Metabolism
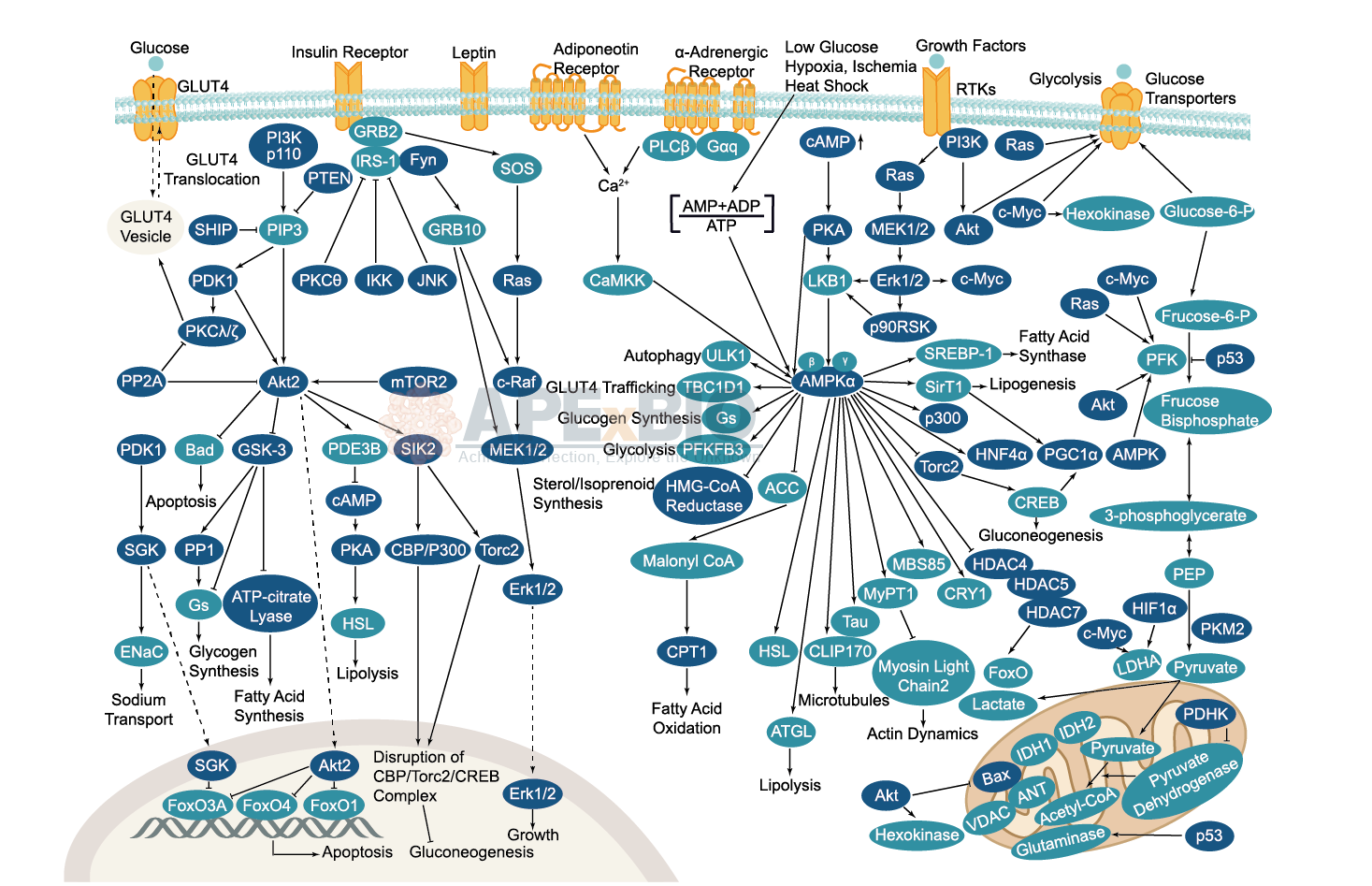
Serine/threonine kinase AMPK upregulates glucose uptake by promoting the expression and function of glucose transporters. AMPK is activated by increased AMP/ATP ratio, resulting from cellular and environmental stress, e.g. low glucose, heat shock, hypoxia and ischemia. AMPK activation positively modulates signaling transductions that refill ATP levels. Moreover, it also stimulates catabolic processes such as fatty acid oxidation and glycolysis through inhibition of ACC and activation of PFK2. AMPK negatively regulates various proteins which are important to ATP-consuming mechanisms, e.g. mTORC2, glycogen synthase, SREBP-1, and TSC2, causing the downregulation/inhibition of gluconeogenesis and glycogen, lipid and protein synthesis.
