Ubiquitination/ Proteasome
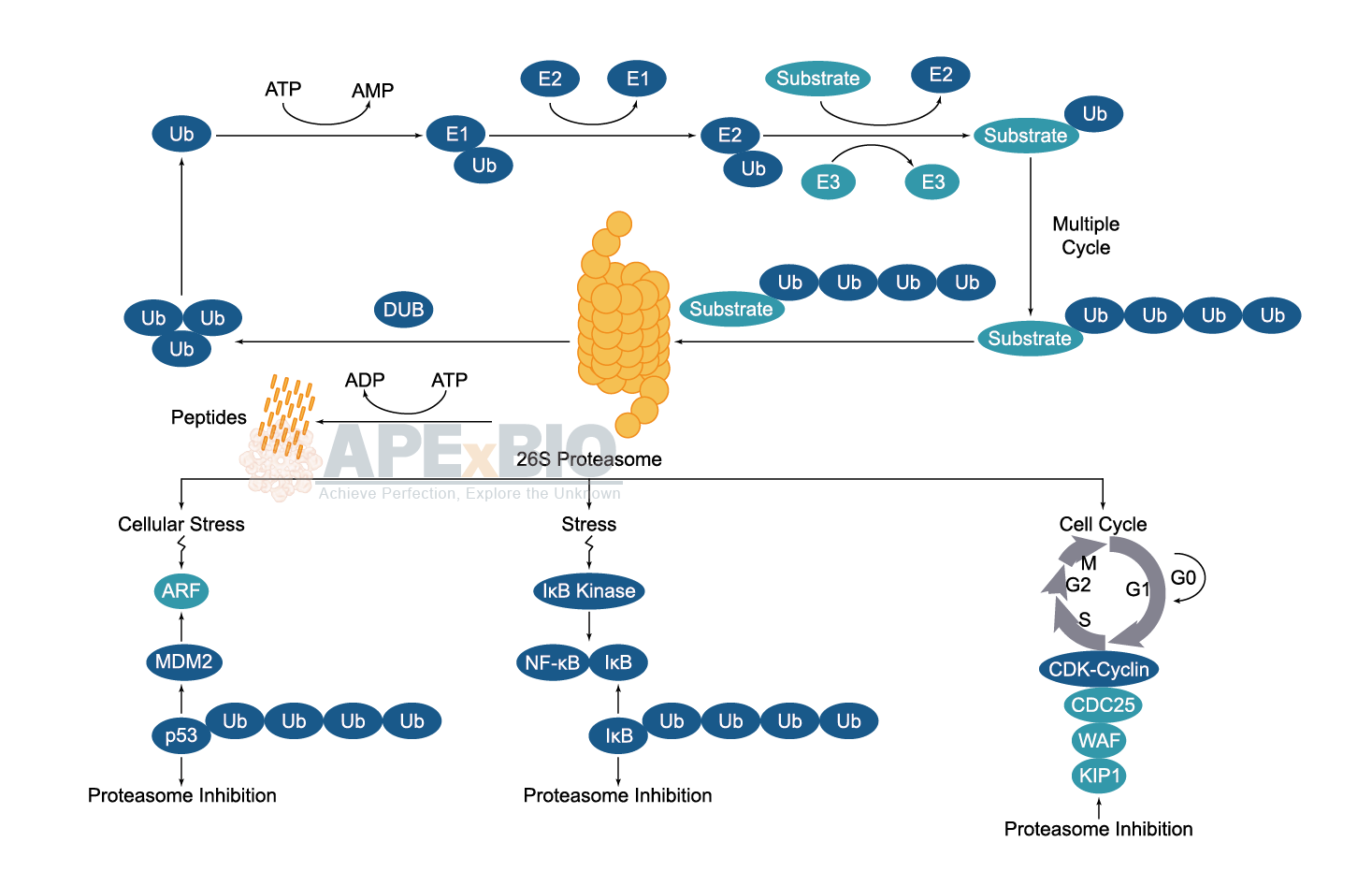
Once the substrate protein is labeled, proteasome will bind to a polyubiquitin chain, allowing the degradation of the labeled protein. The polyubiquitinated target protein is then recognized and degraded by the 26S proteasome. Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) reverse the process of ubiquitination by removing ubiquitin from its substrate protein. Dysregulation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system has been linked to cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases etc.
