MAPK Signaling

Activated MAPKs transduce the phosphorylation and activation of MAPK-activated protein kinases (MAPKAPKs), e.g. RSK, MSK, or MNK family, and MK2/3/5. There are three main MAPK families, signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 (Erk1/2 or p44/42), the c-Jun N-terminal kinases 1-3 (JNK1-3)/ stress activated protein kinases (SAPK1A, 1B, 1C), the p38 isoforms (p38α, β, γ, and δ). ERK signaling is involved in cell division, migration and survival. p38 MAPK and JNK/SAPK pathways are activated by cellular stress. The p38 MAPK pathway regulates cell motility, transcription, and chromatin remodeling. JNK/SAPK signaling affects apoptosis and inflammation. Dysregulation of MAPK pathway results in tumorgenesis and other pathological conditions.
-
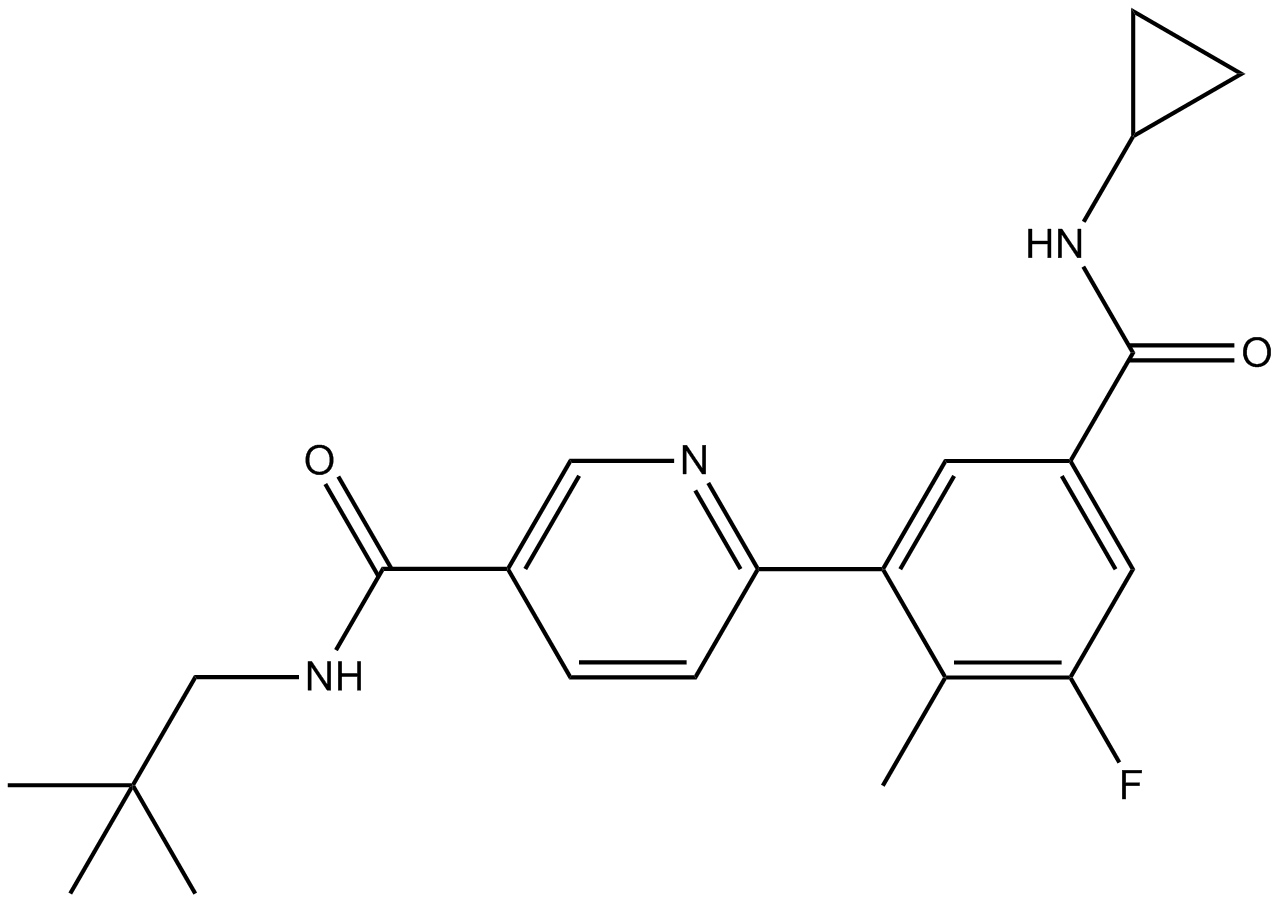 B4620 Losmapimod1 CitationSummary: p38 MAPK inhibitor, orally active
B4620 Losmapimod1 CitationSummary: p38 MAPK inhibitor, orally active -
 B4727 B-Raf IN 1Summary: B-Raf inhibitor
B4727 B-Raf IN 1Summary: B-Raf inhibitor -
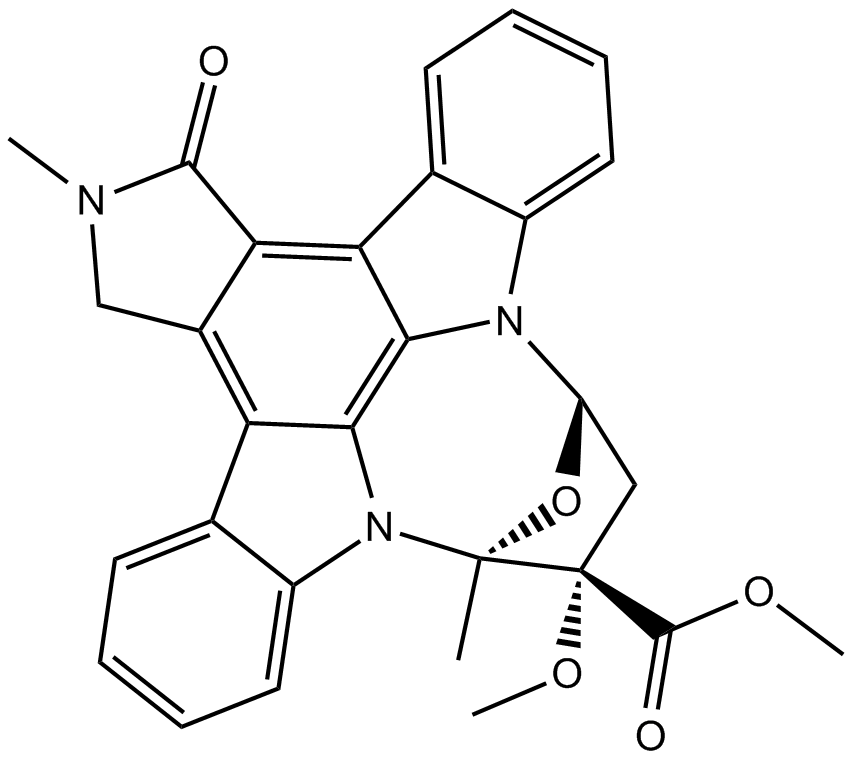 B6673 KT 5823Summary: protein kinase G inhibitor
B6673 KT 5823Summary: protein kinase G inhibitor -
