Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel

Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins which allow the flow of ions across the membrane. The ion channels can be broadly grouped into six families including calcium channels, chloride channels, potassium channels, sodium channels, gap junction proteins and porins. Not all ion channels are gated, such as certain type of K+ and Cl– channels, transient receptor potential superfamily of cation channels, the ryanodine receptors and the IP3 receptors, but most Na+, K+, Ca2+ and some Cl– channels are all gated by voltage. Ligand-gated channels are regulated in response to ligand binding (e.g. neurotransmitters signaling). These ligand-gated neurotransmitter receptors are known as ionotropic receptors. Various neurotransmitters couple to ionotropic receptors such as glutamate, acetylcholine, glycine, GABA, and serotonin.
-
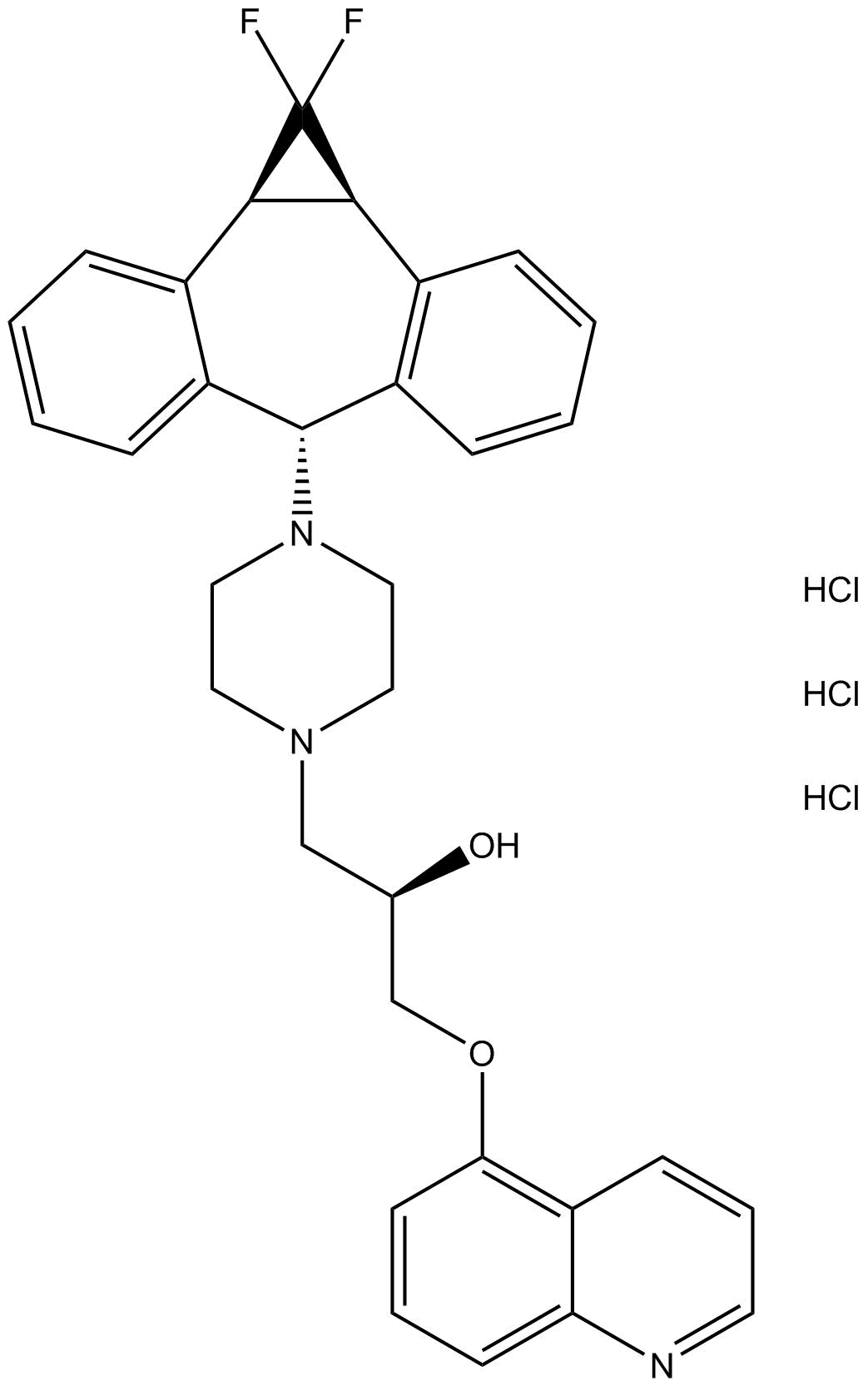 A8549 LY335979 (Zosuquidar 3HCL)1 CitationTarget: P-glycoprotein (P-gp)Summary: Pgp (P-glycoprotein) inhibitor
A8549 LY335979 (Zosuquidar 3HCL)1 CitationTarget: P-glycoprotein (P-gp)Summary: Pgp (P-glycoprotein) inhibitor -