-
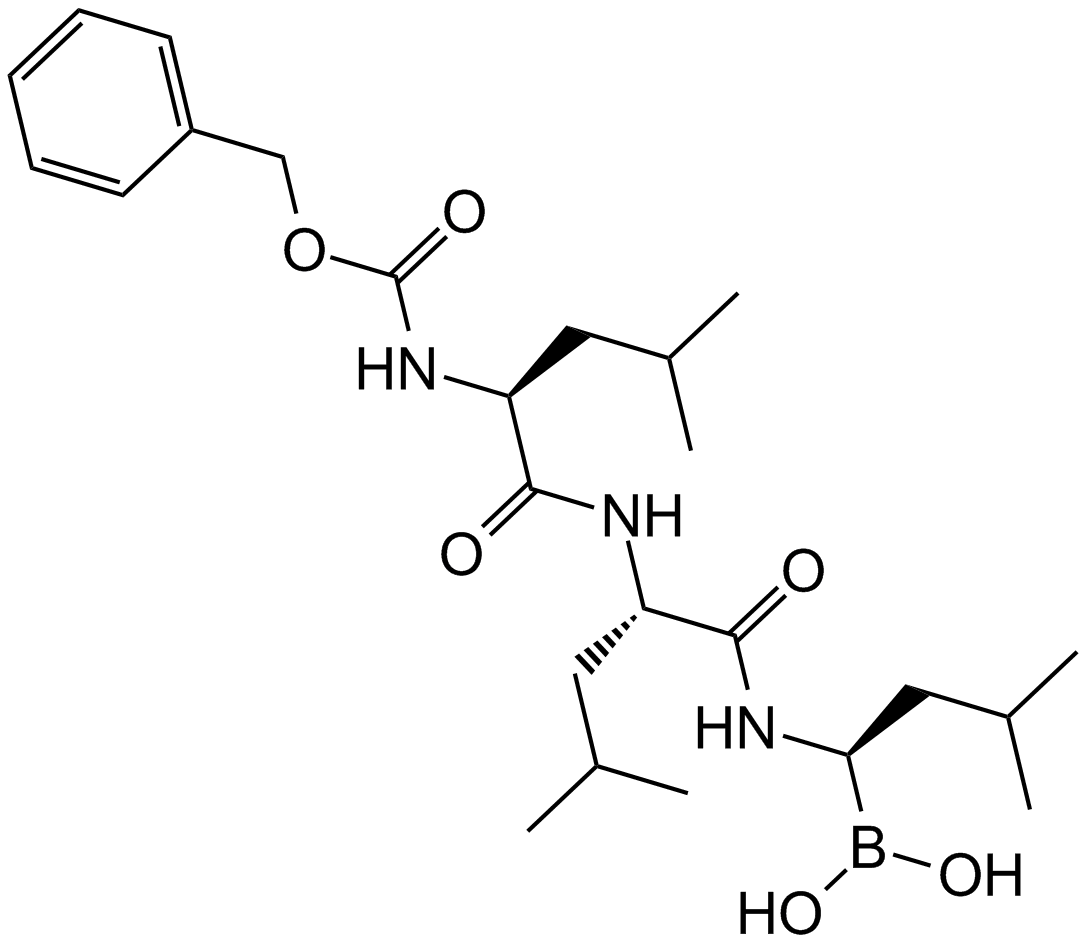 A8179 MG-2621 CitationTarget: ProteasomeSummary: Proteasome inhibitor
A8179 MG-2621 CitationTarget: ProteasomeSummary: Proteasome inhibitor -
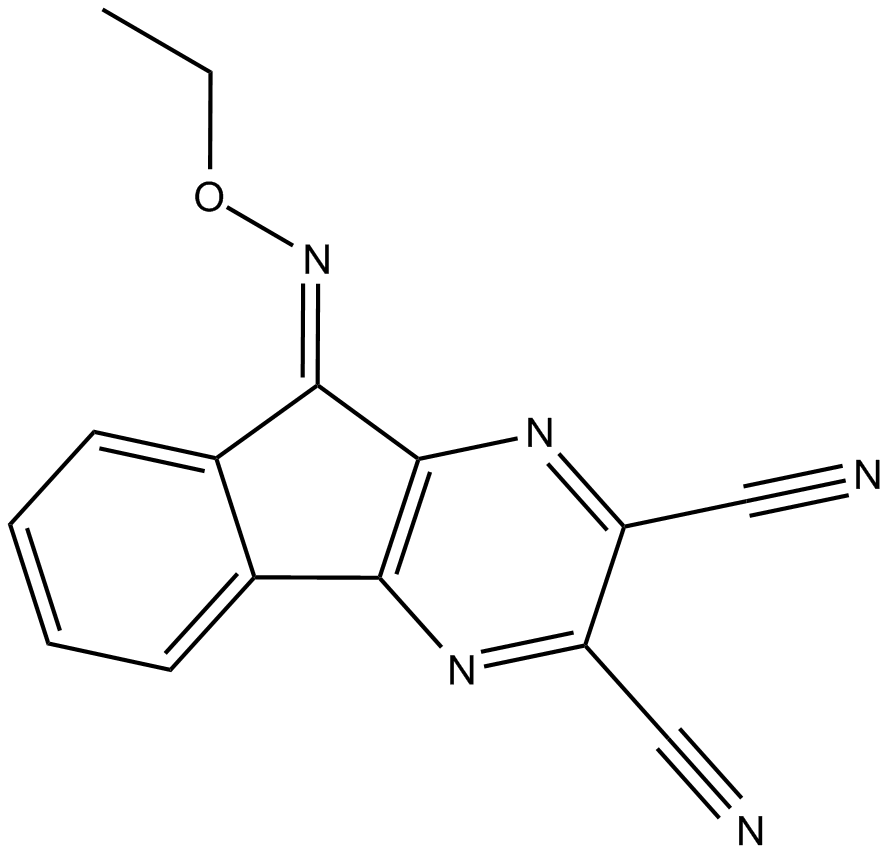 B3515 