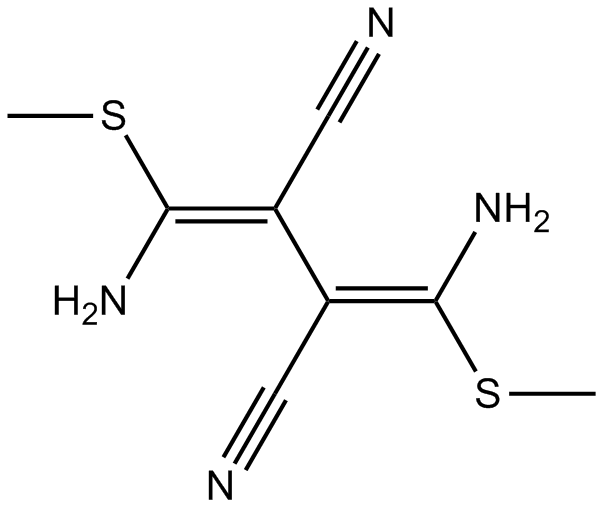 B6882 U0124Summary: Inactive analog of U0126(MEK-1/2 inhibitor), used as a negative control
B6882 U0124Summary: Inactive analog of U0126(MEK-1/2 inhibitor), used as a negative control -
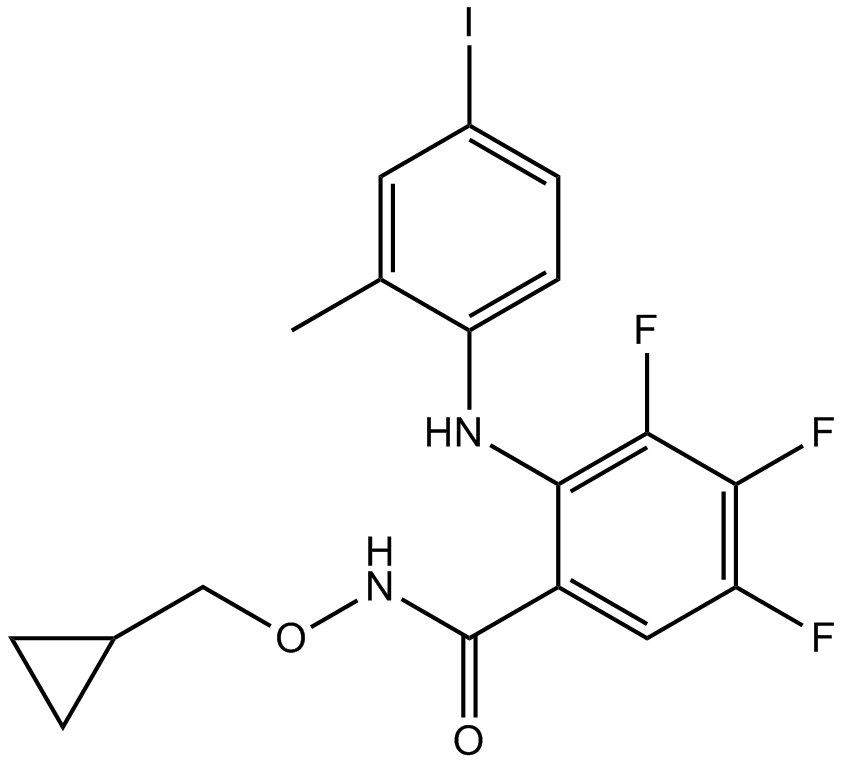 B7124 PD 198306Summary: MEK1/2 inhibitor
B7124 PD 198306Summary: MEK1/2 inhibitor -
 B7246 Rp-8-Br-PET-cGMPSSummary: cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG) inhibitor
