Search results for: 'signaling pathways ubiquitination proteasome'
-
 L1049 DiscoveryProbe™ Ubiquitination Compound LibrarySummary: A collection of 144 ubiquitination compounds supplied as lyophilized powder or pre-dissolved DMSO solutions
L1049 DiscoveryProbe™ Ubiquitination Compound LibrarySummary: A collection of 144 ubiquitination compounds supplied as lyophilized powder or pre-dissolved DMSO solutions -
 L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044 DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling LibrarySummary: A unique collection of 73 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research. -
 L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026 DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Library1 CitationSummary: A unique collection of 556 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch. -
 K2096 Proteasome Activity Fluorometric Assay KitSummary: Specifically detects proteasome activity
K2096 Proteasome Activity Fluorometric Assay KitSummary: Specifically detects proteasome activity -
 K2242 Fluorometric Proteasome 20S Activity Assay KitSummary: A kit for the detection of proteasome 20S activity by the fluorescent substrate LLVY-R110
K2242 Fluorometric Proteasome 20S Activity Assay KitSummary: A kit for the detection of proteasome 20S activity by the fluorescent substrate LLVY-R110 -
 L1044P DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 178 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research.
L1044P DiscoveryProbe™ NF-κB Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 178 NF-κB inhibitors for NF-κB signaling pathway research. -