-
 A3483 IDO inhibitor 1Summary: Indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase inhibitor
A3483 IDO inhibitor 1Summary: Indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase inhibitor -
 A3493 INCB024360 analogueSummary: potent and selective inhibitor of IDO1
A3493 INCB024360 analogueSummary: potent and selective inhibitor of IDO1 -
 A3498 InolitazoneSummary: PPARgamma agonist
A3498 InolitazoneSummary: PPARgamma agonist -
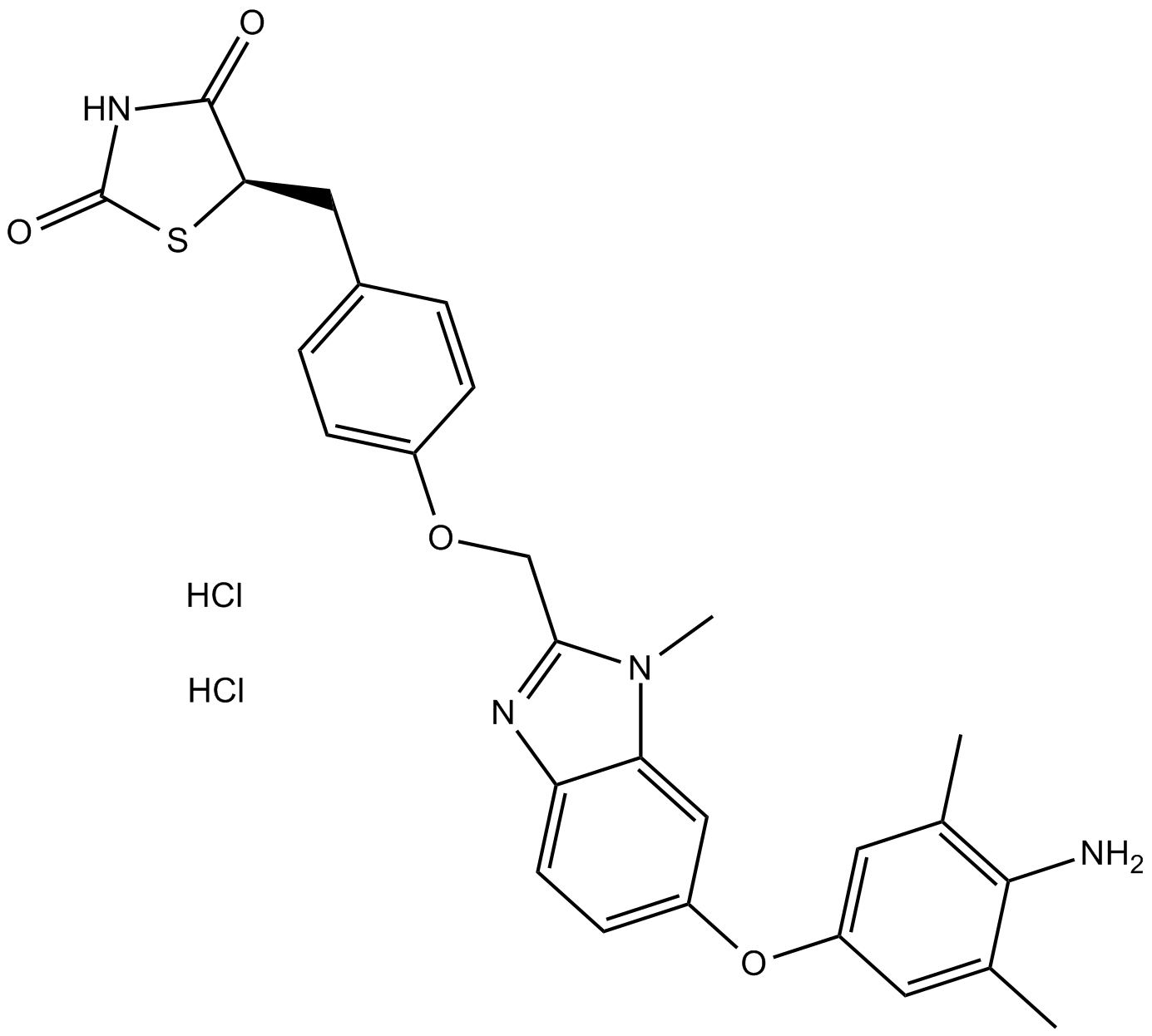 A3499 Inolitazone dihydrochlorideSummary: PPARγ agonist,high-affinity and novel