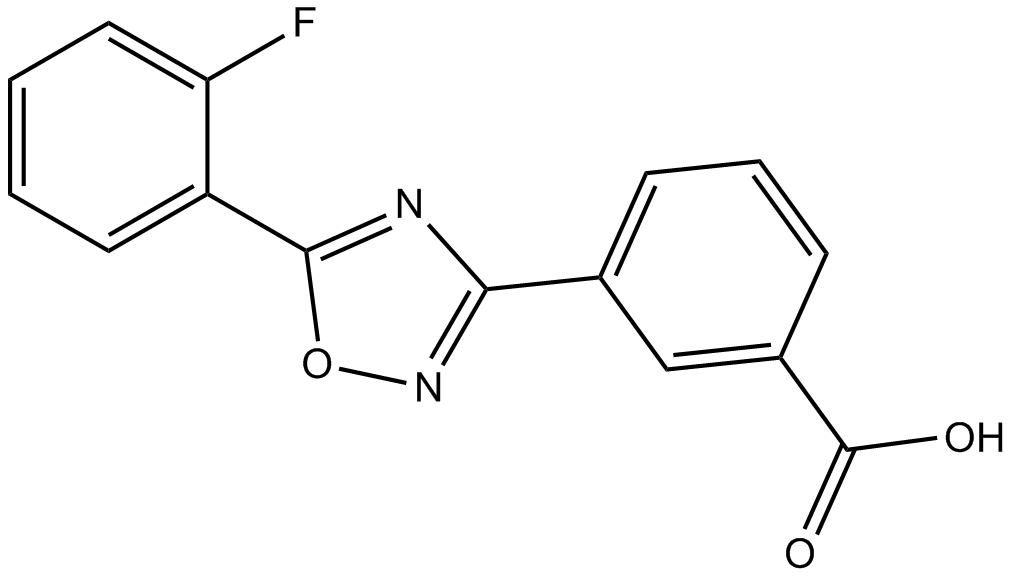 A8553 PTC124 (Ataluren)Summary: CFTR-G542X nonsense allele inhibitor
A8553 PTC124 (Ataluren)Summary: CFTR-G542X nonsense allele inhibitor -
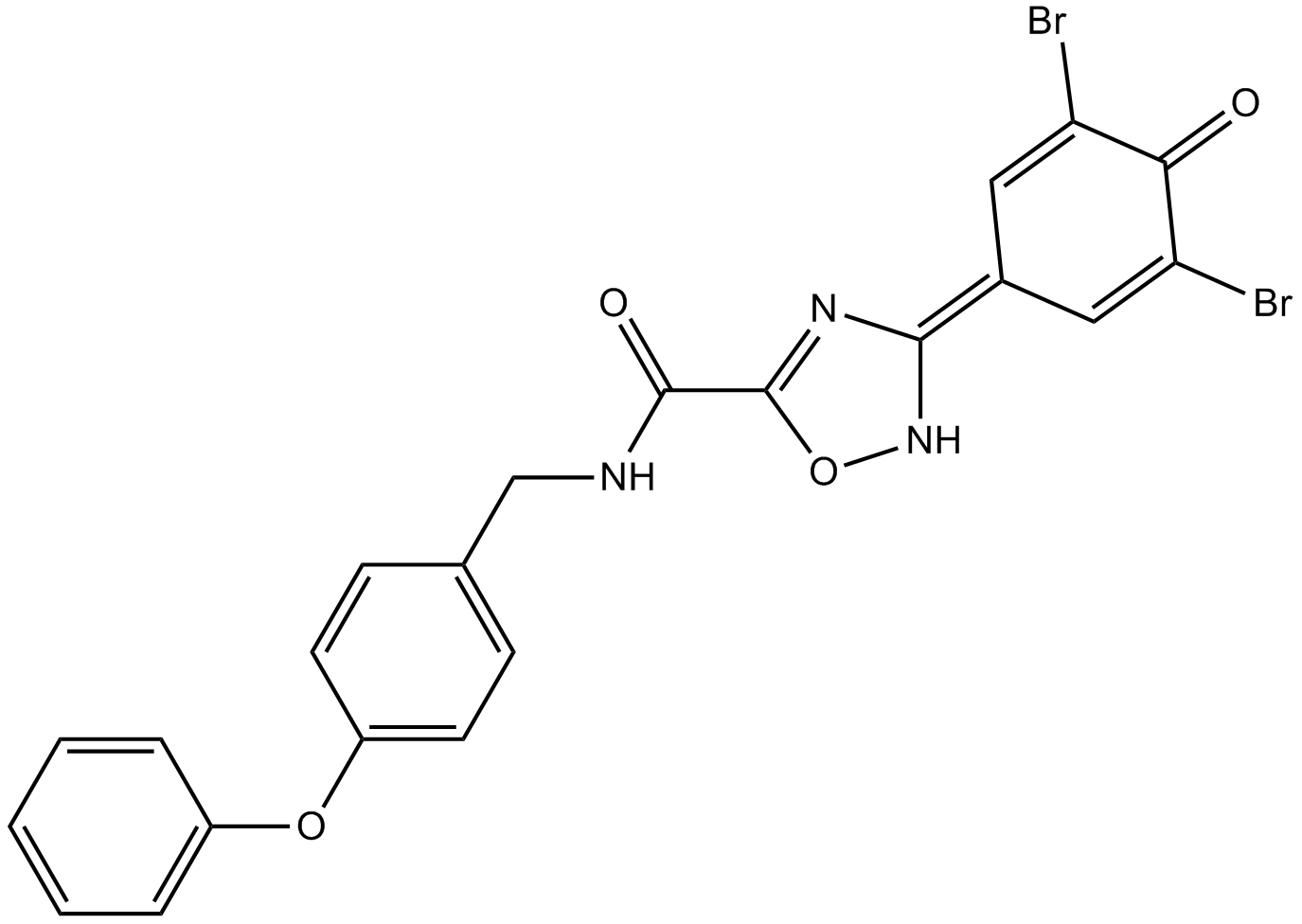 A8637 IOWH-032Target: CFTRSummary: CFTR inhibitor
A8637 IOWH-032Target: CFTRSummary: CFTR inhibitor -
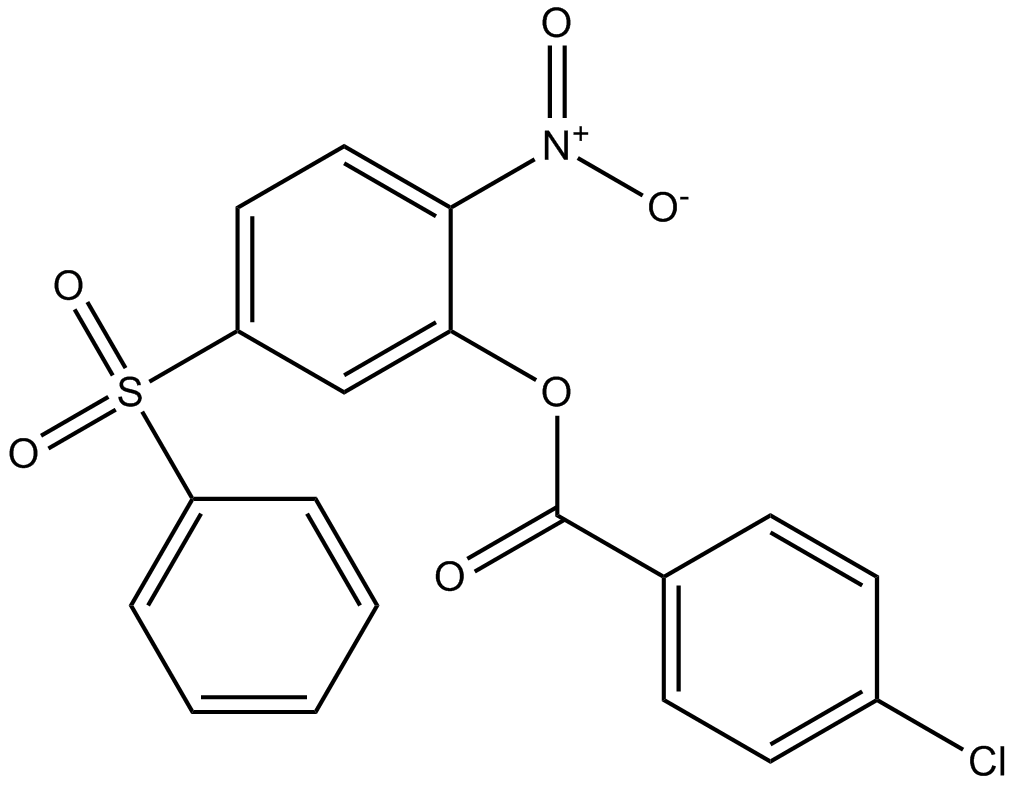 B3041 BTB06584Target: F1 Fo-ATPaseSummary: F1F0 ATP synthases
