Transferase
Transferases are a collection of a large and diverse group of enzymes that specifically catalyze the transfer of one or more functional groups from one molecule (the donor) to another (the acceptor). A few transferases involved in this category include farnesyltransferase (FTase), diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT) and catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT). Ftase catalyzes the transfer of a farnesyl moiety to the cysteine terminal residue (the sulfhydryl cysteine of the CAAS motif)) of substrate proteins. DGAT catalyzes the final step of the triacylglycerol (TG) biosynthetic pathway, where diacylglycerol is esterified to produce TG. COMT catalyzes the methylation of catechol substrates utilizing S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) as a methyl donor and generating O-methylated catechol and S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine.
-
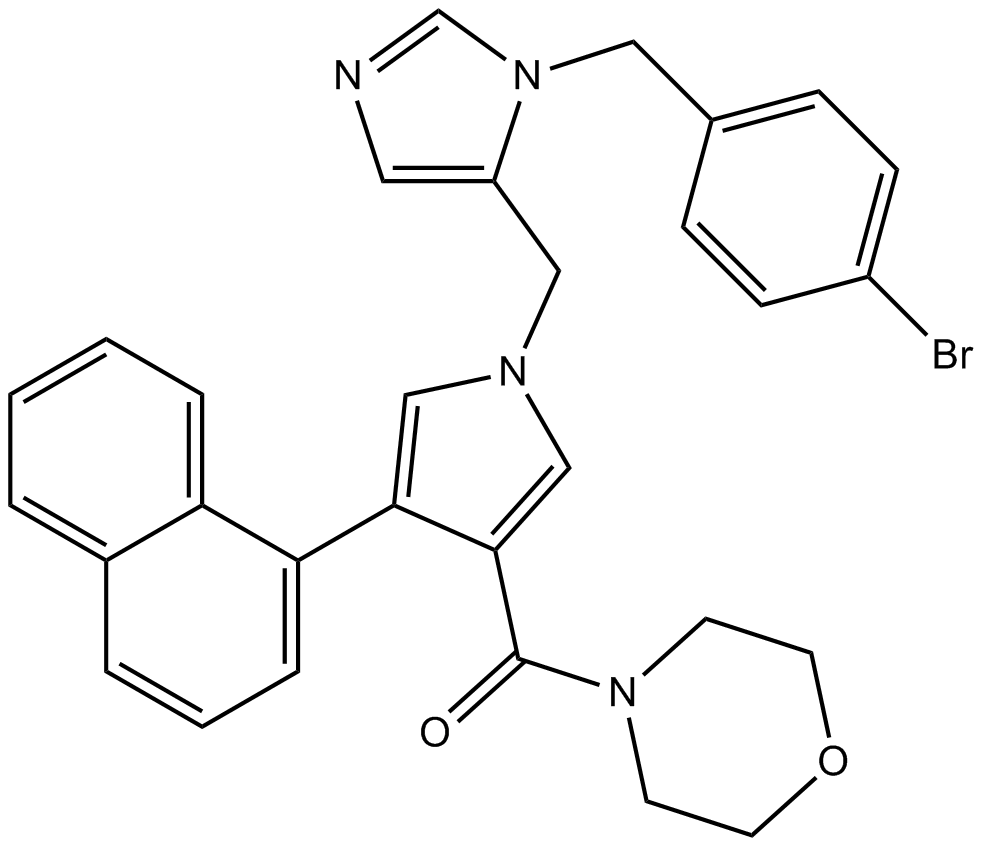 B3703 LB42708Target: FtaseSummary: Selective FTase inhibitor
B3703 LB42708Target: FtaseSummary: Selective FTase inhibitor -