A3499 Inolitazone dihydrochlorideSummary: PPARγ agonist,high-affinity and novel -
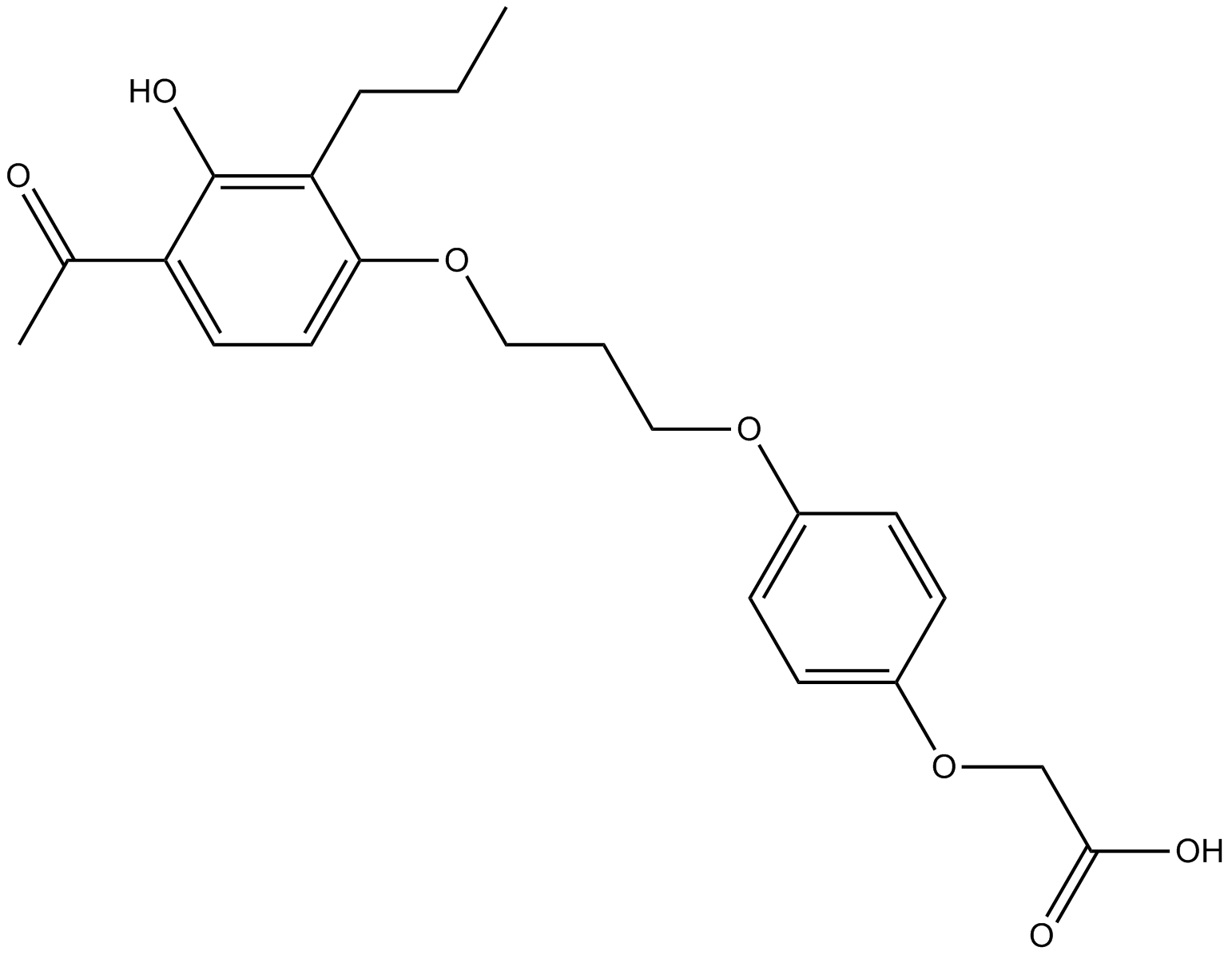 A3536 L-165041Target: PPARSummary: PPARβ/δ agonist,cell permeable,potent and selective
A3536 L-165041Target: PPARSummary: PPARβ/δ agonist,cell permeable,potent and selective -