B7246 Rp-8-Br-PET-cGMPSSummary: cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG) inhibitor -
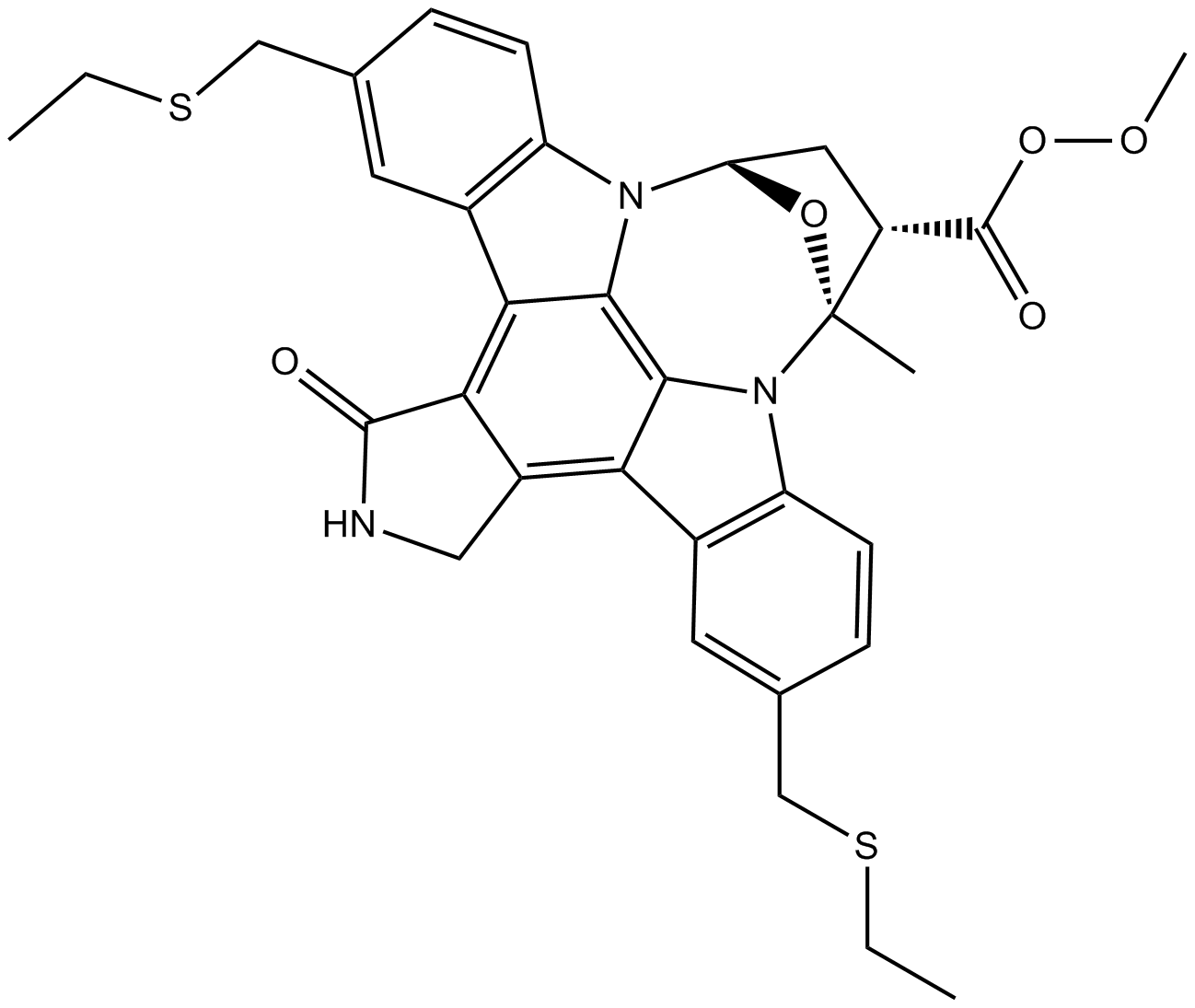 B7720 CEP 1347Summary: JNK inhibitor
B7720 CEP 1347Summary: JNK inhibitor -
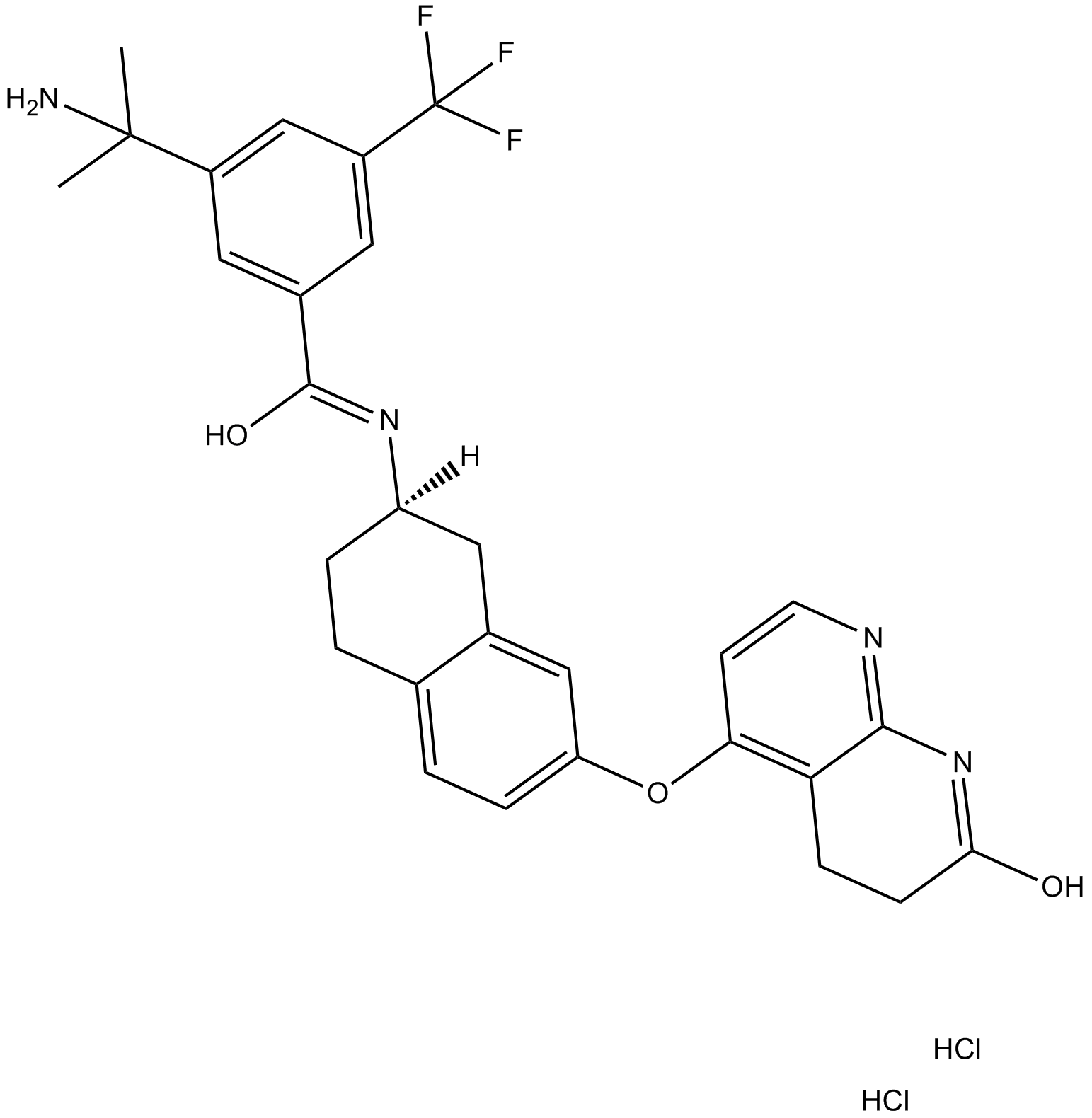 B7736 ML 786 dihydrochlorideSummary: Raf kinase inhibitor
B7736 ML 786 dihydrochlorideSummary: Raf kinase inhibitor -
