Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel

Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins which allow the flow of ions across the membrane. The ion channels can be broadly grouped into six families including calcium channels, chloride channels, potassium channels, sodium channels, gap junction proteins and porins. Not all ion channels are gated, such as certain type of K+ and Cl– channels, transient receptor potential superfamily of cation channels, the ryanodine receptors and the IP3 receptors, but most Na+, K+, Ca2+ and some Cl– channels are all gated by voltage. Ligand-gated channels are regulated in response to ligand binding (e.g. neurotransmitters signaling). These ligand-gated neurotransmitter receptors are known as ionotropic receptors. Various neurotransmitters couple to ionotropic receptors such as glutamate, acetylcholine, glycine, GABA, and serotonin.
-
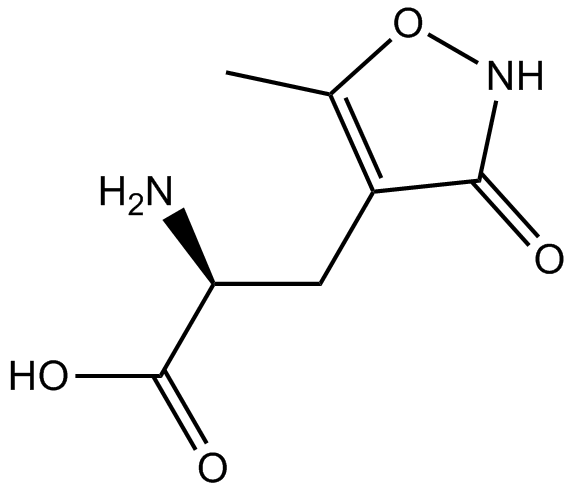 B6213 (RS)-AMPASummary: AMPA agonist
B6213 (RS)-AMPASummary: AMPA agonist -
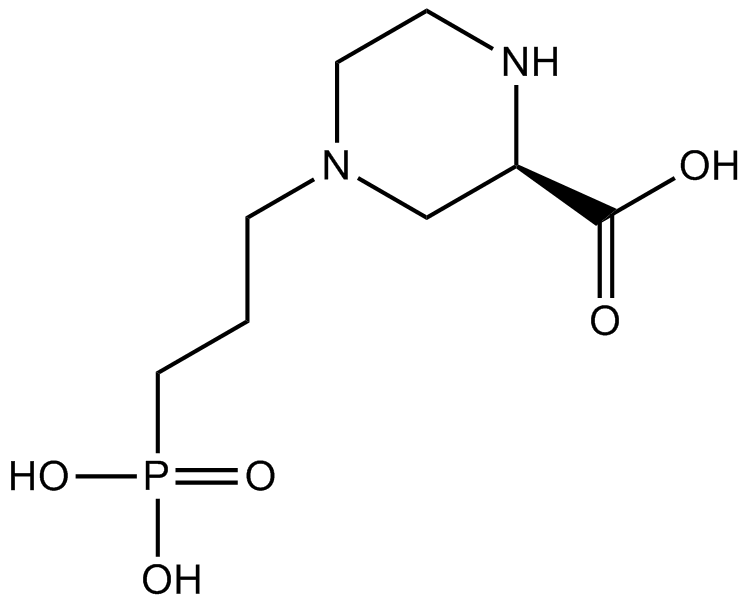 B6214 (RS)-CPPTarget: NMDA ReceptorsSummary: NMDA antagonist
B6214 (RS)-CPPTarget: NMDA ReceptorsSummary: NMDA antagonist -
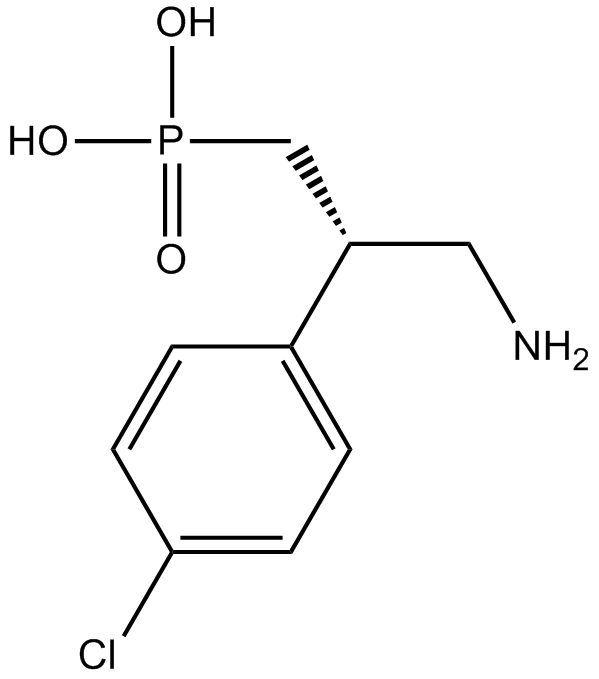 B6215 PhaclofenSummary: GABAB antagonist
B6215 PhaclofenSummary: GABAB antagonist -
 B6216 ZAPA sulfateSummary: GABAA receptors agonist
B6216 ZAPA sulfateSummary: GABAA receptors agonist -
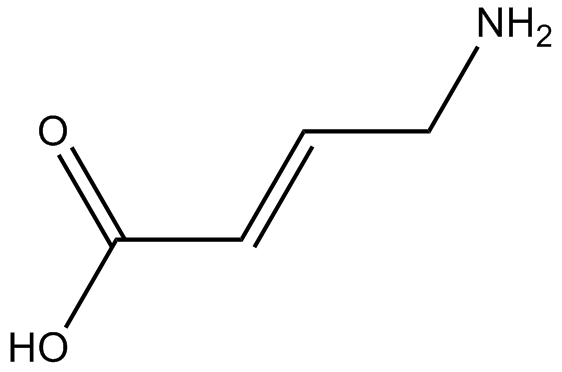 B6217 TACASummary: GABAA agonist
B6217 TACASummary: GABAA agonist -