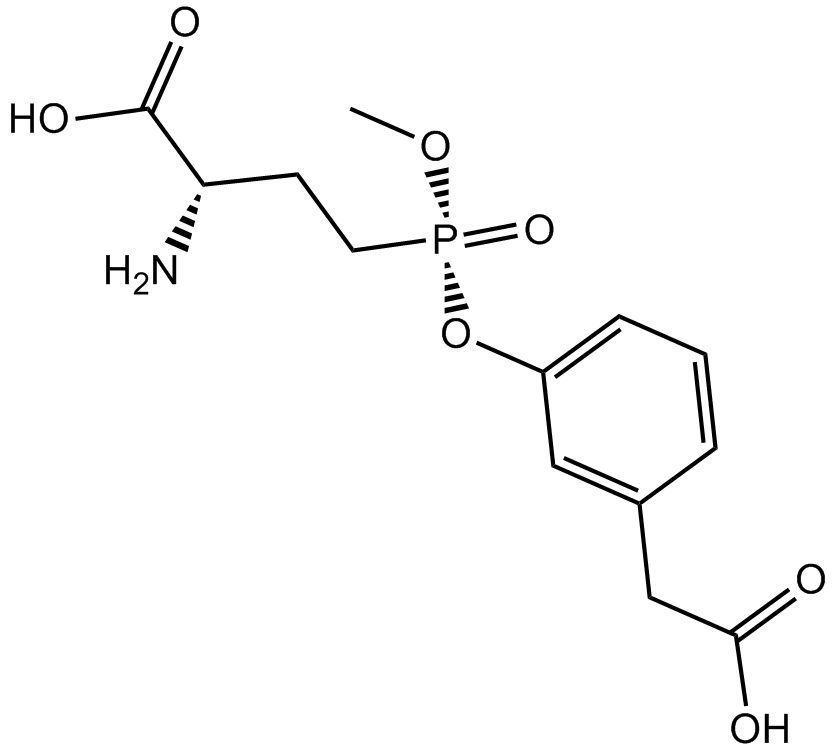 B5602 GGsTopSummary: γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) inhibitor, novel and irreversible
B5602 GGsTopSummary: γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) inhibitor, novel and irreversible -
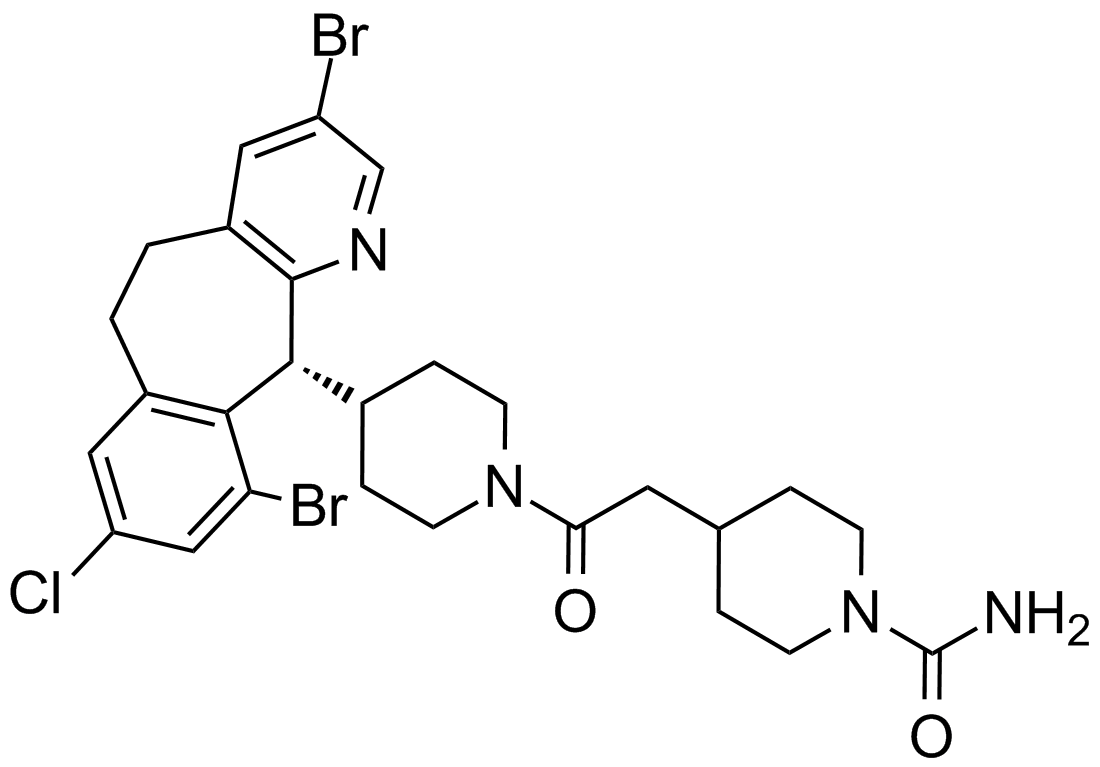 A4379 LonafarnibTarget: FPTaseSummary: Ftase inhibitor,potent and selective
A4379 LonafarnibTarget: FPTaseSummary: Ftase inhibitor,potent and selective -
