Metabolism
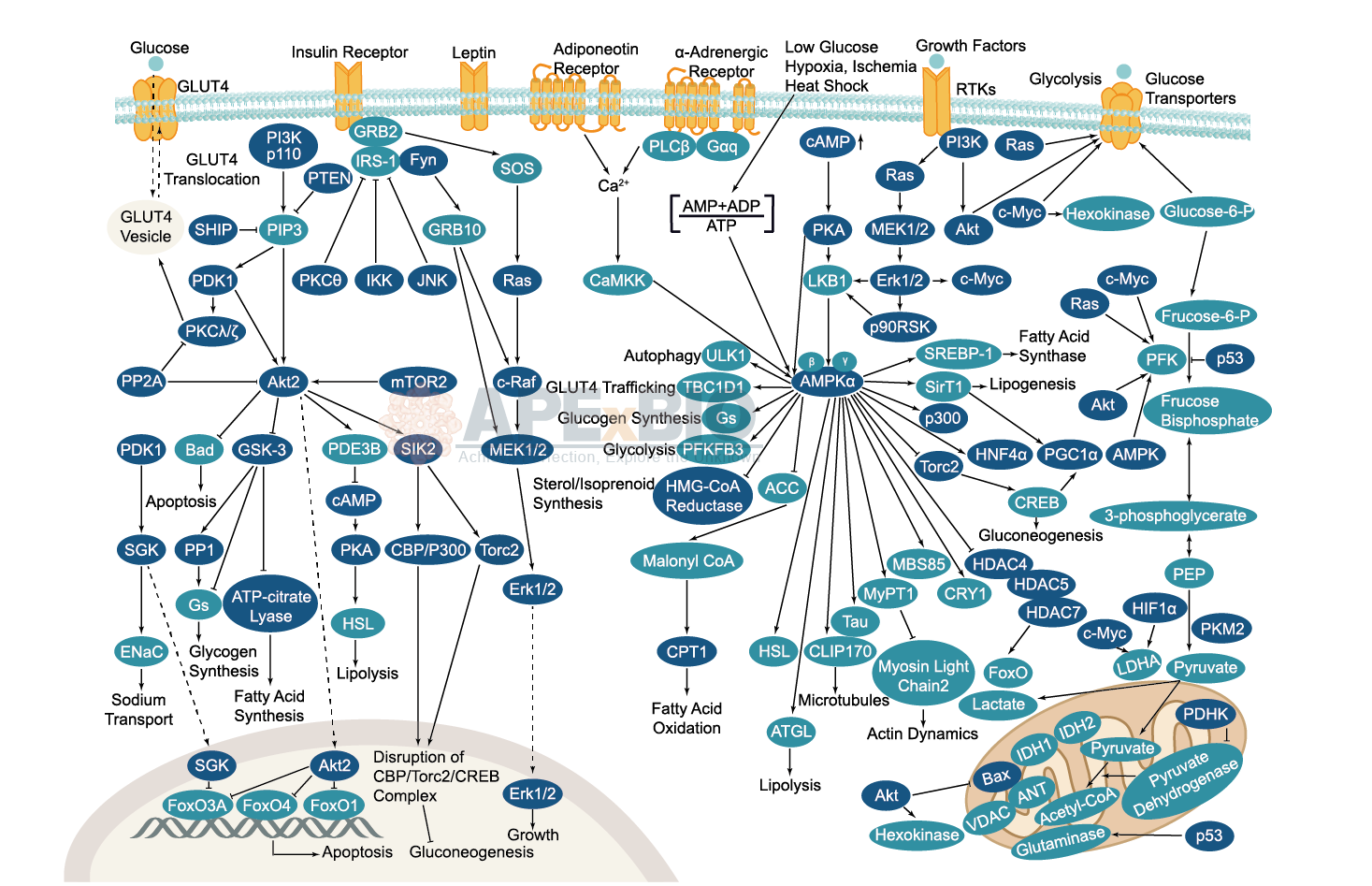
Serine/threonine kinase AMPK upregulates glucose uptake by promoting the expression and function of glucose transporters. AMPK is activated by increased AMP/ATP ratio, resulting from cellular and environmental stress, e.g. low glucose, heat shock, hypoxia and ischemia. AMPK activation positively modulates signaling transductions that refill ATP levels. Moreover, it also stimulates catabolic processes such as fatty acid oxidation and glycolysis through inhibition of ACC and activation of PFK2. AMPK negatively regulates various proteins which are important to ATP-consuming mechanisms, e.g. mTORC2, glycogen synthase, SREBP-1, and TSC2, causing the downregulation/inhibition of gluconeogenesis and glycogen, lipid and protein synthesis.