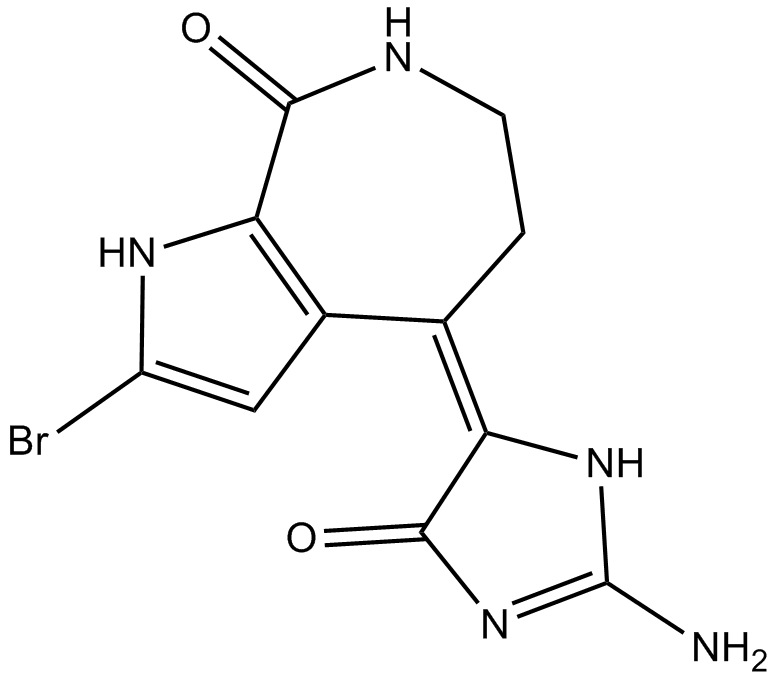 B5126 10Z-HymenialdisineSummary: Pan kinase inhibitor
B5126 10Z-HymenialdisineSummary: Pan kinase inhibitor -
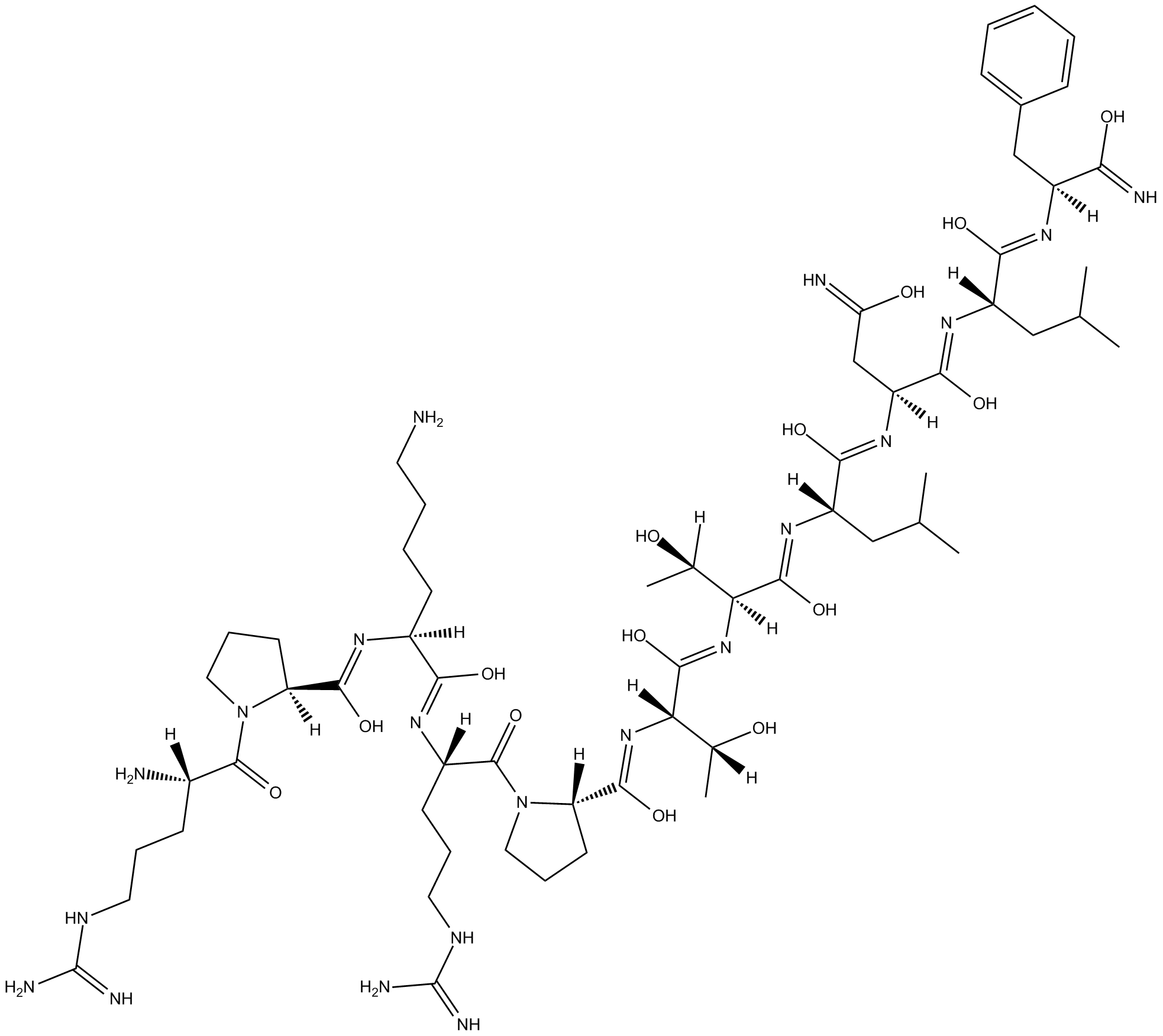 B5130 JIP-1 (153-163)Summary: Peptide inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)
B5130 JIP-1 (153-163)Summary: Peptide inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)