DUBs-IN-2Summary: deubiquitinase enzyme inhibitor
B3515 DUBs-IN-2Summary: deubiquitinase enzyme inhibitor -
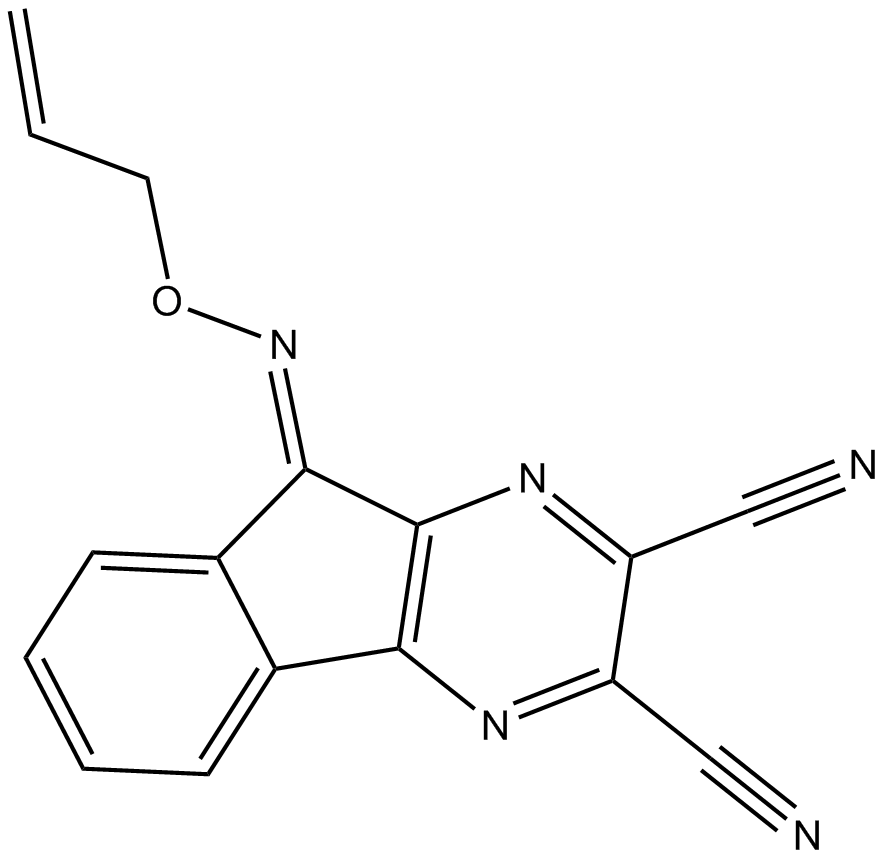 B3516 DUBs-IN-3Summary: potent deubiquitinase enzyme inhibitor
B3516 DUBs-IN-3Summary: potent deubiquitinase enzyme inhibitor -
