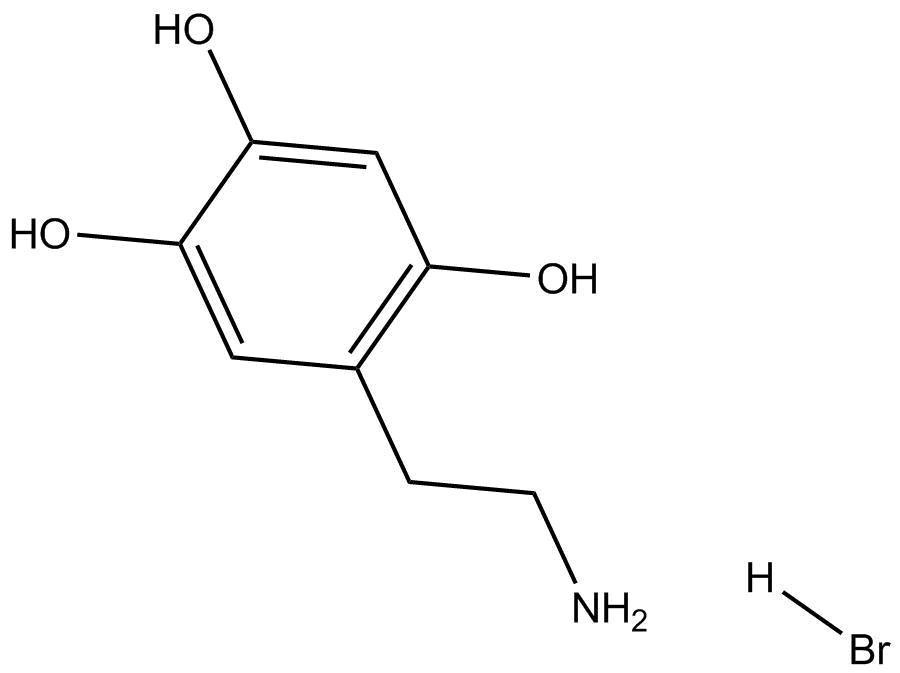
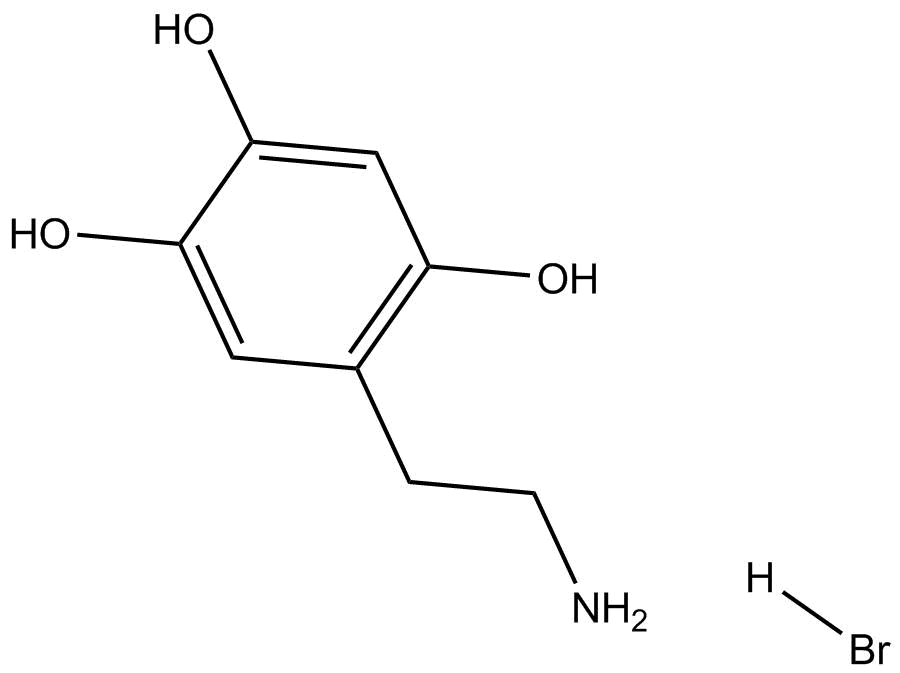
6-Hydroxydopamine hydrobromide
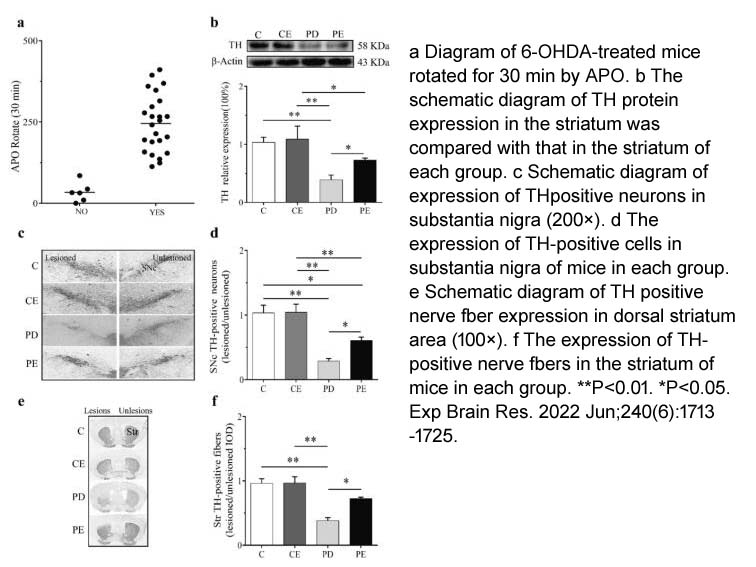
6-OHDA (CAS 28094-15-7)is a catecholaminergic neurotoxin widely utilized to induce dopaminergic lesions and parkinsonian symptoms in rodent models of Parkinson’s disease. Administration of 6-OHDA into the substantia nigra, medial forebrain bundle (MFB), or striatum at doses of 9, 6, and 18 μg, respectively, results in locomotor impairment in mice and a significant loss of tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive neurons in the mouse brain. Intracisternal administration of 6-OHDA (200 μg) has been shown to decrease both dopamine and norepinephrine levels in the rat brain. Furthermore, 6-OHDA induces apoptosis in primary rat cortical cells and PC12 rat adrenal cells at a concentration of 50 μM. At a concentration of 75 μM, 6-OHDA activates caspase-3, -8, and -9 in a time-dependent manner, increases intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in PC12 cells, and induces apoptosis in the rat substantia nigra when stereotaxically injected into the right MFB.
References:
[1] Blum D, Torch S, Lambeng N, Nissou M, Benabid AL, Sadoul R, Verna JM. Molecular pathways involved in the neurotoxicity of 6-OHDA, dopamine and MPTP: contribution to the apoptotic theory in Parkinson's disease. Prog Neurobiol. 2001 Oct;65(2):135-72. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0082(01)00003-x. PMID: 11403877.
[2] Heuer A, Smith GA, Lelos MJ, Lane EL, Dunnett SB. Unilateral nigrostriatal 6-hydroxydopamine lesions in mice I: motor impairments identify extent of dopamine depletion at three different lesion sites. Behav Brain Res. 2012 Mar 1;228(1):30-43. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2011.11.027. Epub 2011 Nov 28. PMID: 22146593.