-
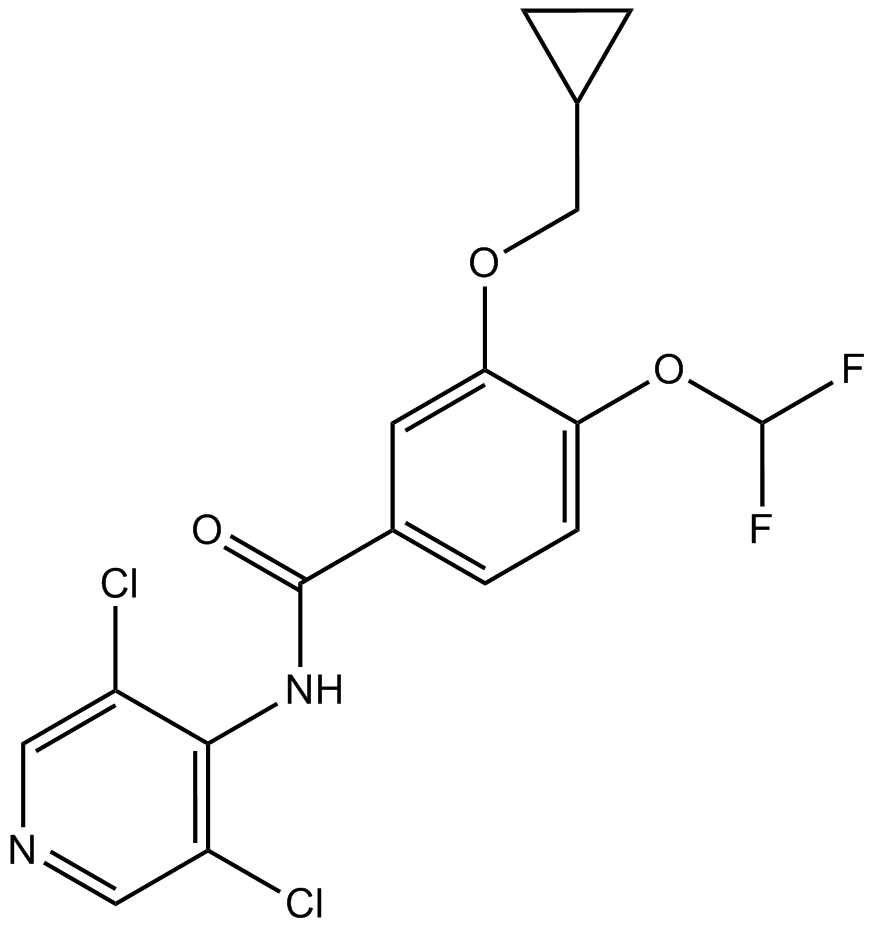 A4319 RoflumilastSummary: PDE-4 inhibitor
A4319 RoflumilastSummary: PDE-4 inhibitor -
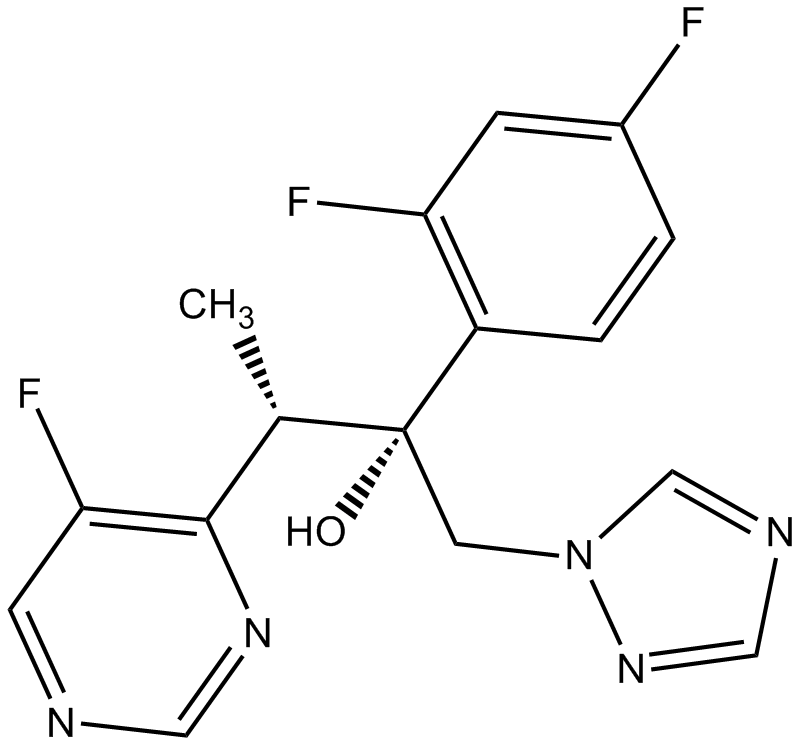 A4320 VoriconazoleSummary: CYP51 inhibitor
A4320 VoriconazoleSummary: CYP51 inhibitor -