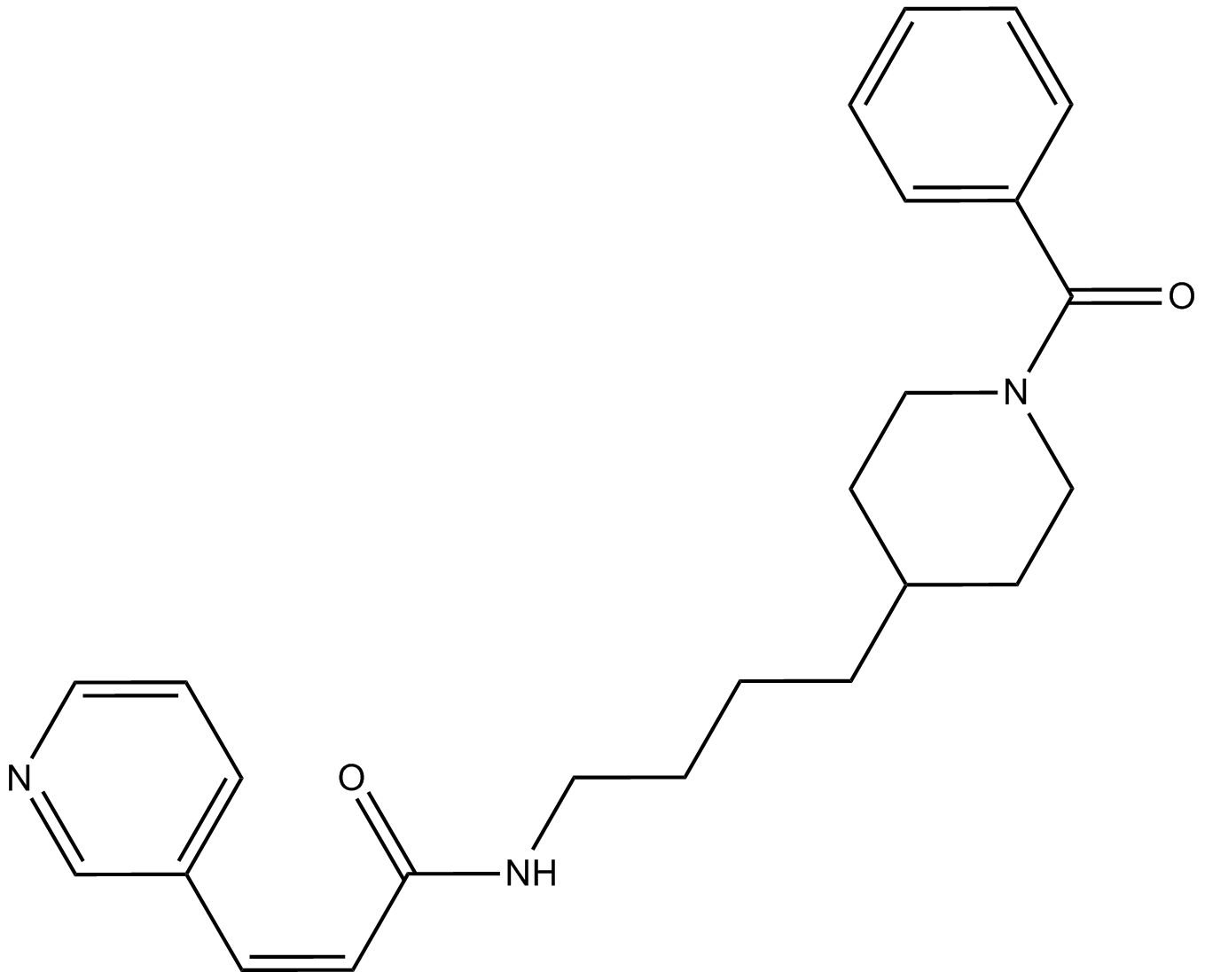 A4381 FK866 (APO866)1 CitationTarget: NamptSummary: NAMPT inhibitor, non-competitive, highly specific
A4381 FK866 (APO866)1 CitationTarget: NamptSummary: NAMPT inhibitor, non-competitive, highly specific -
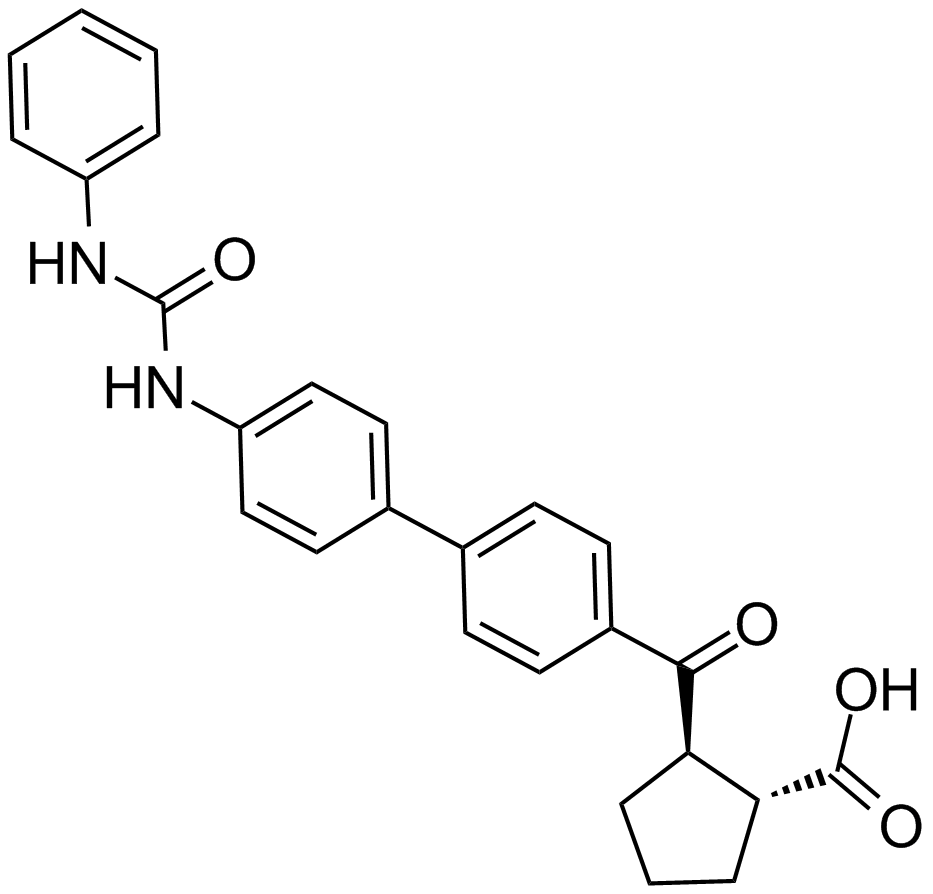 A4382 A922500Target: DGATSummary: DGAT-1 inhibitor
A4382 A922500Target: DGATSummary: DGAT-1 inhibitor -
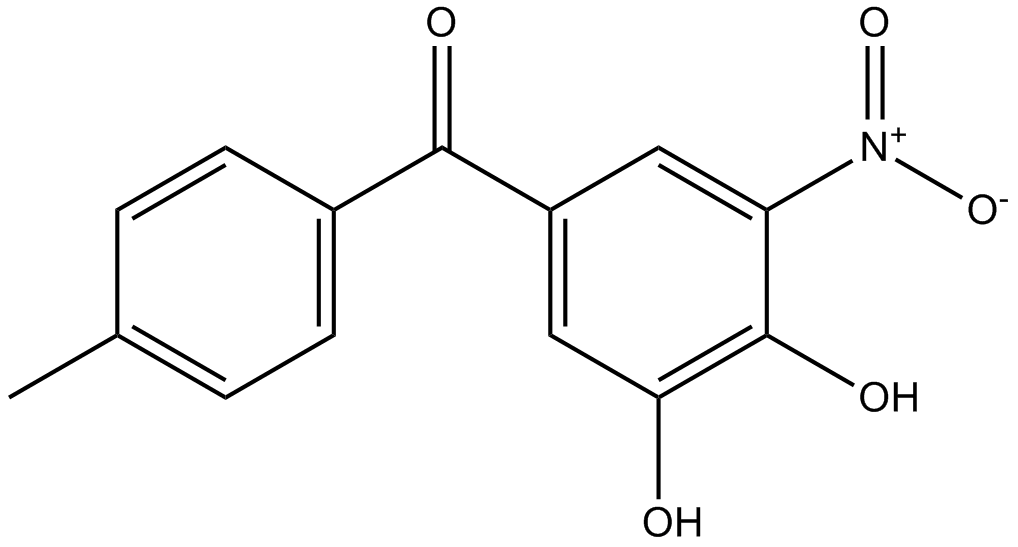 A4383 TolcaponeTarget: Catechol O-Methyltransferase (COMT)Summary: COMT inhibitor
A4383 TolcaponeTarget: Catechol O-Methyltransferase (COMT)Summary: COMT inhibitor