 L1026P DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 948 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch.
L1026P DiscoveryProbe™ Neuronal Signaling Compound Library PlusSummary: A unique collection of 948 neuronal signaling-related small molecules for neuroscience reasearch. -
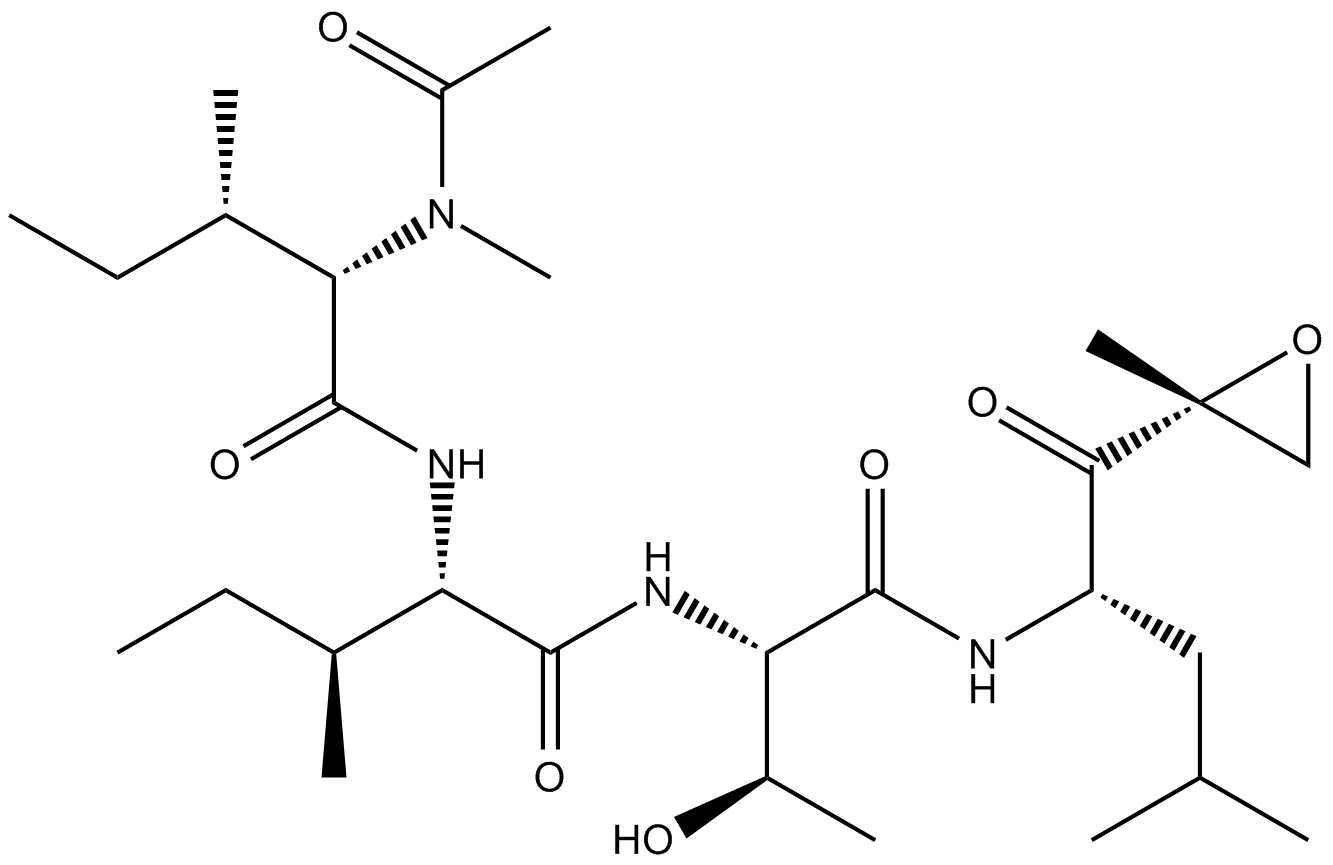 A2606 Epoxomicin25 CitationSummary: proteasome inhibitor
A2606 Epoxomicin25 CitationSummary: proteasome inhibitor -
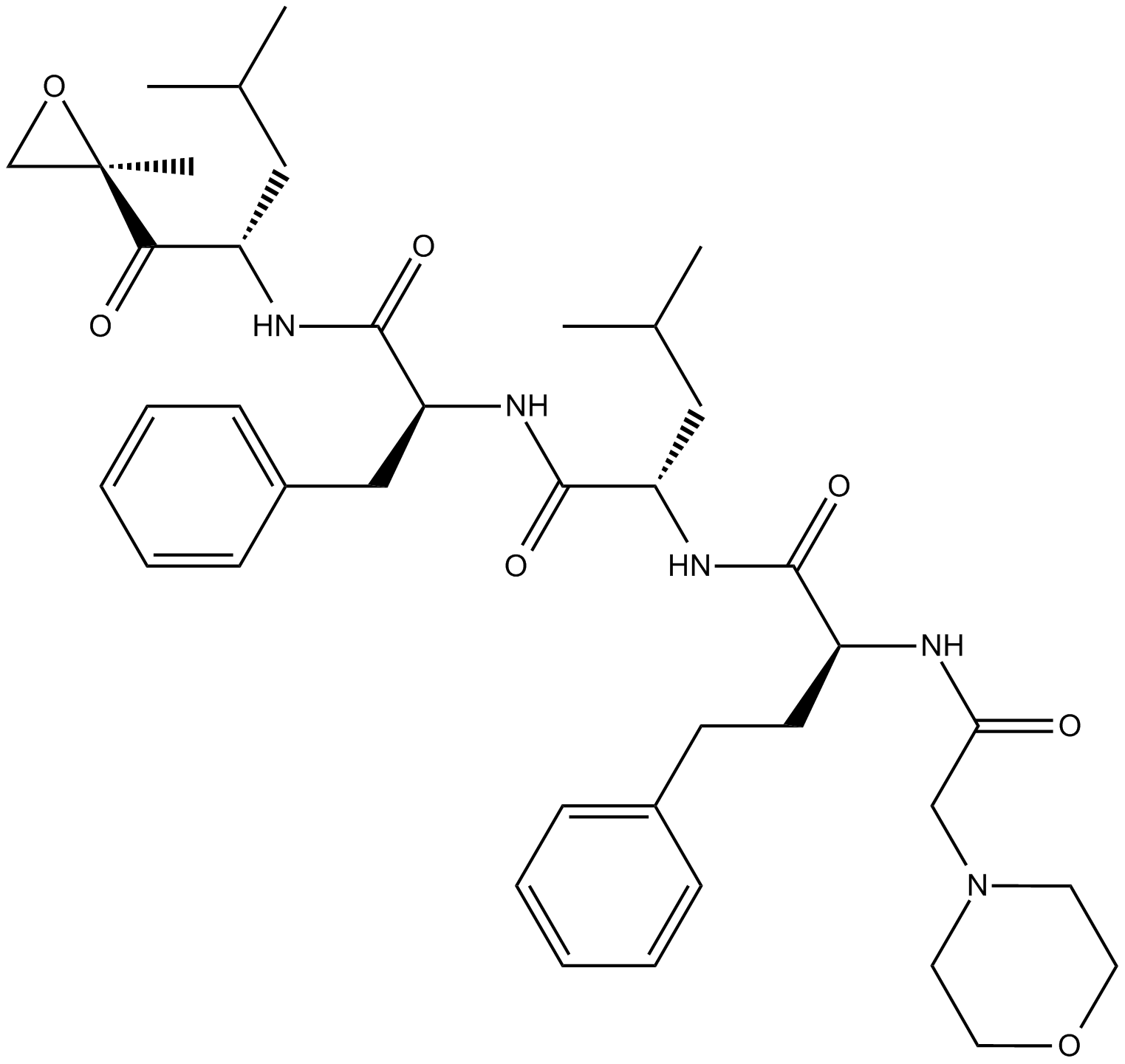 A1933 Carfilzomib (PR-171)10 CitationTarget: ProteasomeSummary: Proteasome inhibitor, epoxomicin analog
A1933 Carfilzomib (PR-171)10 CitationTarget: ProteasomeSummary: Proteasome inhibitor, epoxomicin analog -
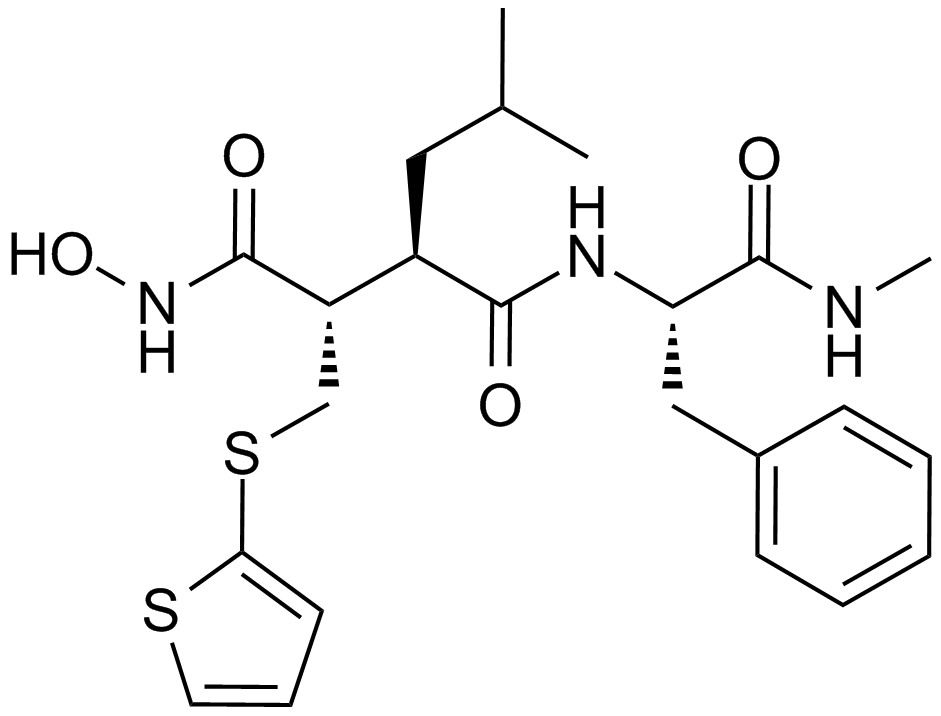 A2577 Batimastat (BB-94)17 CitationSummary: MMP inhibitor
A2577 Batimastat (BB-94)17 CitationSummary: MMP inhibitor