 A4321 Sildenafil CitrateTarget: Phosphodiesterases (PDEs)Summary: Treat erectile dysfunction and PAH
A4321 Sildenafil CitrateTarget: Phosphodiesterases (PDEs)Summary: Treat erectile dysfunction and PAH -
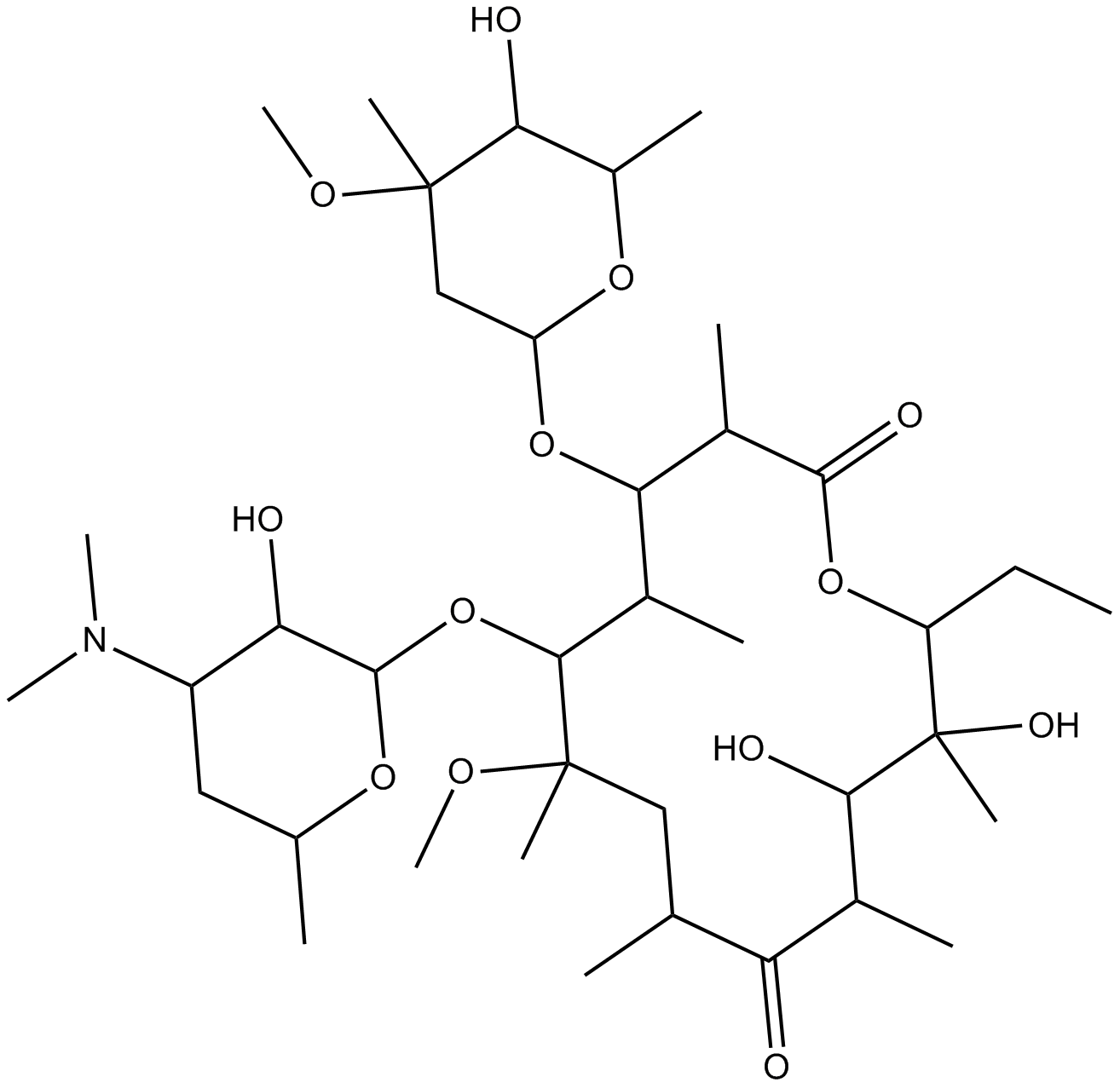 A4322 ClarithromycinTarget: Cytochrome P450 (CYP450)Summary: CYP3A inhibitor, potent