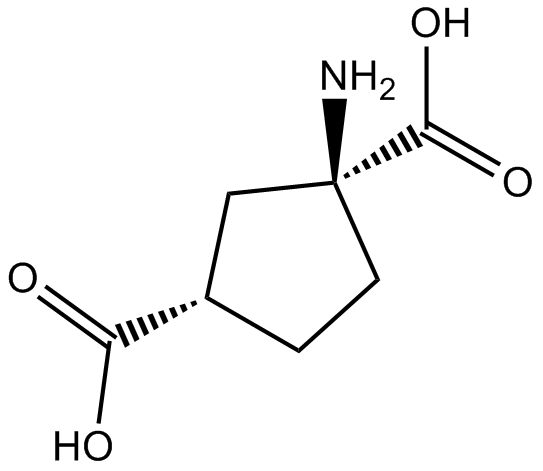 B6219 cis-ACPDSummary: NMDA receptor agonist and group II mGluR agonist
B6219 cis-ACPDSummary: NMDA receptor agonist and group II mGluR agonist -
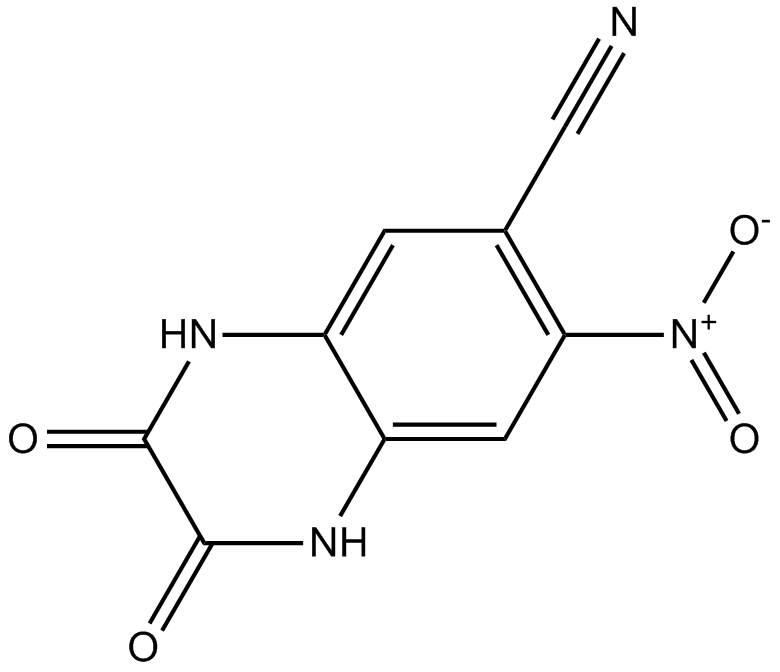 B6222 CNQXSummary: AMPA/kainate receptor antagonist
B6222 CNQXSummary: AMPA/kainate receptor antagonist -
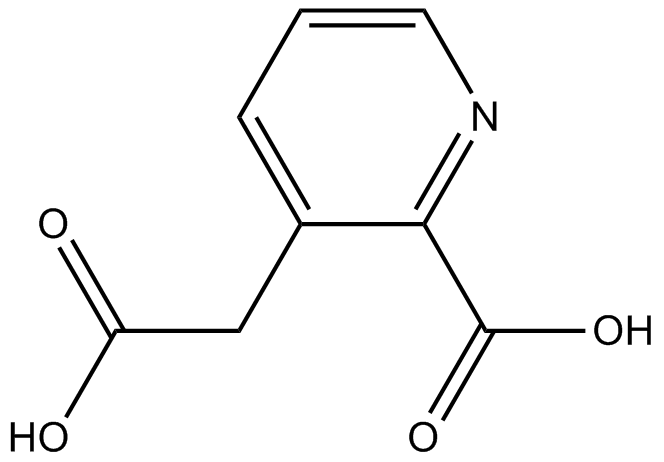 B6223 Homoquinolinic acidSummary: NMDA receptor agonist
B6223 Homoquinolinic acidSummary: NMDA receptor agonist -
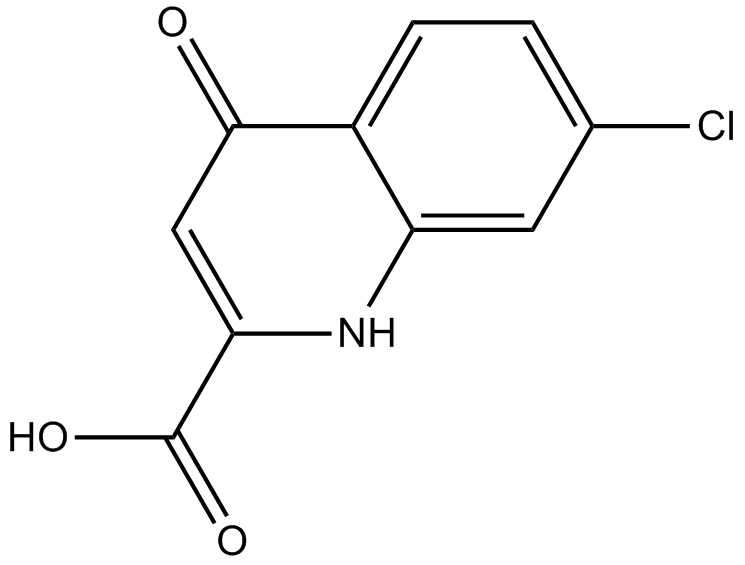 B6232 7-Chlorokynurenic acidSummary: NMDA receptor glycine site antagonist
B6232 7-Chlorokynurenic acidSummary: NMDA receptor glycine site antagonist -
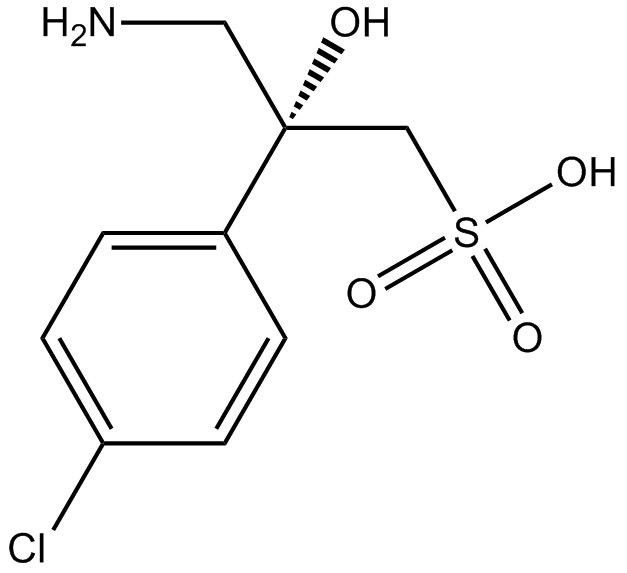 B6234 2-HydroxysaclofenSummary: GABAB receptor antagonist
B6234 2-HydroxysaclofenSummary: GABAB receptor antagonist

