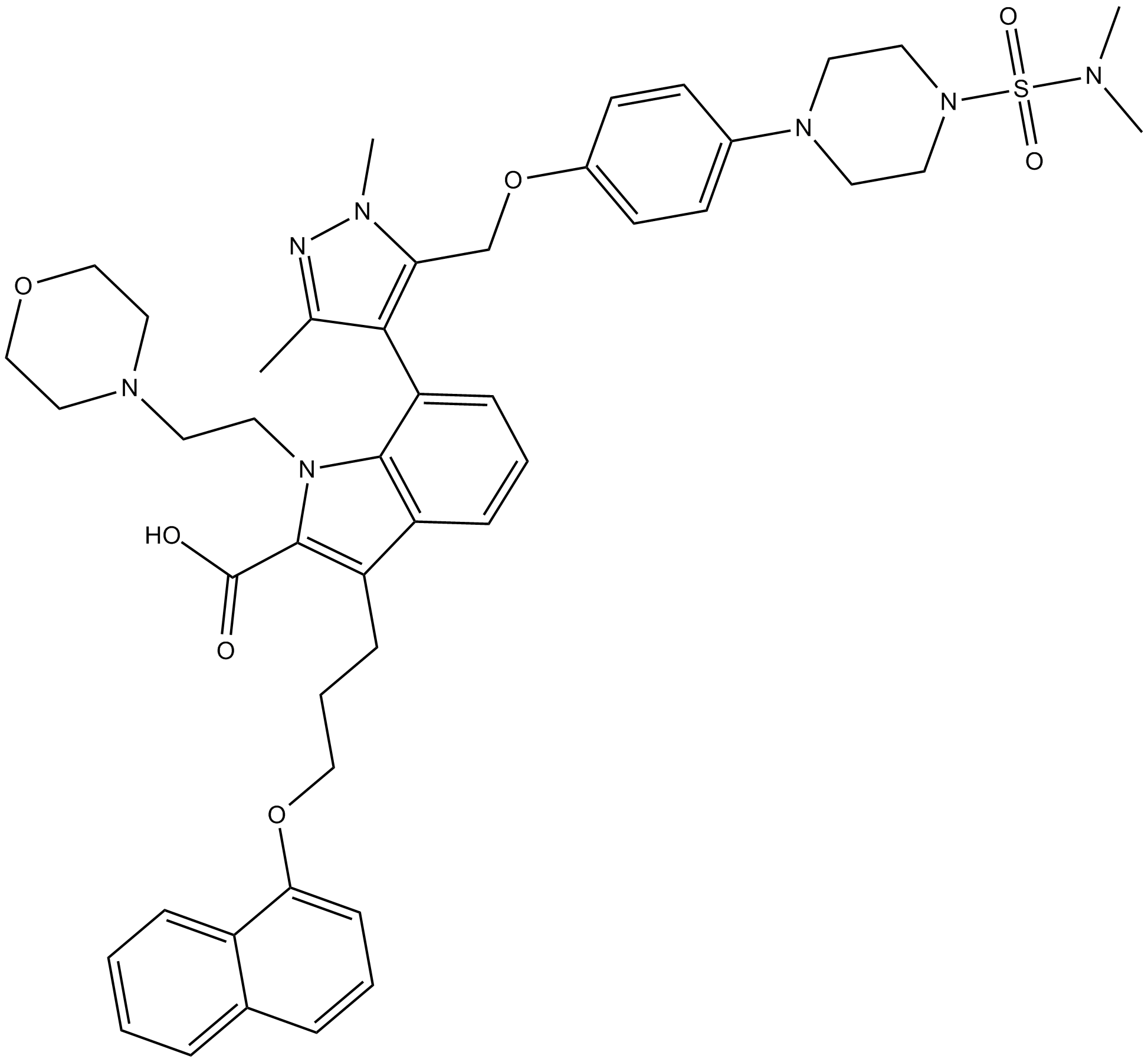
| Chemical Name | 7-(5-((4-(4-(N,N-dimethylsulfamoyl)piperazin-1-yl)phenoxy)methyl)-1,3-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-1-(2-morpholinoethyl)-3-(3-(naphthalen-1-yloxy)propyl)-1H-indole-2-carboxylic acid |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | CC1=NN(C(COC2=CC=C(N3CCN(S(N(C)C)(=O)=O)CC3)C=C2)=C1C4=CC=CC(C(CCCOC5=CC=CC6=CC=CC=C65)=C7C(O)=O)=C4N7CCN8CCOCC8)C |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
| Kinase experiment [1]: | |
|
Binding affinity assays |
TR-FRET-binding affinity assays were performed for BCL-2, BCL-XL and MCL-1 in 4.52 mM monobasic potassium phosphate, 15.48 mM dibasic potassium phosphate, 1 mM sodium EDTA, 0.05% Pluronic F-68 detergent, 50 mM sodium chloride and 1 mM DTT (pH 7.5). For MCL-1 assays, GST-tagged MCL-1 (1 nM) was mixed with 100 nM f-Bak, 1 nM Tb-labeled anti-GST antibody and compound at room temperature for 60 mins. Fluorescence was measured on an Envision plate reader using a 340/35 nm excitation filter and 520/525 (f-Bak) and 495/510 nm (Tb-labeled anti-GST antibody) emission filters. |
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
|
Cell lines |
H929 cells |
|
Preparation method |
This compound is soluble in DMSO. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 °C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below - 20 °C for several months. |
|
Reacting condition |
0 ~ 30 μM; 4 hrs |
|
Applications |
In H929 cells, A-1210477 bound selectively and strongly to MCL-1, and reduced the amount of BIM co-immunoprecipitated with MCL-1 in a dose-dependent manner with an IC50 value in the low-μM range. |
|
References: [1]. Leverson JD, Zhang H, Chen J, et al. Potent and selective small-molecule MCL-1 inhibitors demonstrate on-target cancer cell killing activity as single agents and in combination with ABT-263 (navitoclax). Cell death & disease, 2015, 6(1): e1590. |
|
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data
Related Biological Data