A4322 ClarithromycinTarget: Cytochrome P450 (CYP450)Summary: CYP3A inhibitor, potent -
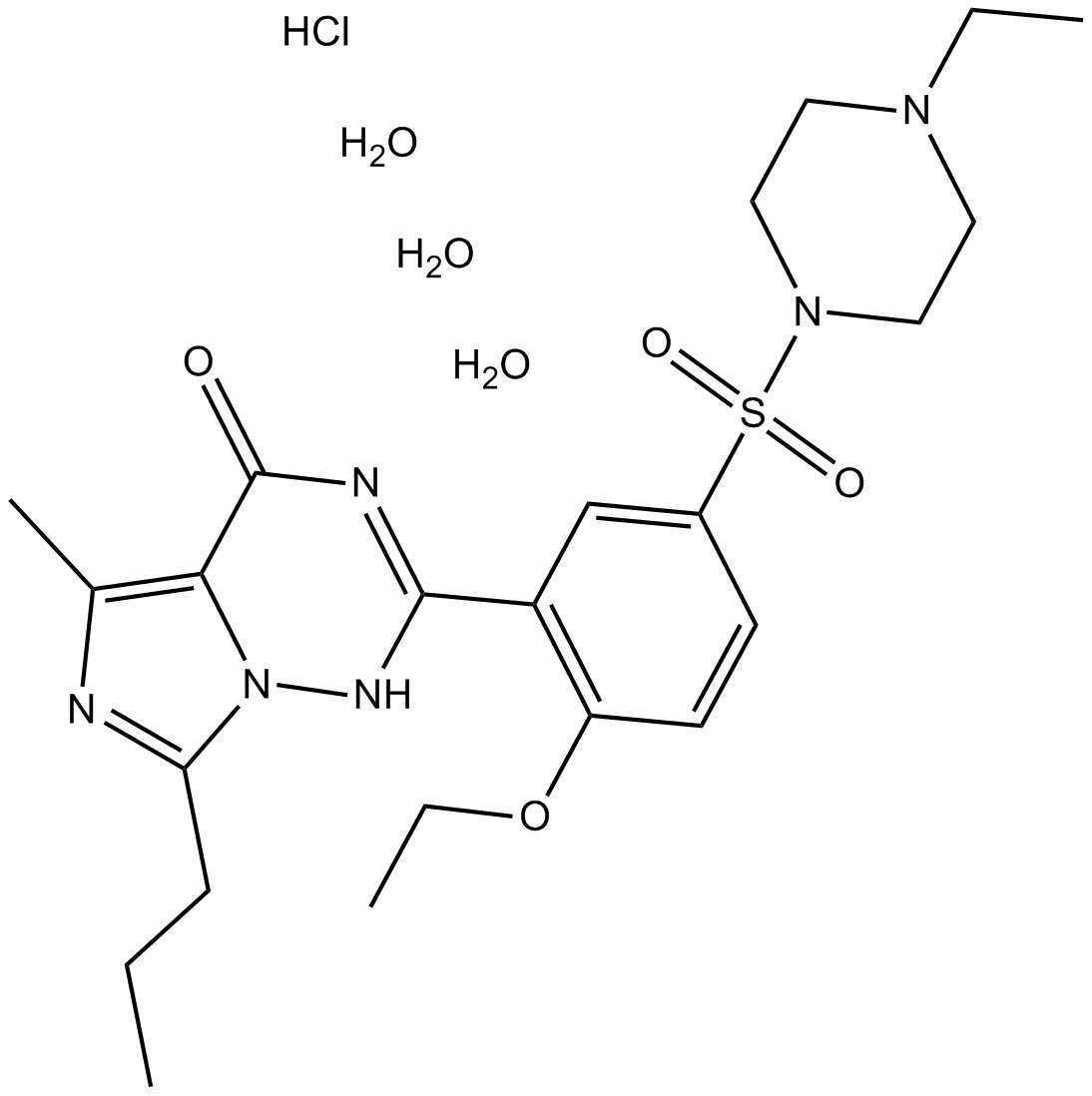 A4323 Vardenafil HCl TrihydrateTarget: Phosphodiesterases (PDEs)Summary: PDE5 inhibitor, potent and selective