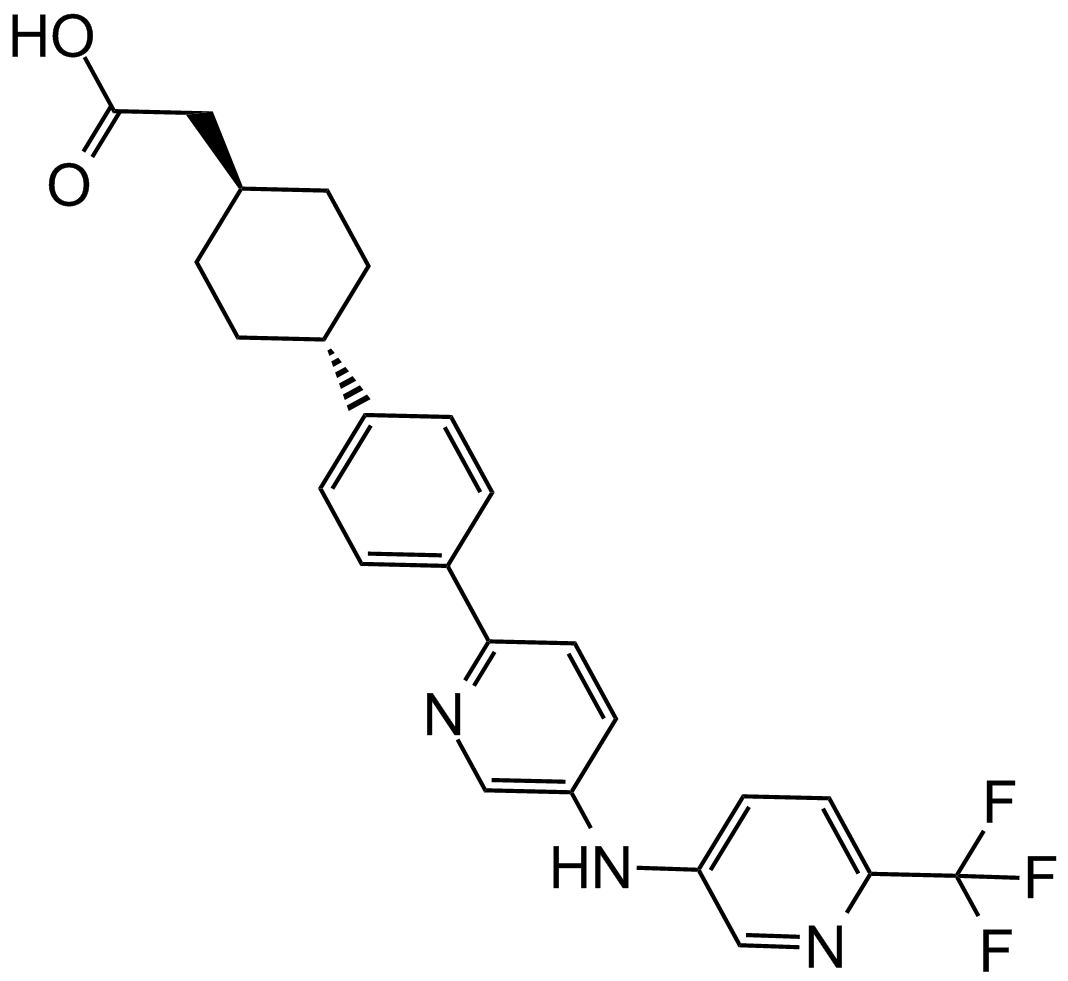 A3542 LCQ-908Summary: DGAT1 inhibitor
A3542 LCQ-908Summary: DGAT1 inhibitor -
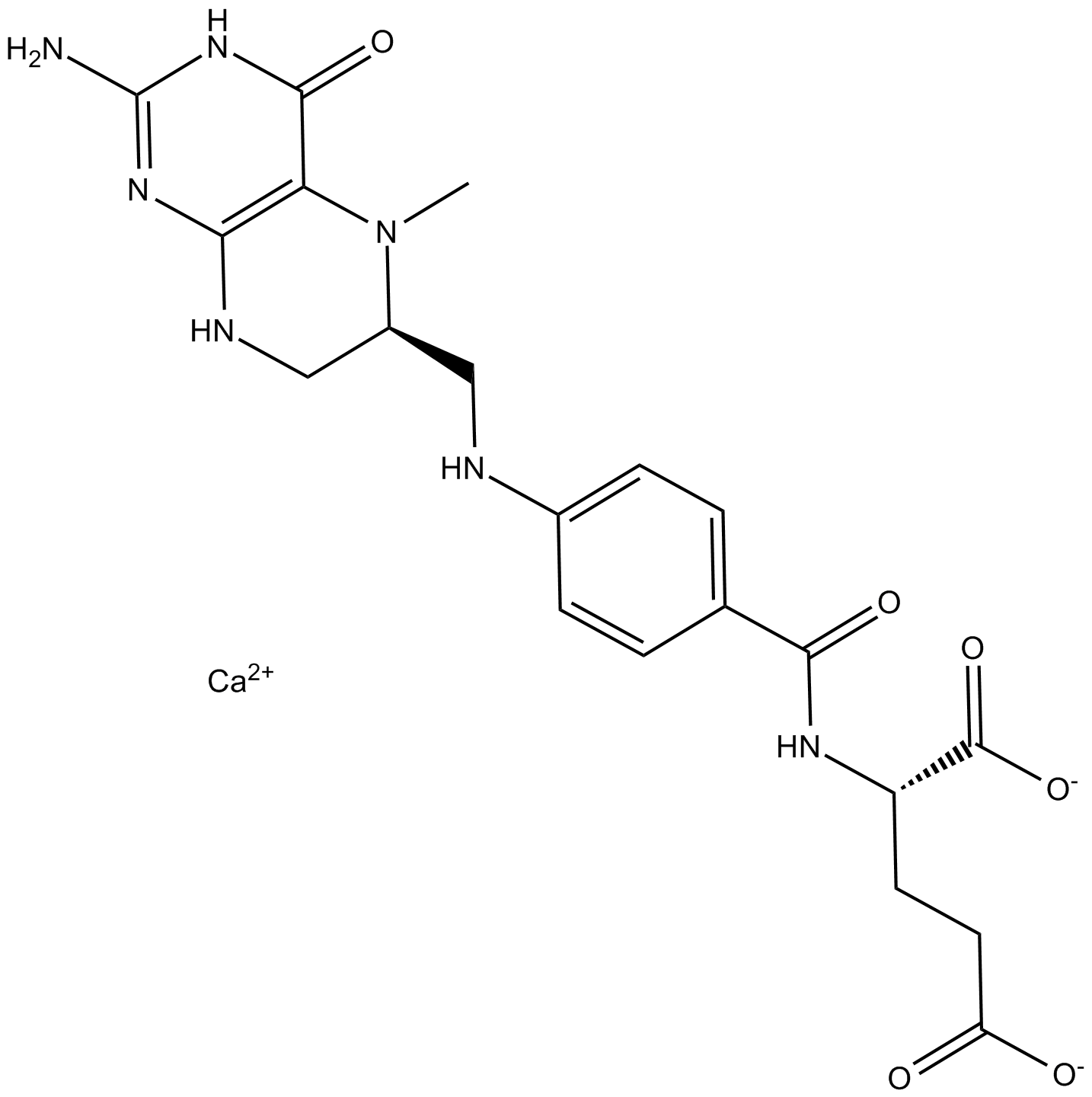 A3552 Levomefolate calciumSummary: Artificial form of folate
A3552 Levomefolate calciumSummary: Artificial form of folate -