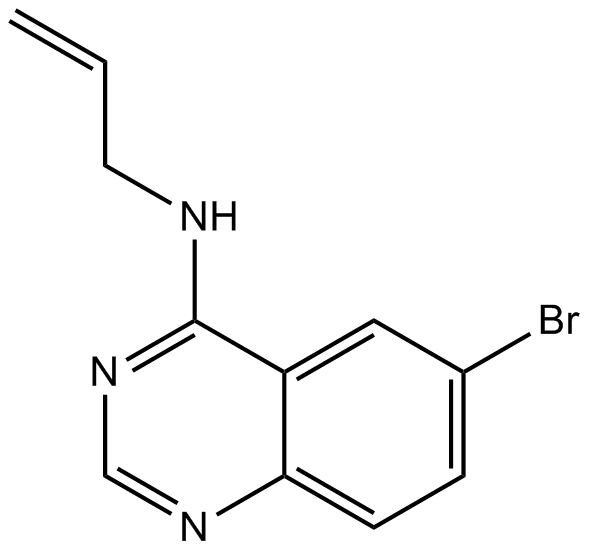 B7637 SMER 28Summary: Positive regulator of autophagy
B7637 SMER 28Summary: Positive regulator of autophagy -
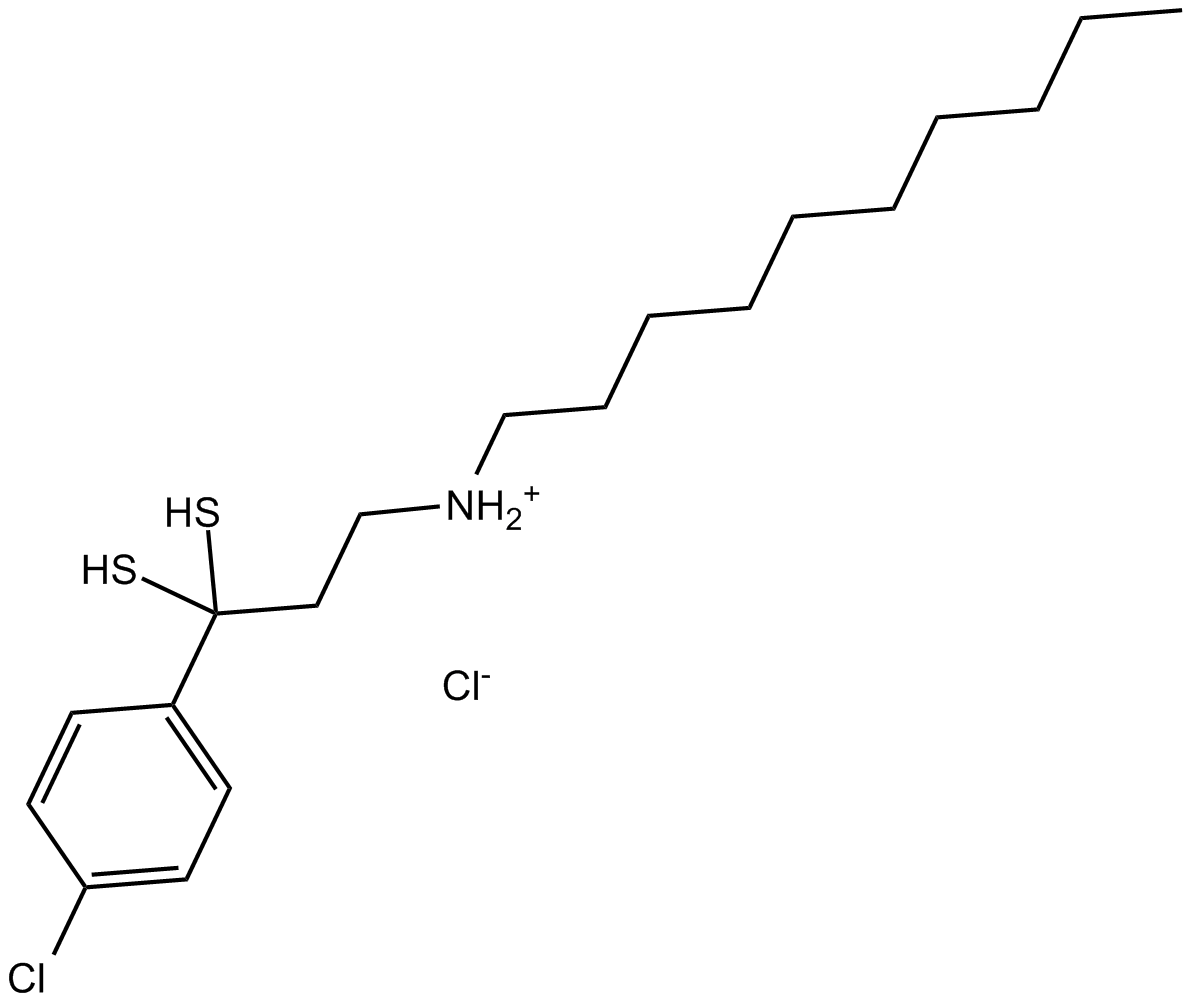 B7727 NSC 