A4323 Vardenafil HCl TrihydrateTarget: Phosphodiesterases (PDEs)Summary: PDE5 inhibitor, potent and selective -
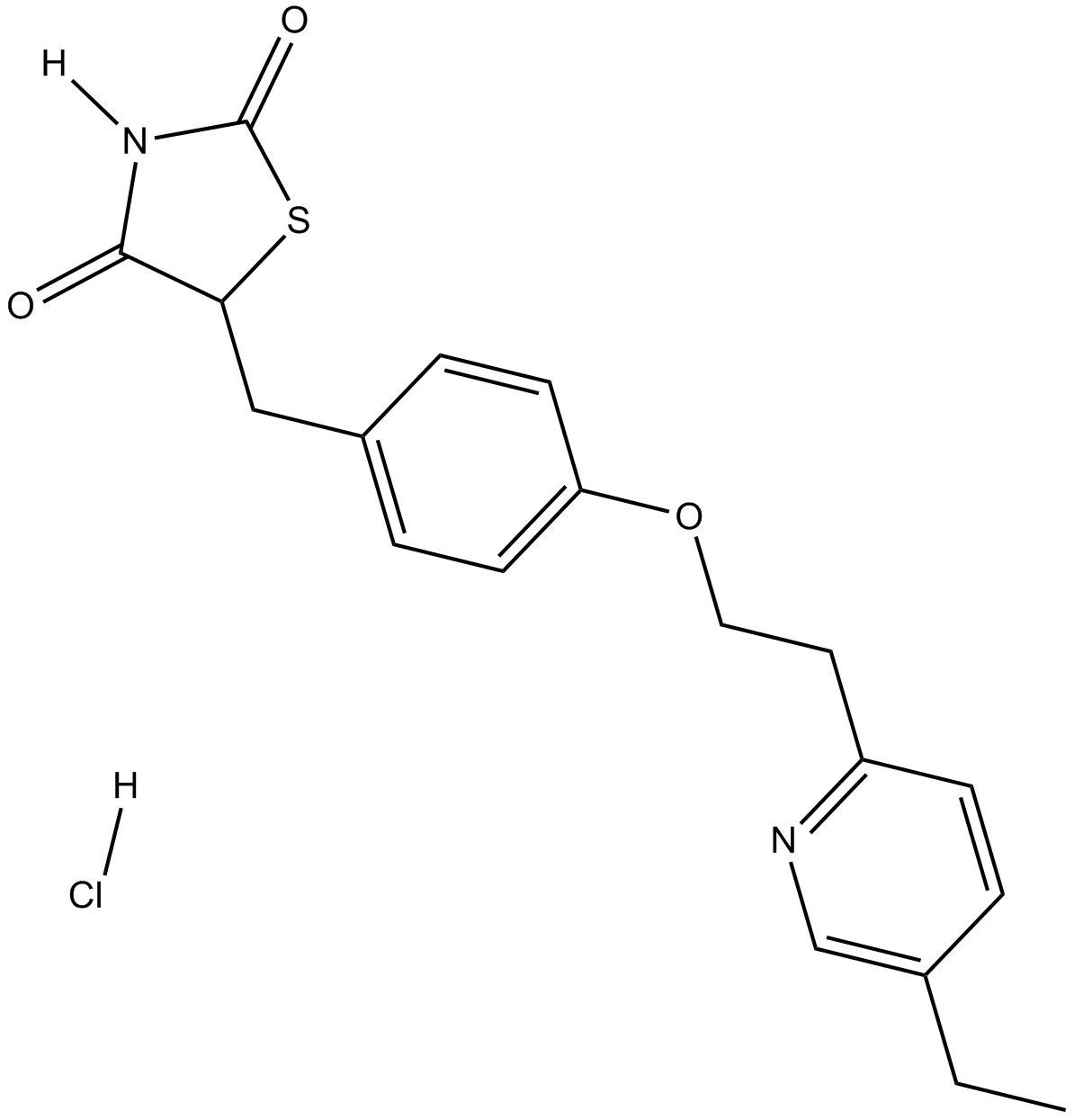 A4324 Pioglitazone HClSummary: PPARγ agonist
A4324 Pioglitazone HClSummary: PPARγ agonist -