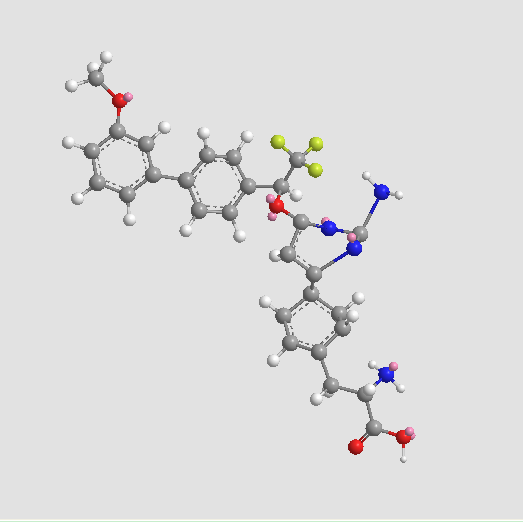 A3565 LX-1031Target: Tryptophan hydroxylases (TPH)Summary: TPH inhibitor
A3565 LX-1031Target: Tryptophan hydroxylases (TPH)Summary: TPH inhibitor -
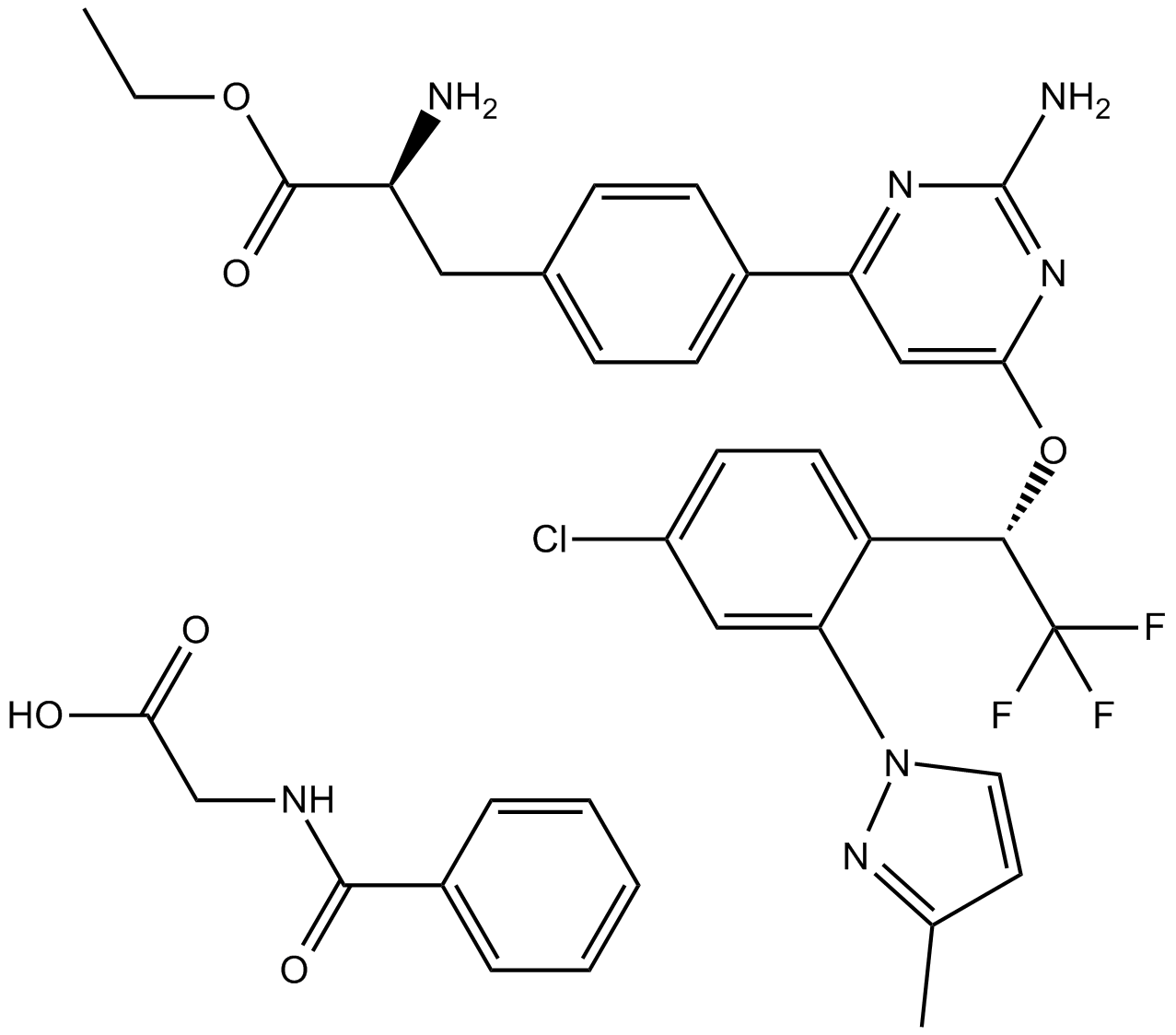 A3566 LX1606Summary: Tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH) inhibitor
A3566 LX1606Summary: Tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH) inhibitor -
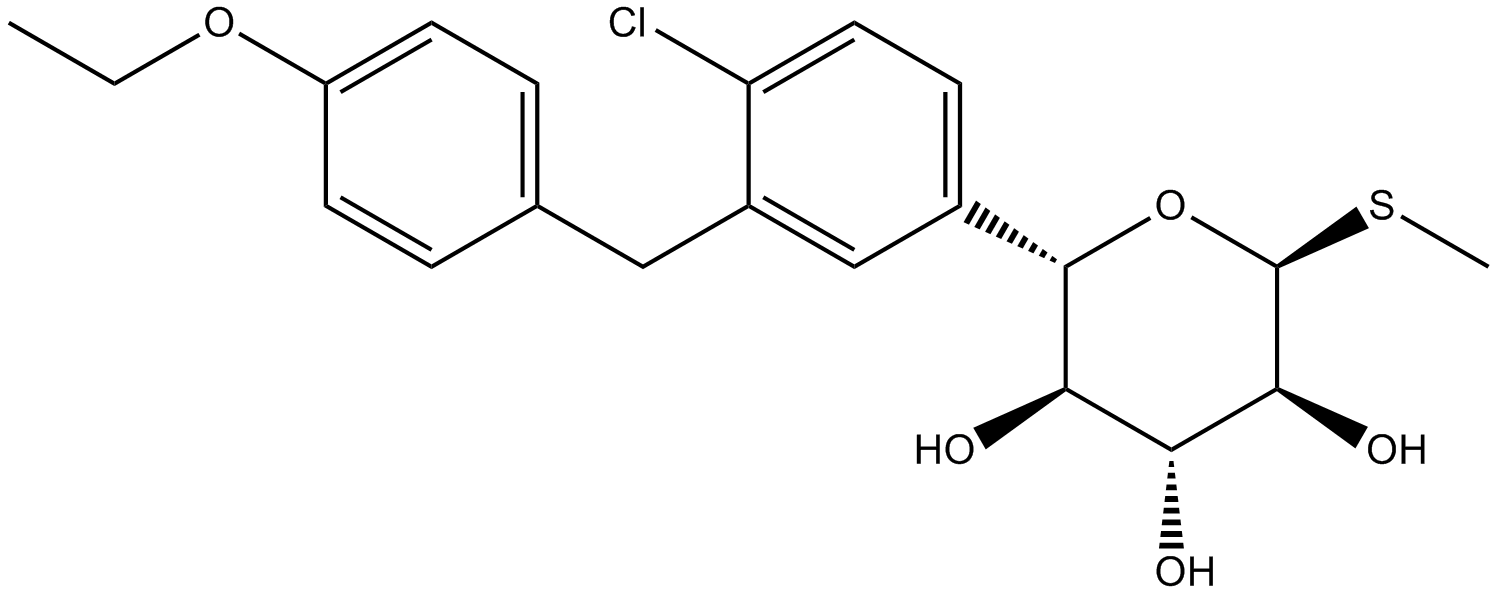 A3567 LX-4211Summary: SGLT1/SGLT2 inhibitor
A3567 LX-4211Summary: SGLT1/SGLT2 inhibitor