B3041 BTB06584Target: F1 Fo-ATPaseSummary: F1F0 ATP synthases -
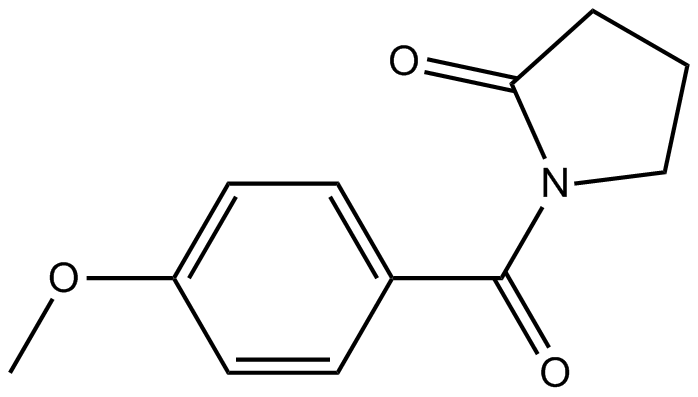 B1210 AniracetamSummary: Nootropic drug for senile dementia
B1210 AniracetamSummary: Nootropic drug for senile dementia -
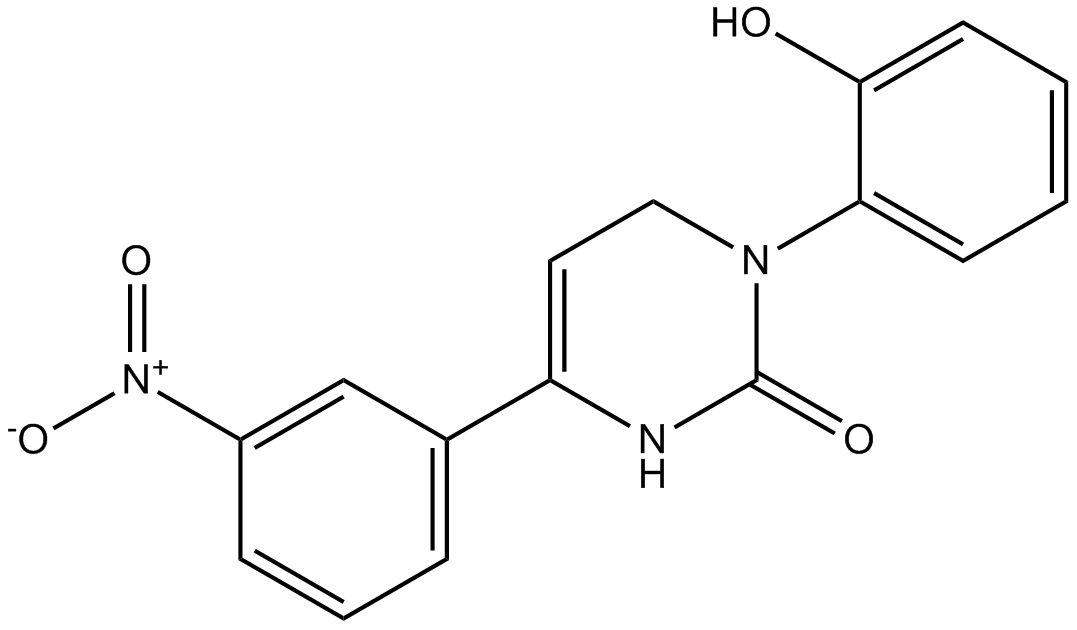 B1055 IcilinTarget: TRP ChannelSummary: TRPM8/ hENaCδ agonist
B1055 IcilinTarget: TRP ChannelSummary: TRPM8/ hENaCδ agonist -