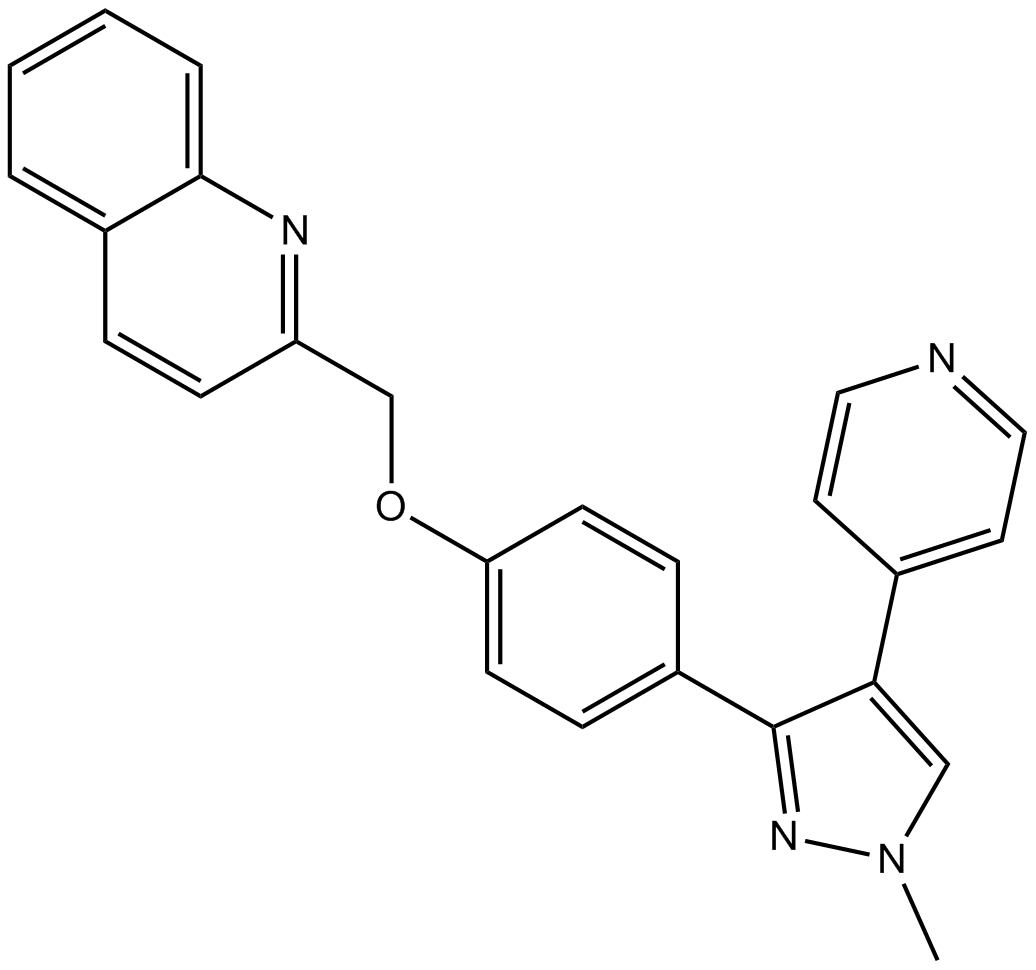 A4325 PF-2545920Target: Phosphodiesterases (PDEs)Summary: PDE10A inhibitor,potent and selective
A4325 PF-2545920Target: Phosphodiesterases (PDEs)Summary: PDE10A inhibitor,potent and selective -
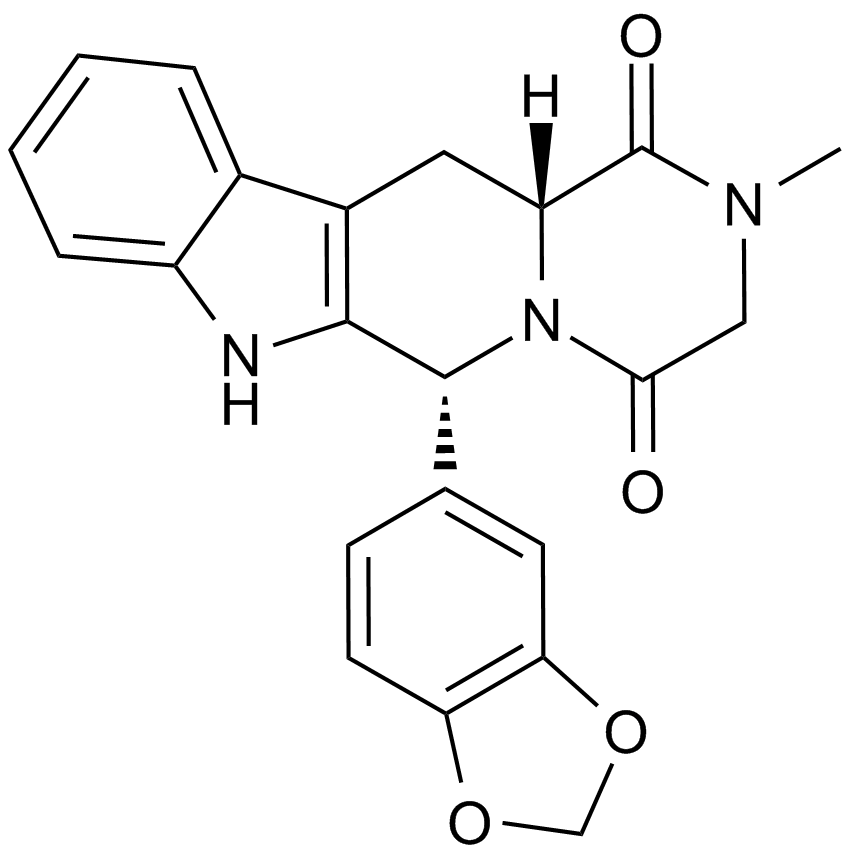 A4327 TadalafilTarget: Phosphodiesterases (PDEs)Summary: PDE5 inhibitor