624206Summary: Ubiquitin-activating enzyme (E1) inhibitor
B7727 NSC 624206Summary: Ubiquitin-activating enzyme (E1) inhibitor -
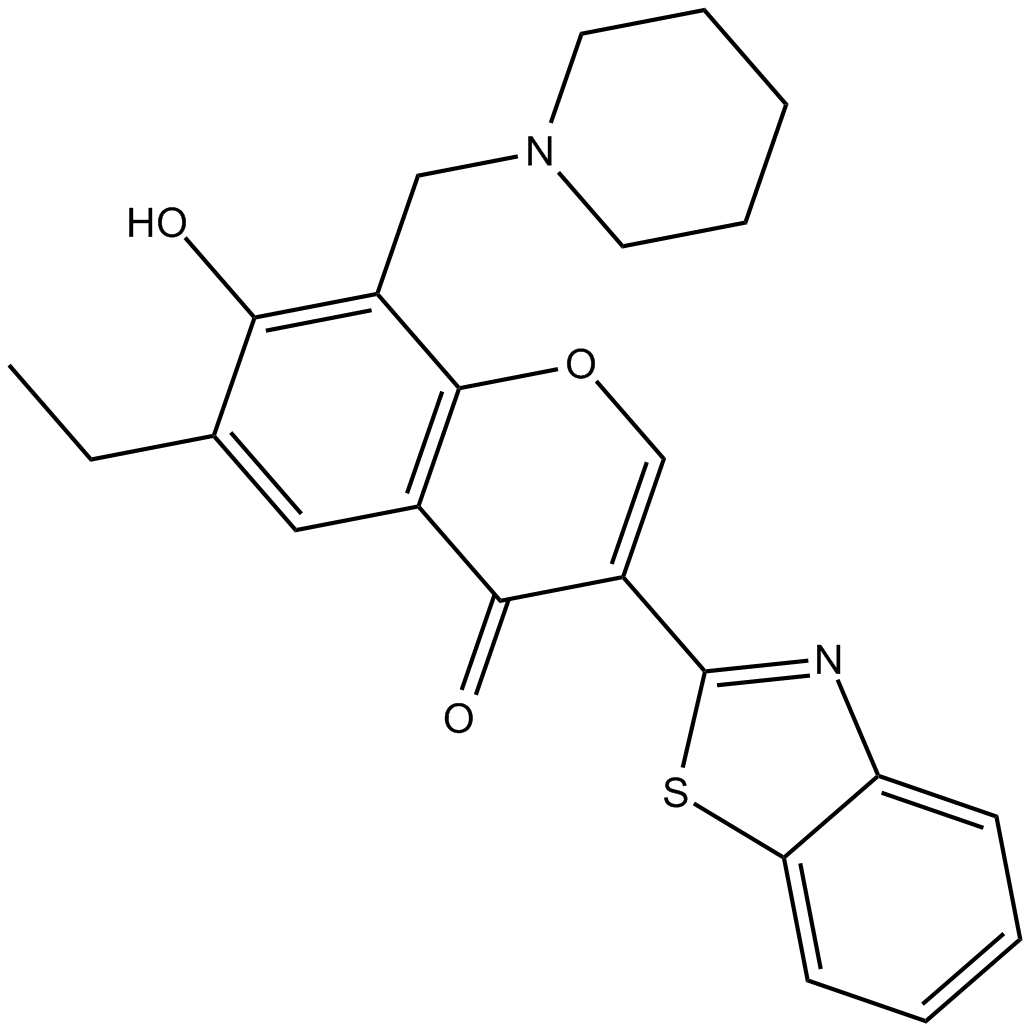 B7745 SZL P1-41Summary: Skp2 inhibitor
B7745 SZL P1-41Summary: Skp2 inhibitor -