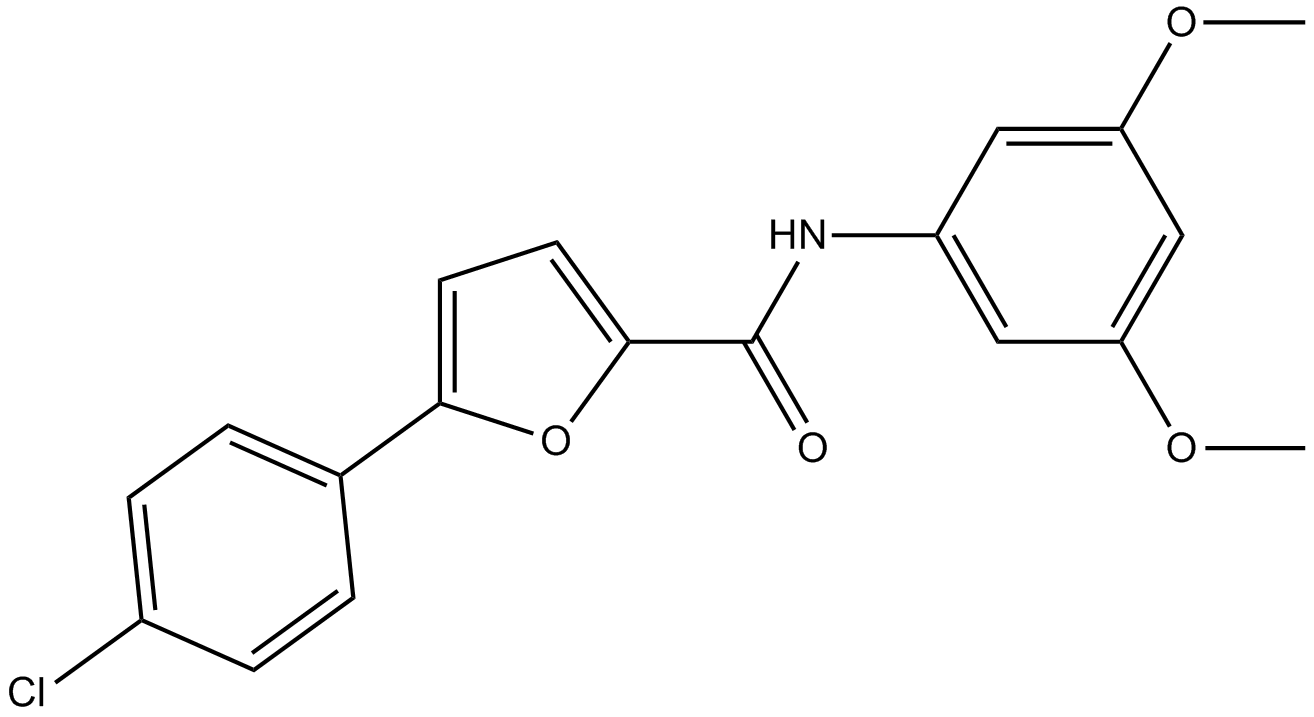 B2277 A-803467Target: Voltage-gated Sodium (NaV) ChannelsSummary: NaV1.8 channel blocker,potent and selective
B2277 A-803467Target: Voltage-gated Sodium (NaV) ChannelsSummary: NaV1.8 channel blocker,potent and selective -
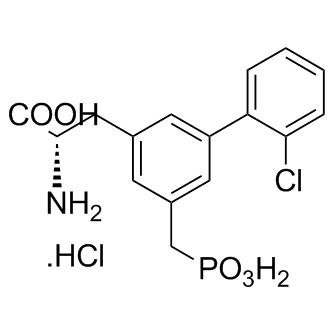 B1142 SDZ 220-581 hydrochlorideSummary: NMDA receptor antagonist
B1142 SDZ 220-581 hydrochlorideSummary: NMDA receptor antagonist -