A4327 TadalafilTarget: Phosphodiesterases (PDEs)Summary: PDE5 inhibitor -
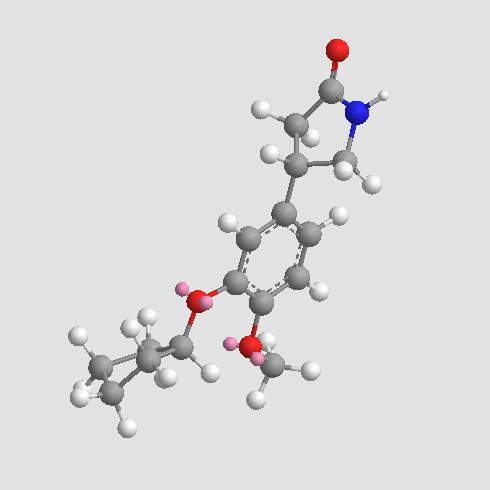 A4328 RolipramTarget: Phosphodiesterases (PDEs)Summary: PDE4-inhibitor and an anti-inflammatory agent
A4328 RolipramTarget: Phosphodiesterases (PDEs)Summary: PDE4-inhibitor and an anti-inflammatory agent -
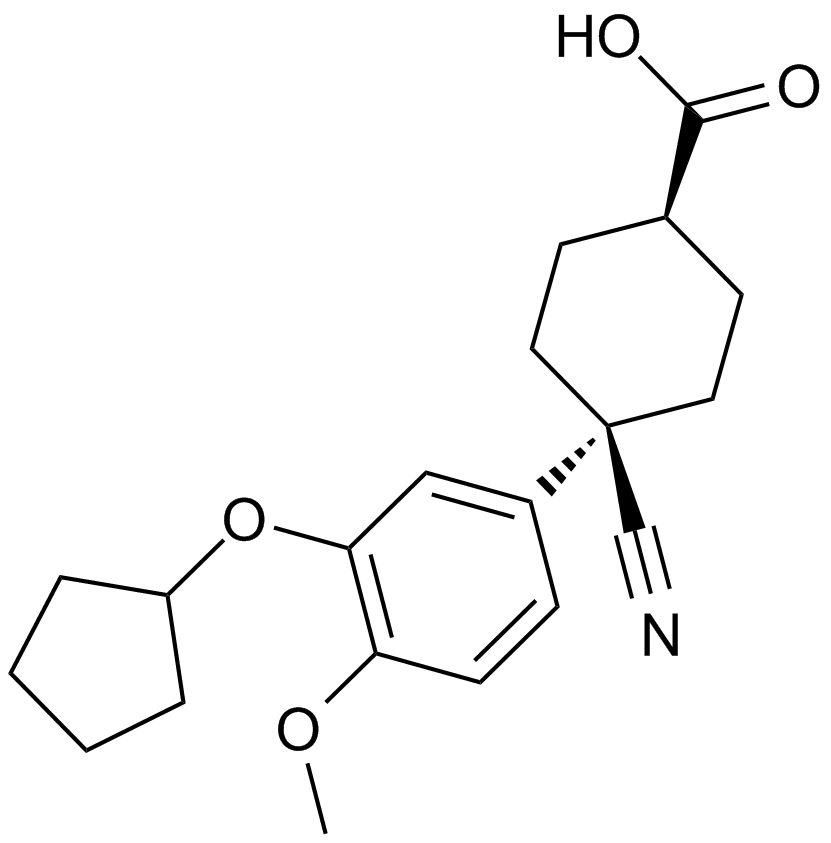 A4329 CilomilastTarget: Phosphodiesterases (PDEs)Summary: Potent PDE4 inhibitor
A4329 CilomilastTarget: Phosphodiesterases (PDEs)Summary: Potent PDE4 inhibitor