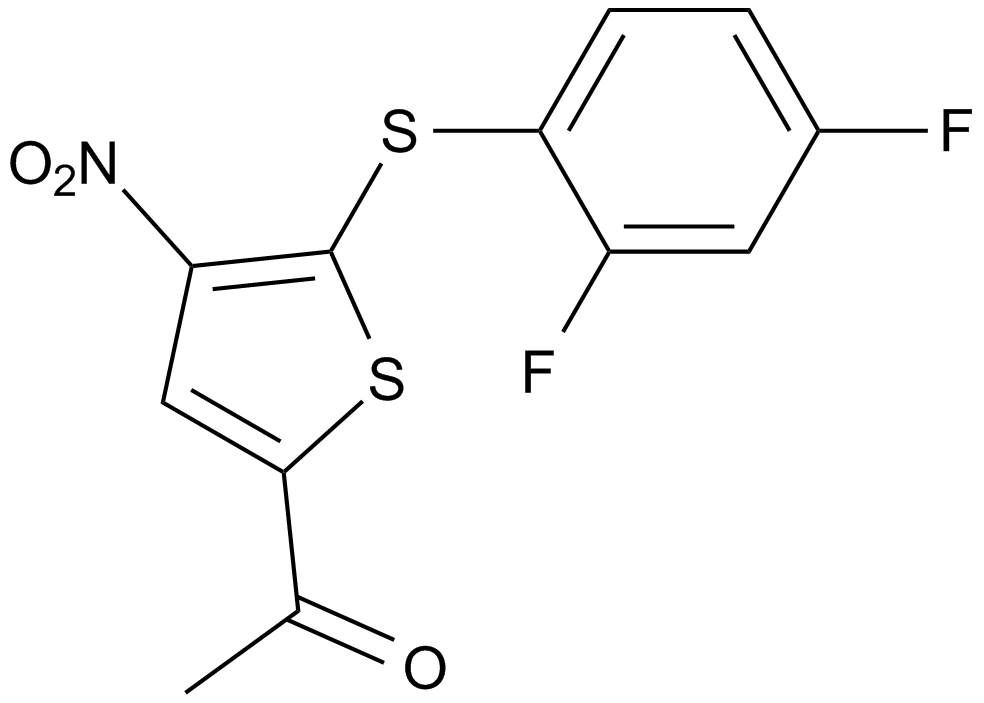 A8198 P 22077Summary: USP7/(DUB)USP47 inhibitor
A8198 P 22077Summary: USP7/(DUB)USP47 inhibitor -
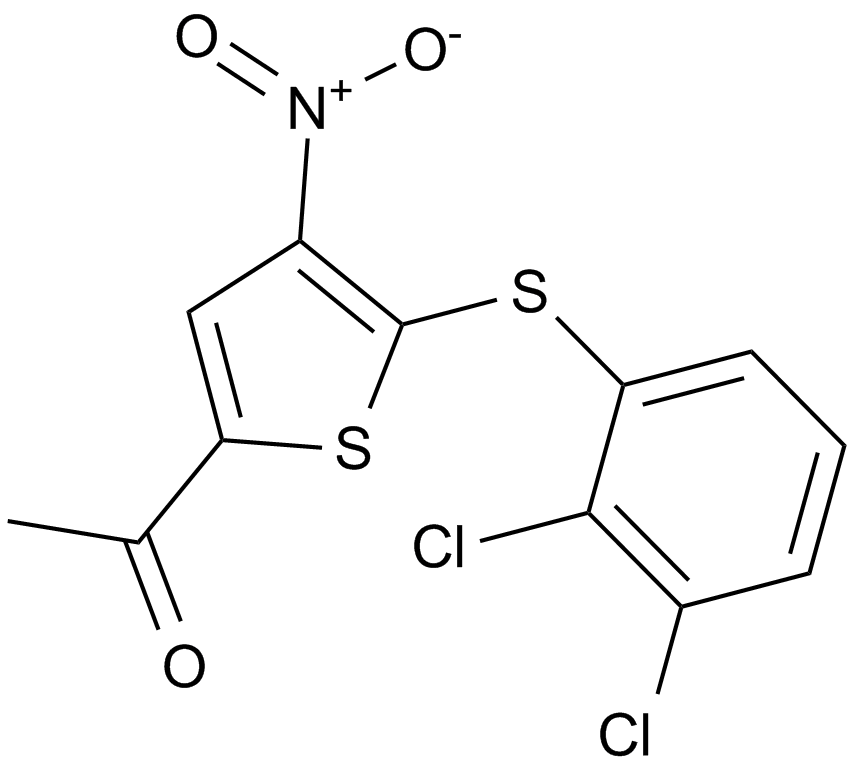 A3023 P0050911 CitationTarget: Ubiquitin-specific