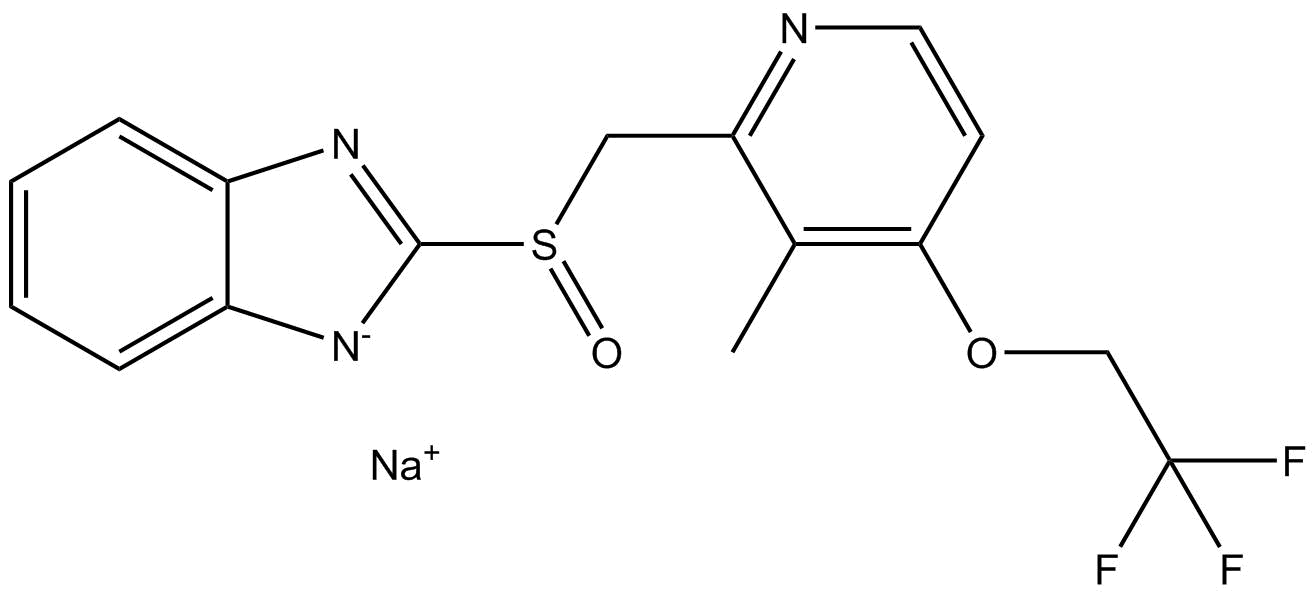 B1290 Lansoprazole sodiumSummary: PPI/cytochrome P450 inhibitor
B1290 Lansoprazole sodiumSummary: PPI/cytochrome P450 inhibitor -
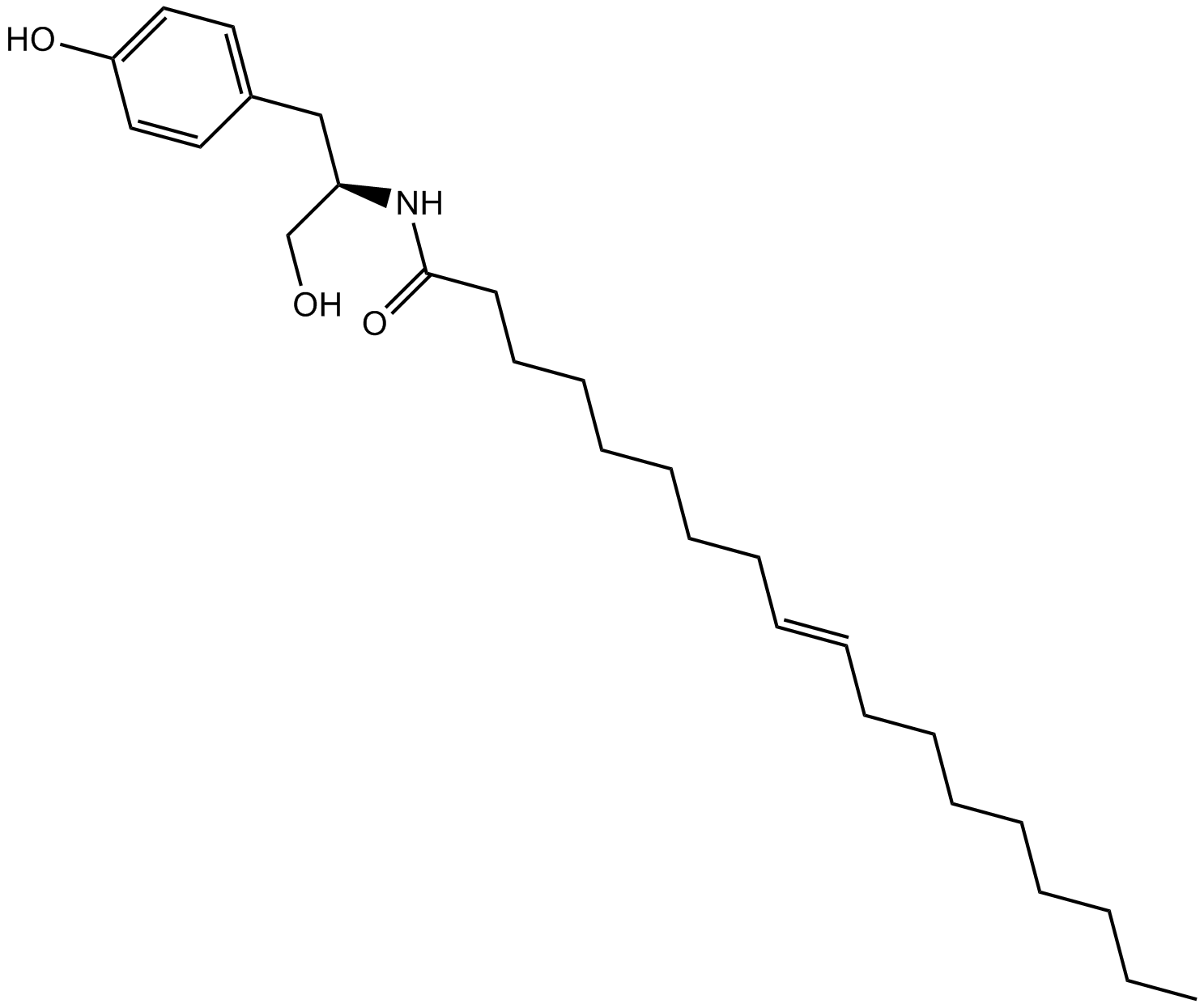 B5177 OMDM-2Summary: Metabolically stable inhibitor of anandamide cellular uptake
B5177 OMDM-2Summary: Metabolically stable inhibitor of anandamide cellular uptake