[3] Breese GR, Traylor TD. Effect of 6-hydroxydopamine on brain norepinephrine and dopamine evidence for selective degeneration of catecholamine neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 Sep;174(3):413-20. PMID: 5456173; PMCID: PMC3055658.
[4] Han BS, Noh JS, Gwag BJ, Oh YJ. A distinct death mechanism is induced by 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium or by 6-hydroxydopamine in cultured rat cortical neurons: degradation and dephosphorylation of tau. Neurosci Lett. 2003 May 1;341(2):99-102. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(03)00173-3. PMID: 12686375.
[5] Fujita H, Ogino T, Kobuchi H, Fujiwara T, Yano H, Akiyama J, Utsumi K, Sasaki J. Cell-permeable cAMP analog suppresses 6-hydroxydopamine-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells through the activation of the Akt pathway. Brain Res. 2006 Oct 3;1113(1):10-23. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.06.079. Epub 2006 Aug 30. PMID: 16945353.
[6] He Y, Lee T, Leong SK. 6-Hydroxydopamine induced apoptosis of dopaminergic cells in the rat substantia nigra. Brain Res. 2000 Mar 6;858(1):163-6. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(99)02459-2. PMID: 10700609.
| Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| M.Wt | 250.09 |
| Cas No. | 636-00-0 |
| Formula | C8H11NO3·HBr |
| Solubility | insoluble in EtOH; ≥25 mg/mL in DMSO with ultrasonic; ≥45.4 mg/mL in H2O |
| Chemical Name | 5-(2-aminoethyl)benzene-1,2,4-triol hydrobromide |
| SDF | Download SDF |
| Canonical SMILES | NCCc(c(O)c1)cc(O)c1O.Br |
| Shipping Condition | Small Molecules with Blue Ice, Modified Nucleotides with Dry Ice. |
| General tips | We do not recommend long-term storage for the solution, please use it up soon. |
Quality Control & MSDS
- View current batch:
Chemical structure
Related Biological Data