proteasesSummary: Ubiquitin-specific protease 7 (USP7) inhibitor
A3023 P0050911 CitationTarget: Ubiquitin-specific proteasesSummary: Ubiquitin-specific protease 7 (USP7) inhibitor -
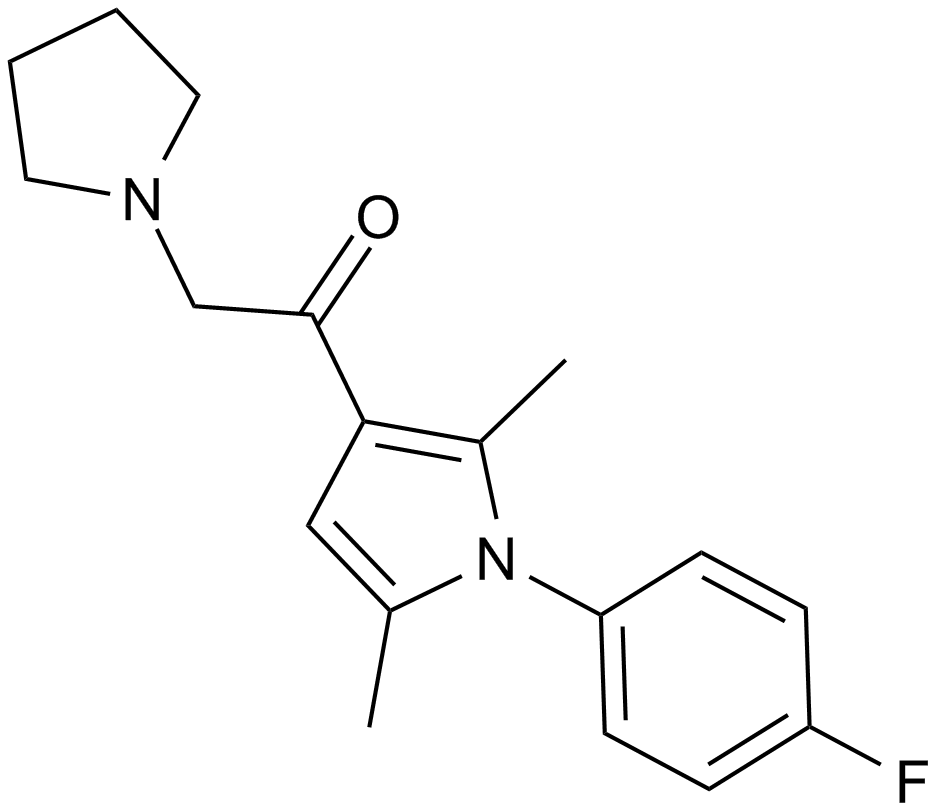 A4002 IU1Summary: Usp14 inhibitor
A4002 IU1Summary: Usp14 inhibitor -
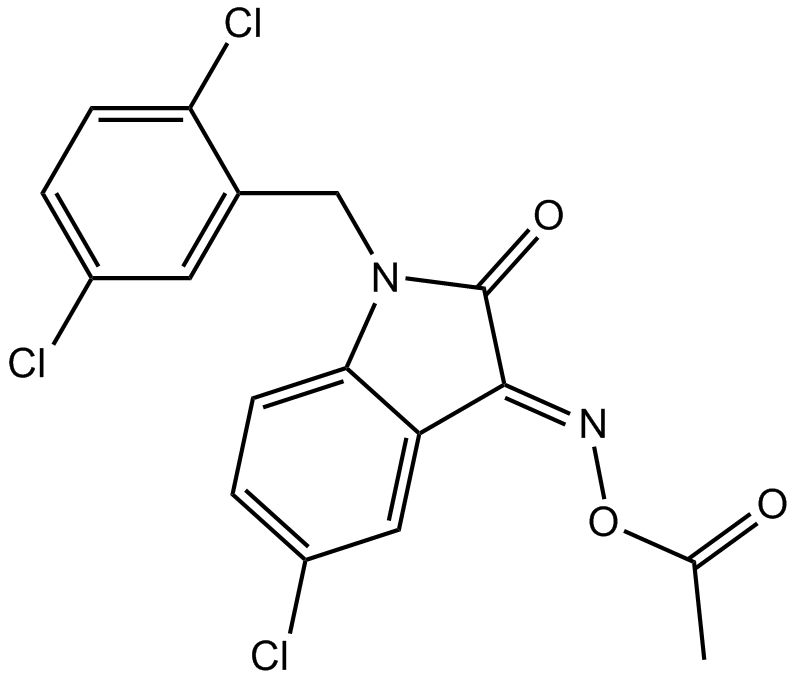 A4003 LDN 57444Target: UCHSummary: UCH-L1 inhibitor,reversible competitve
A4003 LDN 57444Target: UCHSummary: UCH-L1 inhibitor,reversible competitve

